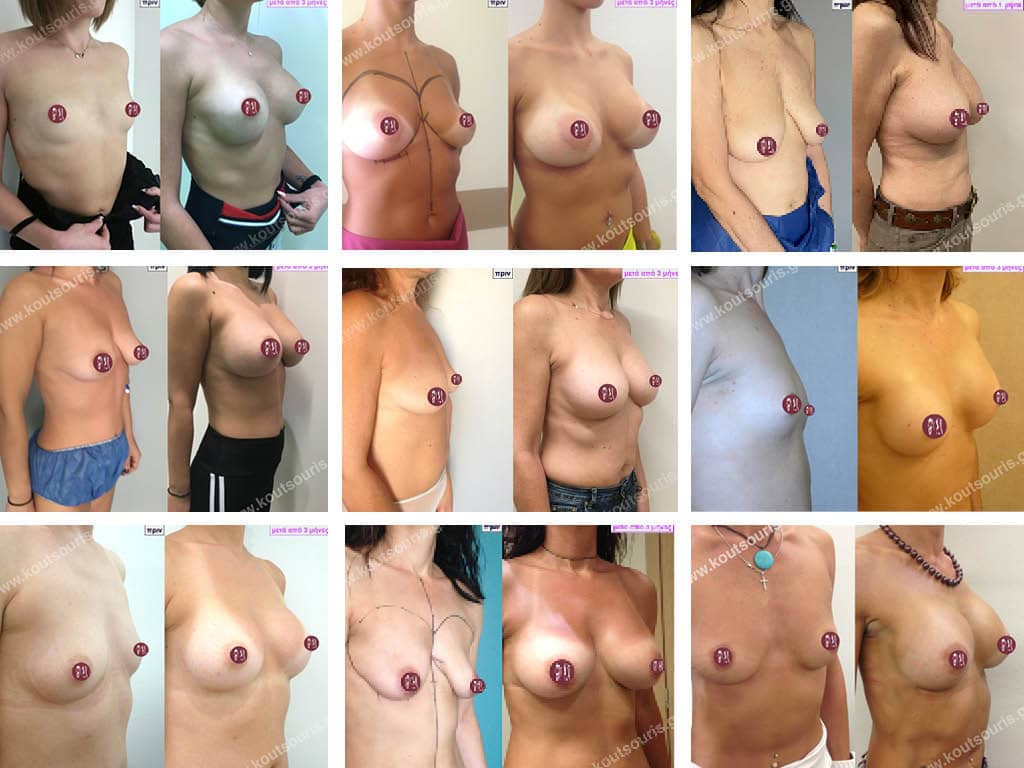
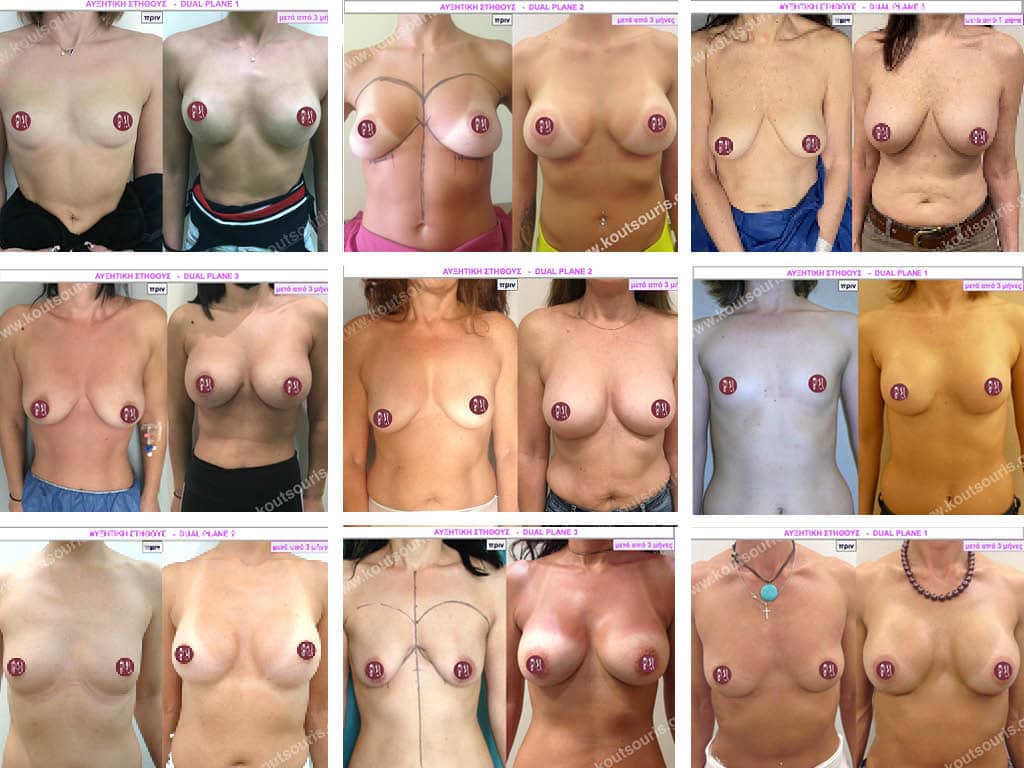
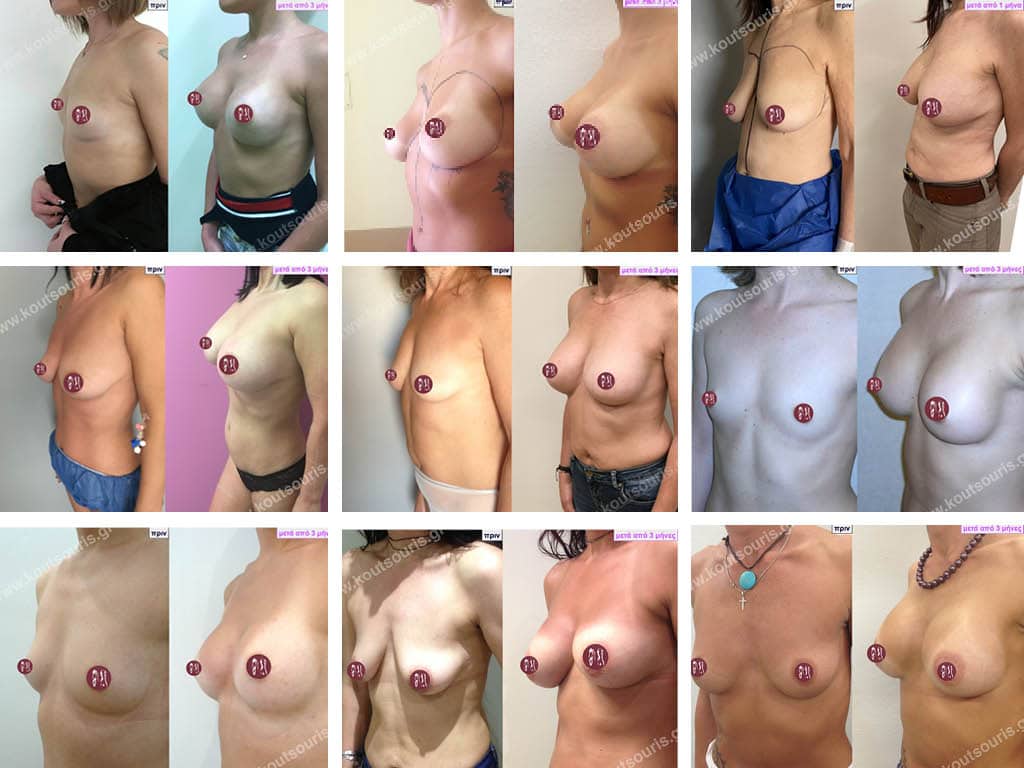
Breast augmentation
“I want Breast Augmentation to make me feel better about myself.” I’m not concerned with what other people think or say. I want it for myself…”
This is exactly what most women today have in mind and this is what we are told in the clinic. They are not concerned about what their partner, their friends or their acquaintances will say. They are interested in “fixing their breasts” so that they themselves can feel good about their bodies and their image in the mirror. This is the ultimate goal for us as well..

Breast Augmentation (or Breast Augmentation) along with Liposuction and Rhinoplasty are the most common procedures performed today in Plastic Surgery Clinics in Greece.

What influences breast shape?
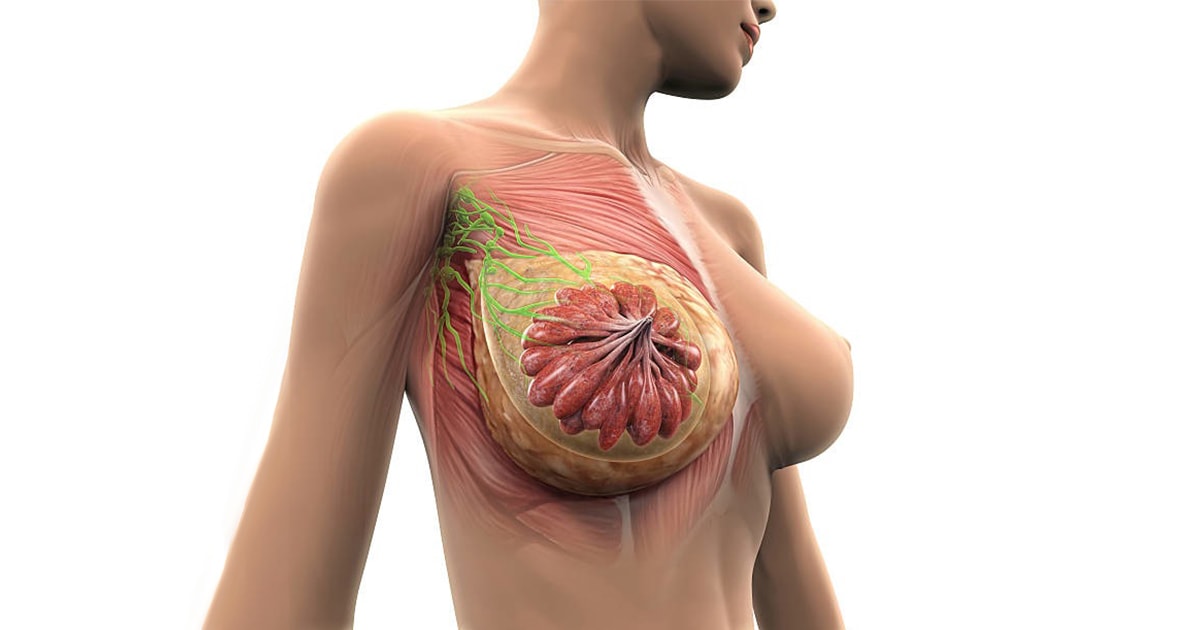
The female breast consists of multiple small glands (mass glands) and milk ducts which are surrounded by fatty tissue. The shape and feel to the touch of the breast is due to these very tissues. Just below the breast is the pectoralis major muscle. Weight fluctuations, pregnancies, the effects of gravity and the passage of age lead to atrophy of the tissues, loosening of the skin and eventually a reduction and alteration in the shape of the breast.
How is breast augmentation done today?
Breast augmentation today is mainly done using silicone implants. The use of silicone for breast augmentationΗ αυξητική στήθους σήμερα γίνεται κατεξοχήν χρησιμοποιώντας ενθέματα σιλικόνης. The use of silicone for breast augmentation was first applied in the early 1960s. It is a special silicone with absolute indications for medical use and as a result many women who had breast augmentation forty or fifty years ago have not had to change them and have the same implants today.
Breast augmentation today is mainly done using silicone implants.
Another way of breast augmentation is by fat grafting.However, it is a technique with many limitations and limited evidence.
Breast augmentation with Hyaluronic acid is not done today as it is not approved by the scientific community due to the reduced safety of the technique.
Modern silicone breast implants are high-tech achievements and are accompanied by excellent effectiveness and safety.
What is silicone?
Silicone is a polymeric synthetic material and can be liquid, gel or solid. It is widely used in our everyday life as countless materials and tools contain silicone parts. However, medical silicone is a completely specialized elastomer and has nothing to do with industrial silicone.

Medical silicone in addition to breast implants is widely used in medicine today. For example medical catheters, heart pacemakers, intraocular lenses or tissue expanders are very often made of silicone.
Is silicone safe?
Leading scientists from different medical specialties have studied the potential health risks associated with silicone breast implants. They came to the following conclusions:
European Parliament (Scientific and Technical Options Assessment Programme (STOA):
“Studies do not suggest an association between silicone implants and serious health risks such as breast cancer and connective tissue diseases.” “…studies have concluded that there appears to be no evidence of harmful effects in infants nursed by women with implants silicone breast implants…”
US Congress (Institute of Medicine (IOM):
“There is no increased risk of connective tissue disease for women with silicone breast implants. Women with breast implants are no more likely than the rest of the population to develop breast cancer, immune diseases, or neurological problems. – Lactation is safe and beneficial. – There are no second-generation effects on the children of women with breast implants.”
UK Department of Health (Independent Review Group (IRG):
“There is no epidemiological evidence of any association between silicone breast implants and any documented connective tissue disease. If there is a risk of connective tissue disease, it is too small to be quantified. – The overall biological response to silicone is consistent with conventional forms of response to foreign bodies rather than an unusual toxic response. – There is no evidence that children of women with breast implants are at increased risk of connective tissue disease.”
What is a silicone breast insert?
Silicone breast implants consist of a sheath of successive branched layers of elastomeric silicone. Their content can be:
- liquid silicone gel (gel)
- saline, or
- gel and saline combination (gel & saline).
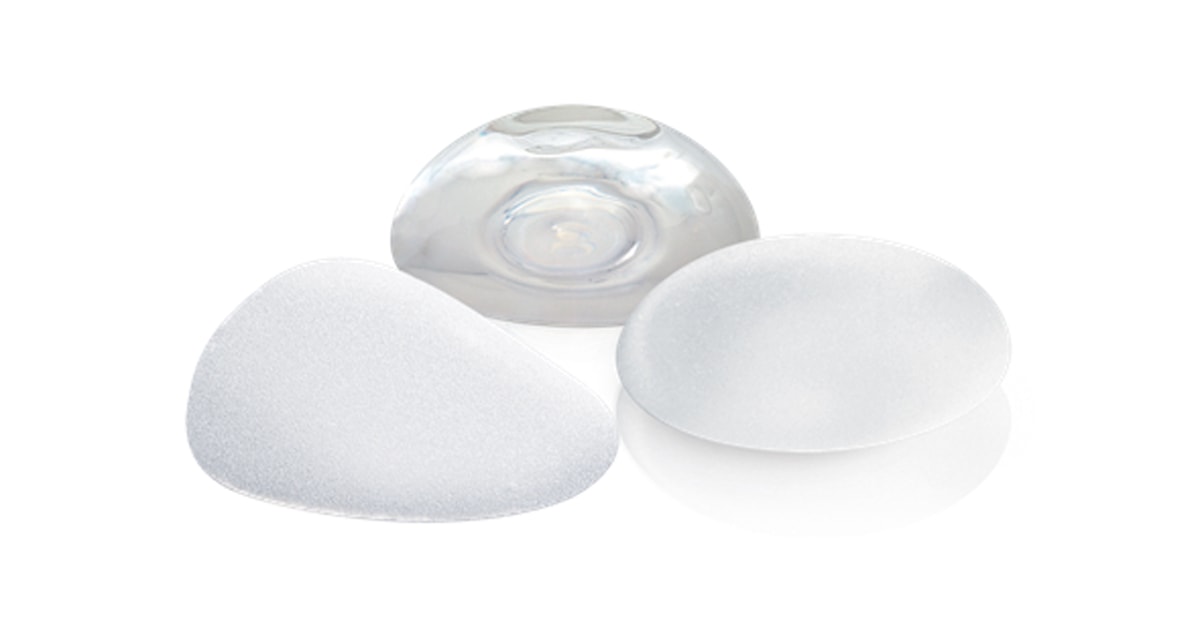

The implants we use extensively in Greece – but also worldwide – are the liquid silicone gel breast implants (gel breast implants).
Liquid silicone gel inserts are soft in texture and behave like a body. They have a uniform shape and retain a natural plasticity that resembles that of natural breast tissue. They generally feel better, do not fold and do not form a ripple in the breast and in the rare case of rupture, the silicone stays in place and does not “spill” into the breast.
When do we use silicone breast implants?
We use silicone inserts when we want to do:
- Aesthetic breast augmentation. In women with small, underplastic breasts or with shape problems.
- Breast reconstruction. In women after partial or total mastectomy due to malignancy or injury or after congenital (congenital) hypoplasia or aplasia of the breast.
- Breast implant revision or replacement. In patients with previous breast augmentation or breast reconstruction surgery to improve the result.
When do we NOT use silicone breast implants?
Silicone breast implants are contraindicated when there is:
- Active infection anywhere in the body
- Tissue healing disorders
- Systemic lupus erythematosus or cutaneous lupus
- Scleroderma
- Haematological diseases or diseases with coagulation disorder of the blood
- Precancerous breast disease
- Malignancy
- Immunodeficiency or use of immunosuppressive drugs
- Pregnancy or lactation
- History of euthanasia to silicone or foreign material
- Unrealistic or unreasonable expectations
From what age onwards is breast augmentation with silicone allowed?
After the age of 18, breast augmentation with silicone implants is recommended. The European Parliament “recommends that silicone implants should only be inserted in women under 18 years of age for medical reasons”.
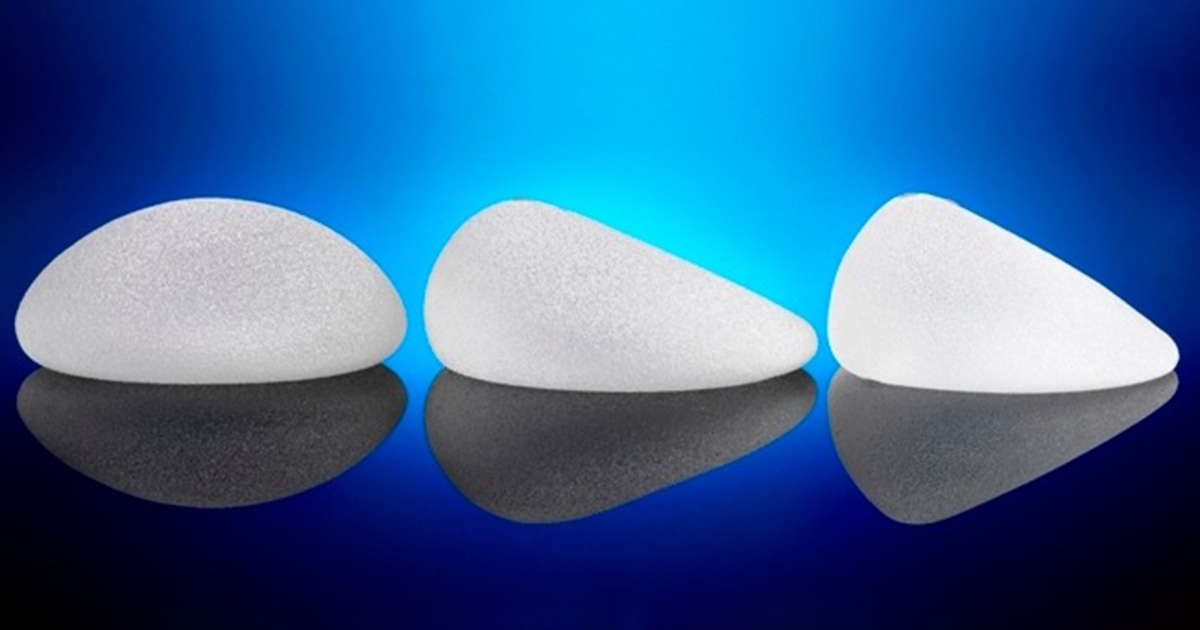
Types of silicone inserts
Depending on the texture
Depending on the touch on their surface, silicone inserts are divided into:
- rough and
- smooth surface

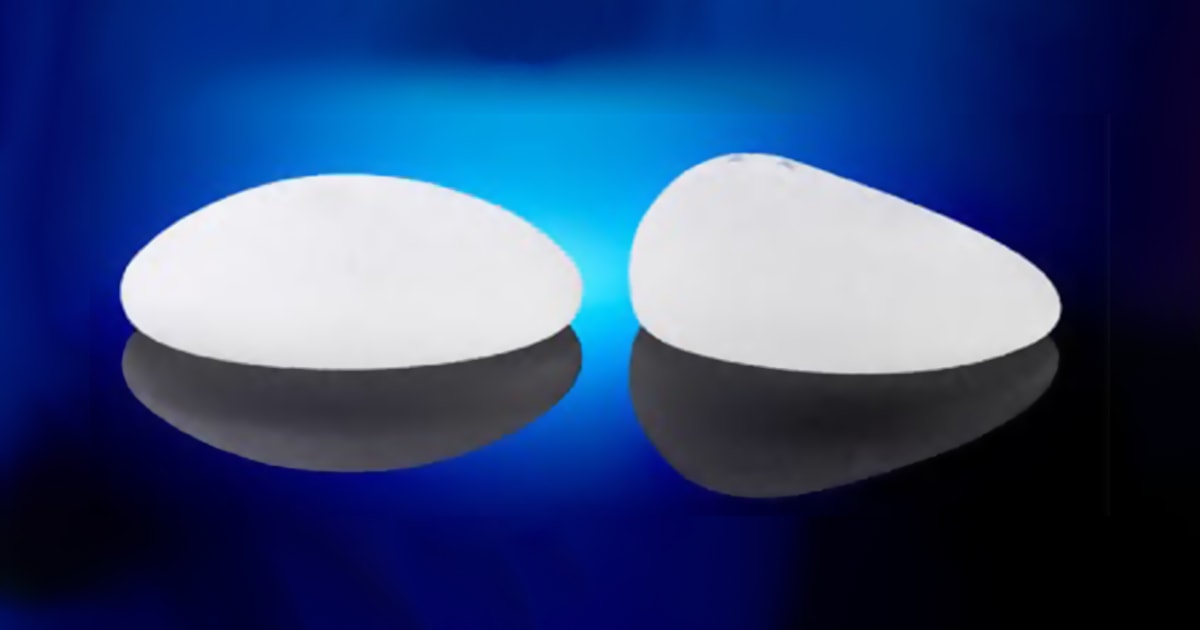
The smooth-surfaced silicone inserts are smooth to the touch and slide when placed in their case. They do not integrate easily with tissues and have therefore been progressively replaced by trabecular surface implants.
Tracheal silicone implants are a new generation of implants as they come in direct contact with the tissues, give a very natural result and generally have far fewer application problems.
Depending on the shape
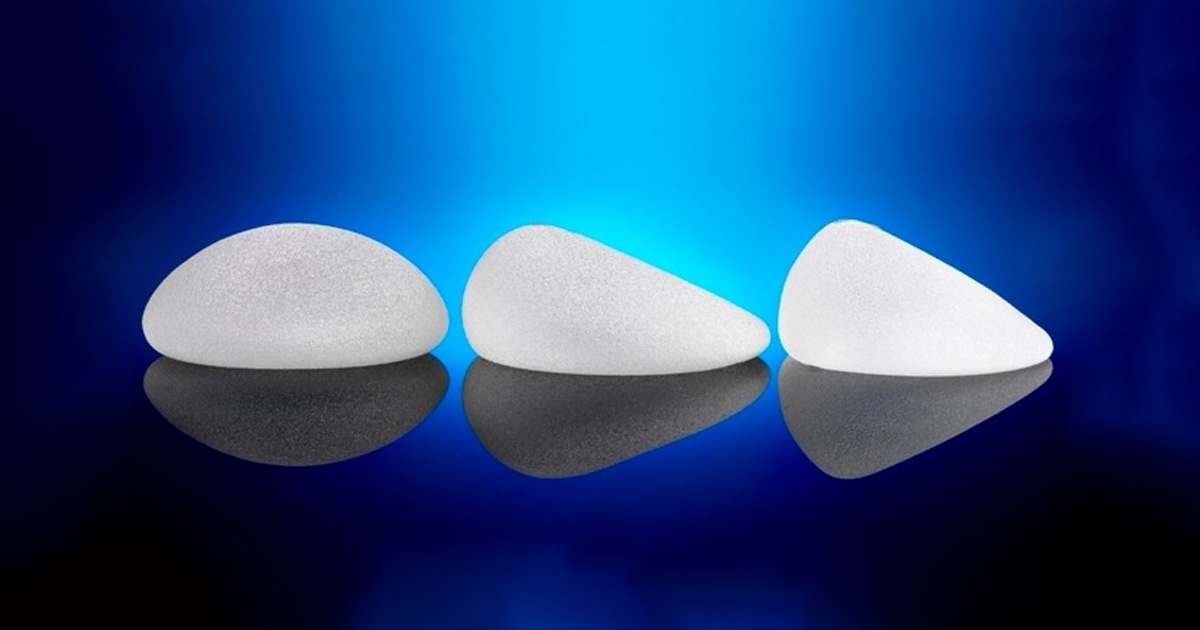
Depending on their shape, silicone inserts are divided into:
- round (round) and
- anatomical tear-like inserts.

Round silicone implants are the most popular, the safest and the ones we use in breast augmentation all the time.
Anatomical silicone implants are usually used in extremely small breasts or in rehabilitation problems.
They are excellent inserts and have very nice results however due to their shape they have the disadvantage that they can rotate in their case and change position. In these cases an intervention is required to correct the problem.
There are several studies that claim that whether you have round or anatomical silicone breast implants, in the majority of cases, after one year there is no significant difference in the aesthetic result.
Depending on the profile
The round inserts have a round base and project forward. As far as the projection is concerned, there are gradations, so depending on the width of the chest and the size of the projection we want to achieve, the inserts are divided into:
- Low profile
- Moderate plus
- High profile and
- Εxtra Ηigh profile

Can I know in advance what my new breasts will look like?
Today, before the breast augmentation surgery, we can choose together and with great accuracy both the size and the shape of the new breast.
For this purpose, when we perform a clinical examination in the clinic we use special testers – sizers (i.e. special silicone insert testers) with which we can simulate the new breast.
As mentioned above, this is done in the clinic where we use a thin bra to place the silicone test inserts into the bra. In this way we can both touch the breast and see with our eyes in the mirror in real time how our breast will look like after the operation.
Selection of the size and shape of the silicone insert.
Our goal is always a beautiful, natural, full, harmonious chest. To achieve this, we recommend implants that are beautifully covered by the existing gland and fit the woman’s body type.
We generally do not recommend very large Hollywood-type inserts. The larger the insert the more the breast grows but in this case it is less and less covered by the mass gland and the less protected it is.
Also the larger the insert the heavier it is resulting in faster sagging and dropping of the breast.Very large inserts have a much higher potential for complications and need a lot of thought whenever we need to use them.

The insert should be neither too small nor too large. If the insert is the right size then we will not catch the silicone when we touch the breast and the breast will not look like a balloon but will look very natural.
In any case, the choice of the appropriate insert is very important and requires very careful planning.
In addition to the patient’s desire for larger breasts, it is very important to consider:
- the distance between the two breasts,
- the height of each breast,
- the diameter of the base,
- the position and size of the nipple,
- the position of the underarm,
- any asymmetries of the breasts.
Also the height of the girl, the distance between the shoulders, the circumference of the hips and the waist are of decisive importance for the perfection of the result.
When is the silicone insert palpable?
The silicone insert is more tactile, i.e. it can be felt by touching the breast:
- when it is large in size so the larger the insert the more we “grab it” (usually at the lower inner or outer breast pole)
- the less it is covered by the normal gland and skin because the less it is protected.
- when it is placed subauricularly or subfacially i.e. just under the gland or fascia and not under the muscle.
Before breast augmentation surgery.
A simple preoperative Blood, Cardiology and Chest X-ray and a COVID test is recommended.
We recommend that all women undergo a digital mammogram preoperatively, which is used as a reference mammogram for the condition of the breast. Young women or women with very dense breasts can have a breast ultrasound instead of a mammogram.
For greater safety and better recovery, we recommend avoiding smoking, alcohol, aspirin-type anticoagulants and contraceptive drugs for two to three weeks before the surgery.
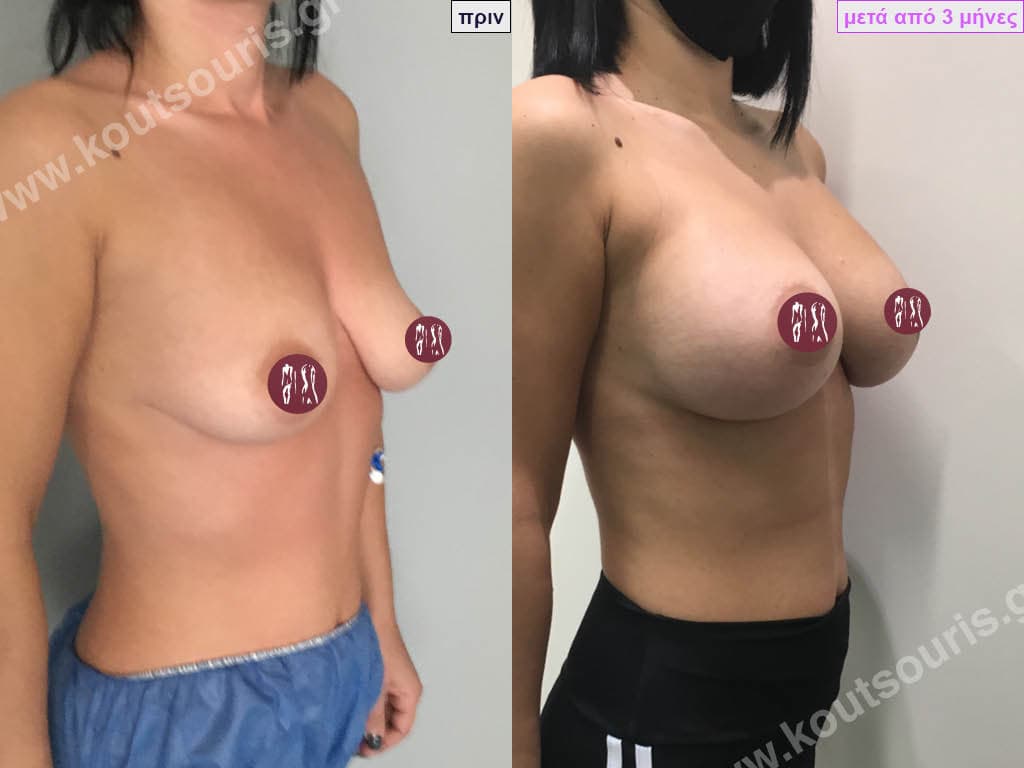
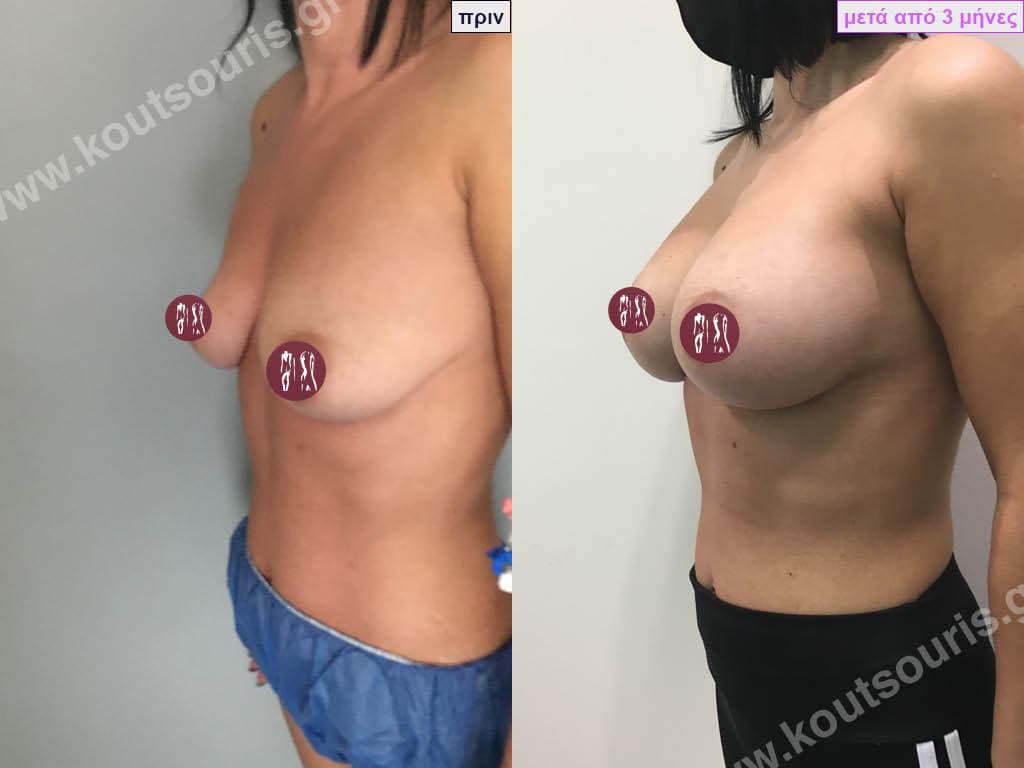
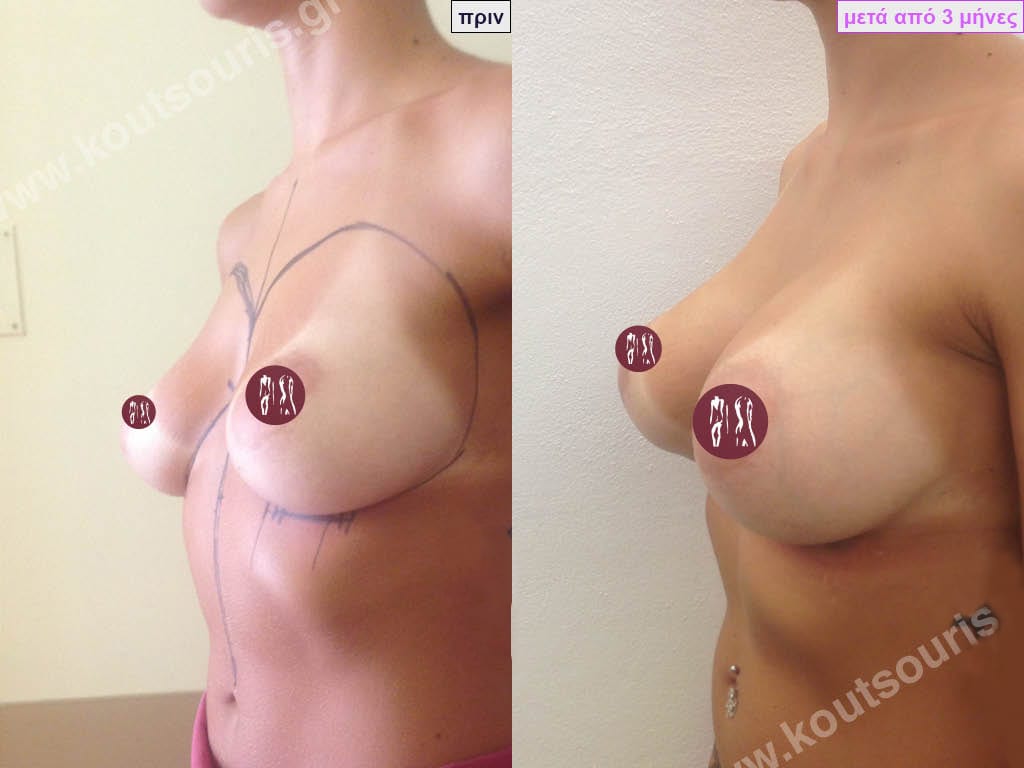
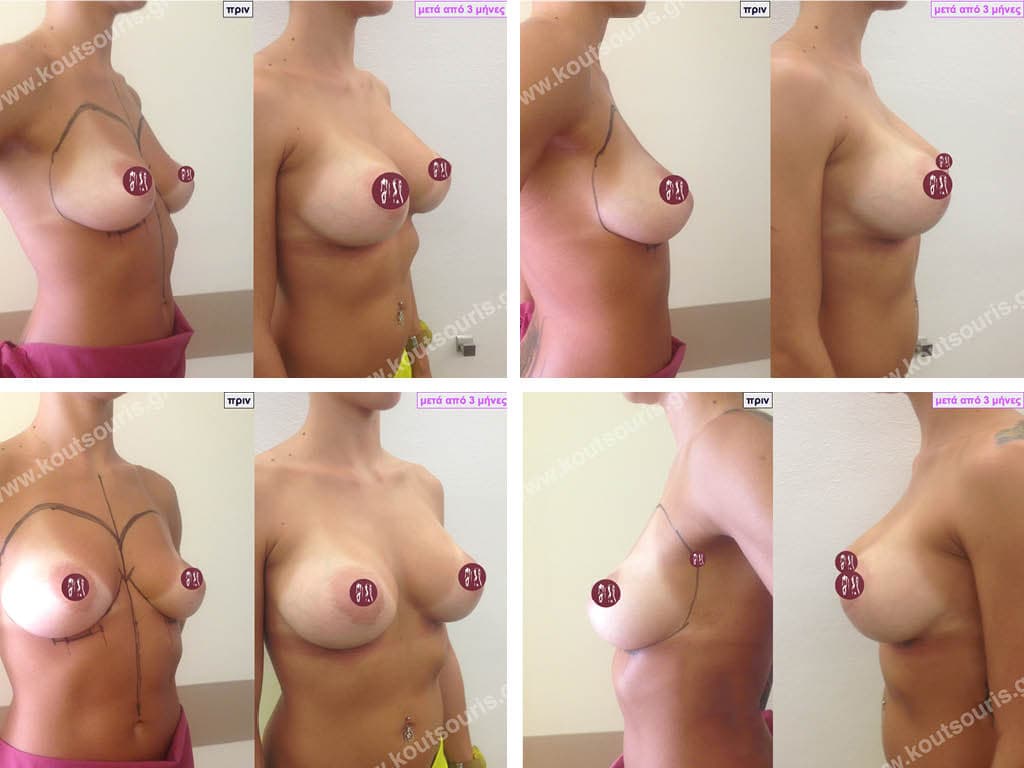
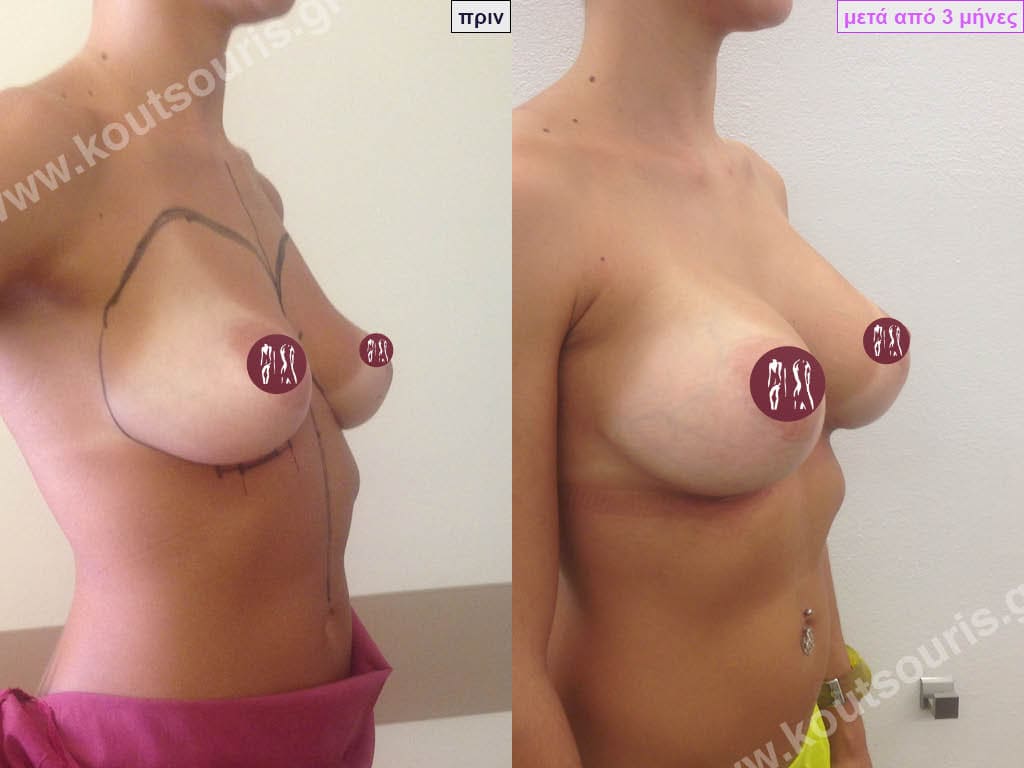
How is breast augmentation surgery performed?
Breast augmentation surgery is performed in an organised surgical clinic. The patient is put under general anaesthesia and then the surgeon makes a thin incision in the skin through which he or she creates the pocket of the implant. The silicone insert is inserted into the sheath atraumatically and placed in place. The incision is then closed with absorbable sutures and then with thin tape.
What anesthesia do we use for breast augmentation?
While breast augmentation surgery can be performed both with local and general anesthesia, we prefer general anesthesia. This way our procedure is very controlled and completely painless. In the Dual Plane technique (which we prefer primarily and is described below) we need a good depth of anaesthesia to have a completely non-traumatic and bloodless procedure.
Intersection position
The incision for insertion of the implant can be made:
- in the inframammary fold, i.e. just below the breast
- in the peri-mammary line ie around the areola of the nipple and
- in the armpit.
A fourth place for the incision is from the umbilicus.However, it is more of an “experimental” positioning than an applicable technique. It was described in America and has many problems because the insert that is placed is not made of silicone but of saline and as a technique it has extremely limited indications.
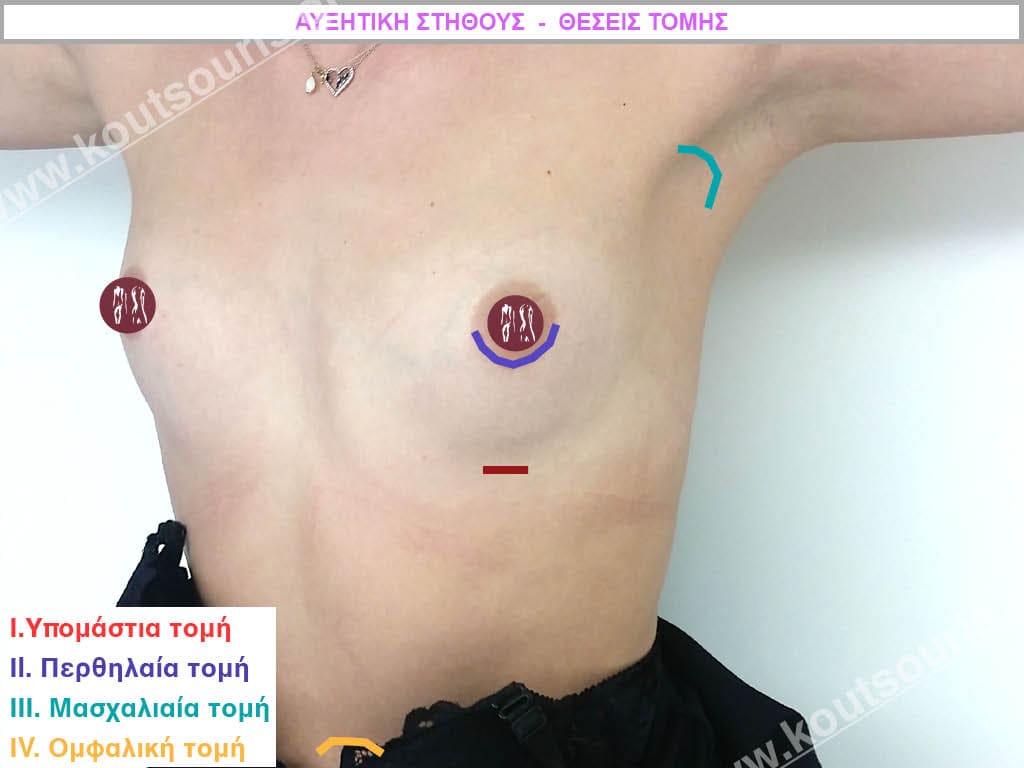
Which incision location do we recommend?
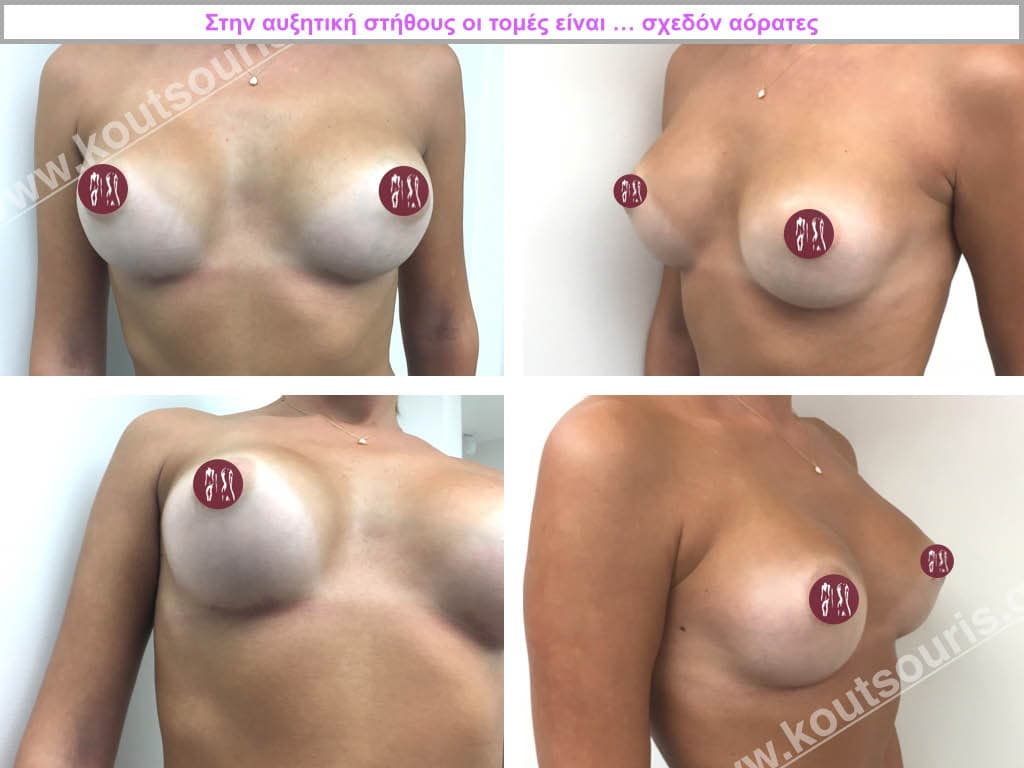
The best position for the incision in breast augmentation is the one that has the best aesthetic result, i.e. it is not visible or barely visible and has the fewest functional problems.
While I can make any incision for breast augmentation the incision I recommend is in the inframammary fold.
This because:
- it heals very well, softens and “disappears” slowly after a few months
- the parts of the breast related to future breastfeeding (mammary glands) are not affected at all
- it is completely non-traumatic for the mammary gland since the entire operation is performed under the gland without touching it at all, so no microcalcifications are formed
- it is not visible at all when looking at the breast since it is extremely hidden under the breast itself.
- offers very good visibility to the surgeon intraoperatively.
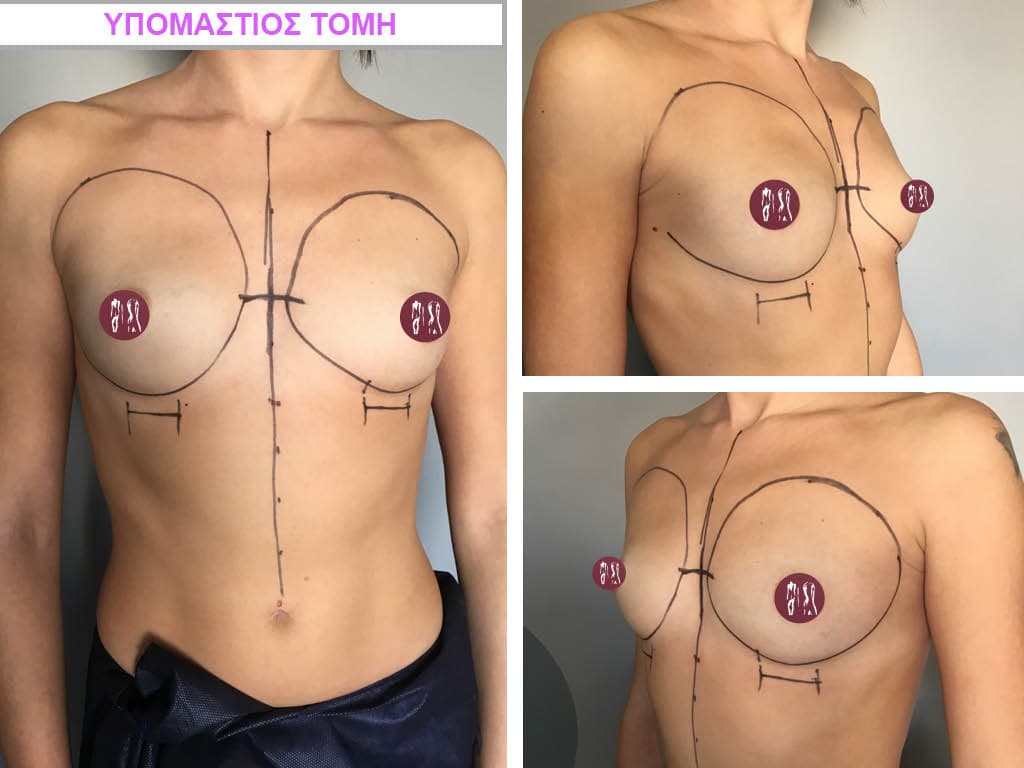
It is very important that the incision is made not where the inframammary fold is before the operation but where it will be after the breast augmentation.
For these advantages, most breast augmentations today are done through an incision in the inframammary fold.
What happens when we do a perineal incision?
The periapillary incision looks like a crescent moon and is made around the areola. The areola is the dark colored part of the skin around the nipple. It usually appears as a white line around the areola, meaning it is usually not completely invisible.
With the periammillary incision, in order to be able to get under the gland or the pectoralis major muscle, we must cut the gland in half, that is, injure the gland. This injury to the mass gland can create three problems:
- to reduce nipple sensation or to have hypersensitivity.
- reduce the possibility that the woman will be able to breastfeed after a future pregnancy.
- to create microcalcifications – microcalcifications inside the gland.
Microcalcifications are benign lesions that appear as small whitish spots on a mammogram and may form in the breast after a nipple-incision augmentation. This in itself does not create a problem. However, it has been observed that if a woman (who has not had a breast augmentation) develops a malignancy in the breast, then she can simultaneously present microcalcifications in the area of the tumor.
The problem arises if a woman has breast augmentation with a periammillary incision and after a few years microcalcifications appear. Then we should definitely consider whether the microcalcifications are due to breast augmentation and not to the development of a cancerous lesion. The process of excluding malignancy after breast augmentation is an extremely stressful situation for both the patient and her environment. This is another reason we avoid the nipple incision.
What happens when we do an axillary incision?
With axillary rosacea, the incision can be seen more strongly in the armpit, while technically there are many problems due to the long distance from the inframammary fold. In difficult breasts, reconstruction may be very difficult or even impossible with an axillary incision. The less we injure the mammary gland during breast augmentation, the safer our operation is.
Cut length
The length of the incision has to do with the size of the insert. For a 225-275ml insert we usually make a 4cm long incision while for a 300-350ml insert the incision is about 4 to 4.5cm.
If someone tries to make a smaller incision then they risk:
- to abuse or even break the insert and
- the incision to be misshapen due to skin injury from the manipulations.
How can we be absolutely sure that we have chosen the right type and size of insert?
In difficult breasts with asymmetry or with a lot of sagging, in order to decide on the final size or shape of silicone to be placed, we can during the surgery – immediately after the creation of the case – use special sterile test inserts-sizers which show us what will the breast look like after augmentation, in real time.
After trying different test inserts – sizers, we come to the one that gives us the best aesthetic result, so we completely remove the sizer and put the normal silicone insert. This way we can be very sure about choosing the right insert and precisely planning our intervention.
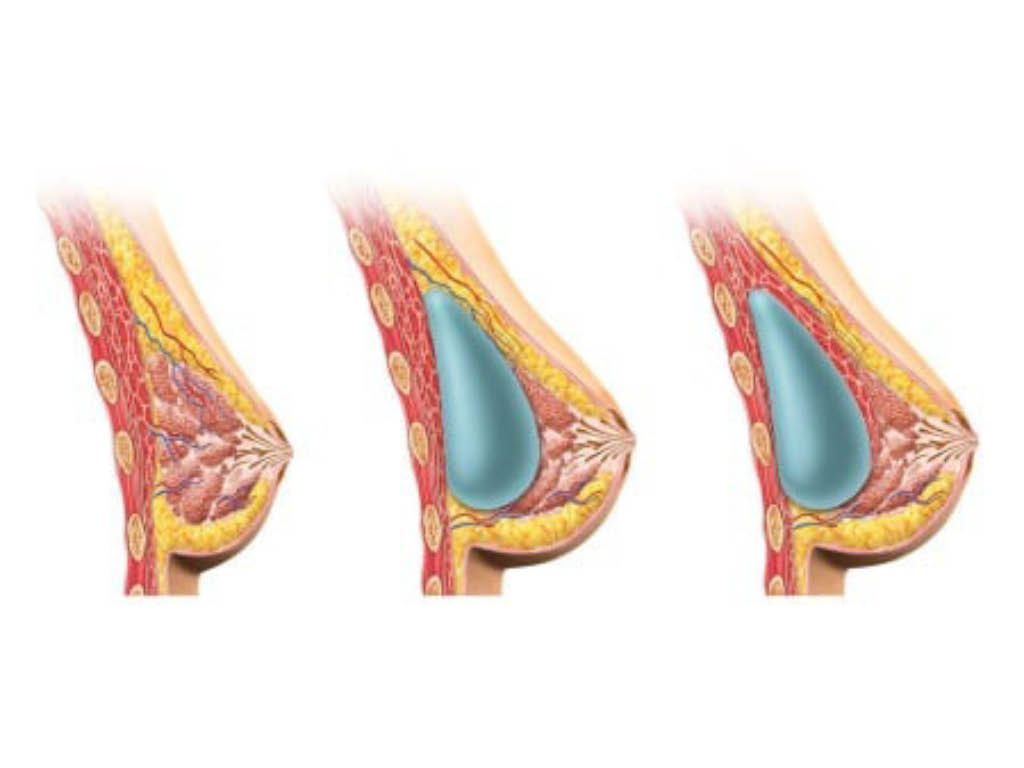
Placement of the silicone insert
Silicone implants are surgically placed in an anatomical pocket under the tissues in the breast area. The better they are covered by the overlying tissues, the more protected they are and the safer our intervention.
There are four places to place the inserts:
- subglandular i.e. just below the gland and on the pectoralis major muscle
- submuscular i.e. deep below the pectoralis major muscle and on the ribcage
- subfascial i.e. under the fascia of the pectoralis major
- dual plane technique, i.e. the upper half of the insert is covered by the muscle and the lower half of the insert is just below the gland.
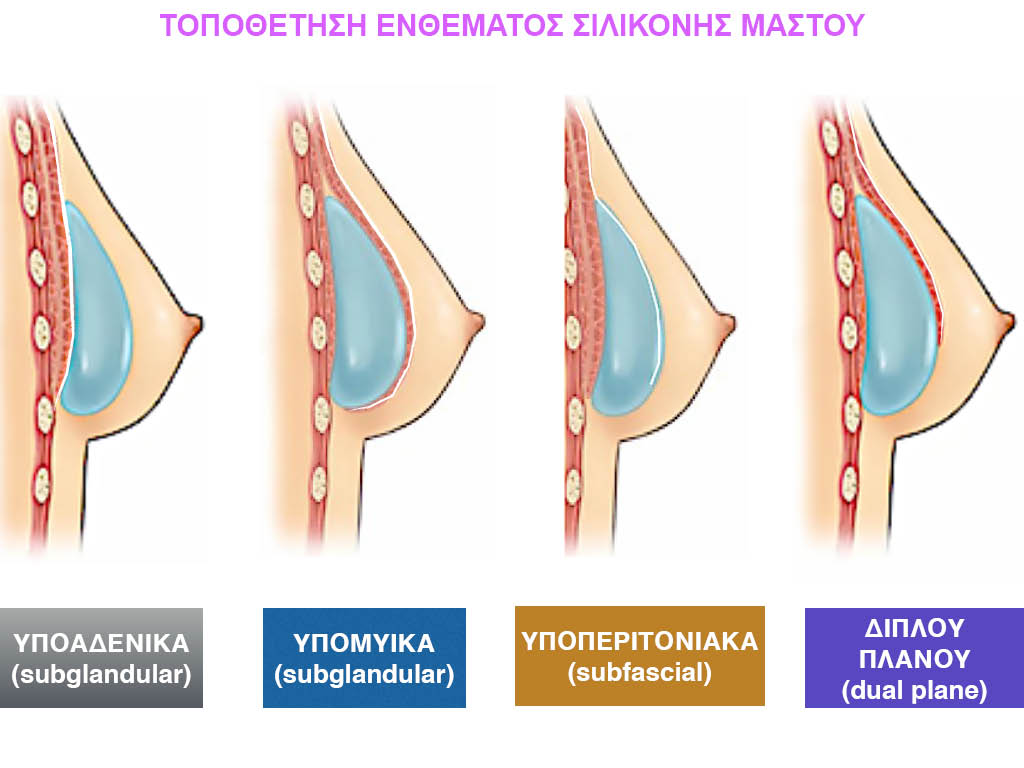
Subglandular placement of a silicone insert.
Placing the subglandular insert is technically an easy and quick operation. The problem with placing the implant under the gland is that in small and loose breasts the silicone can be felt as well as seen under the skin. The larger the implant, the more it can be seen – usually in the upper pole of the breast – which gets worse over the years. In the subglandular placement of the implant, the rate of forming a systolic capsule around the silicone is very high (about 17 to 20%). The only advantage to subglandular placement is that imaging the breast on mammography is easier.
Submuscular placement of a silicone insert.
Placing the submuscular implant is technically much more difficult than subglandular and has a longer recovery time. It can also be more painful and make some future elective surgeries more difficult if, for example, there is sagging and drooping of the breast.
In muscular women with thin breasts after submuscular placement of silicone, the insert may move up and down with the contraction of the muscles of the trunk and arms. Usually imaging the breast with a mammogram is more difficult.
Subfascial placement of a silicone insert
The insertion of the subfascial insert is done over the pectoralis major muscle, in a pocket under the muscle fascia. The fascia of the muscle is a very thin membrane that covers the muscle.
This is a very difficult technique that often fails since the fascia is very thin in most breasts and tears in our attempt to create the sheath.
In those cases where there is strong fascia, then the result is satisfactory, with a quick recovery. In thin and muscular women, we avoid the subfascial technique because it has a high rate of complications with the formation of a sagging capsule and a visible or palpable insert.
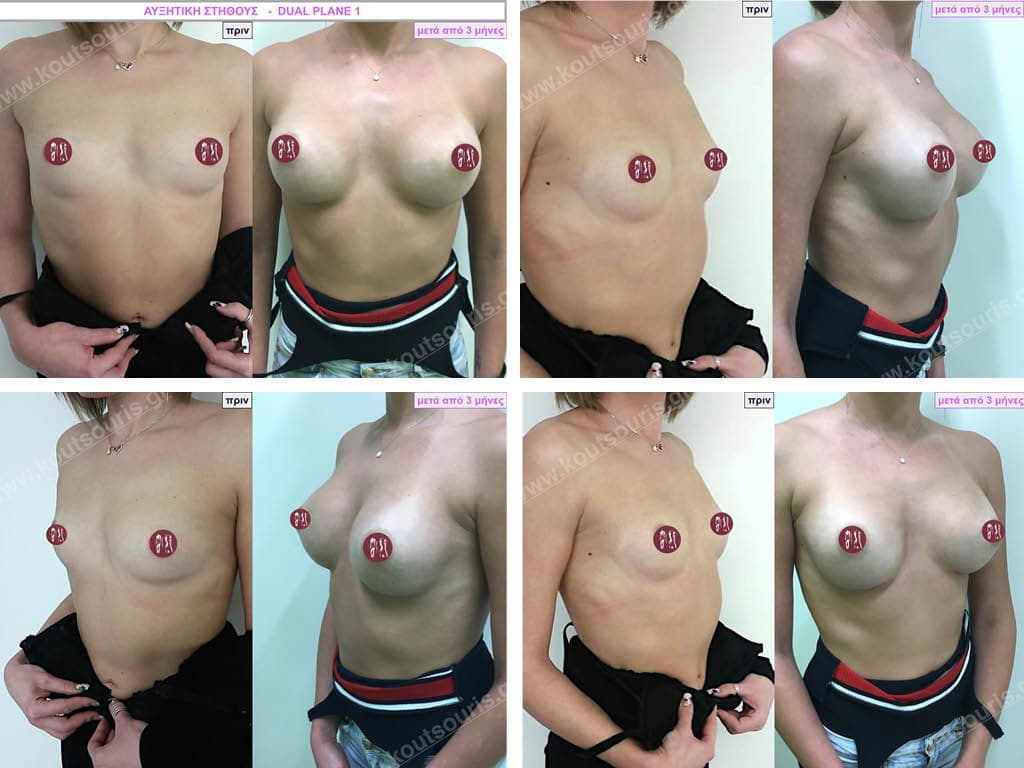
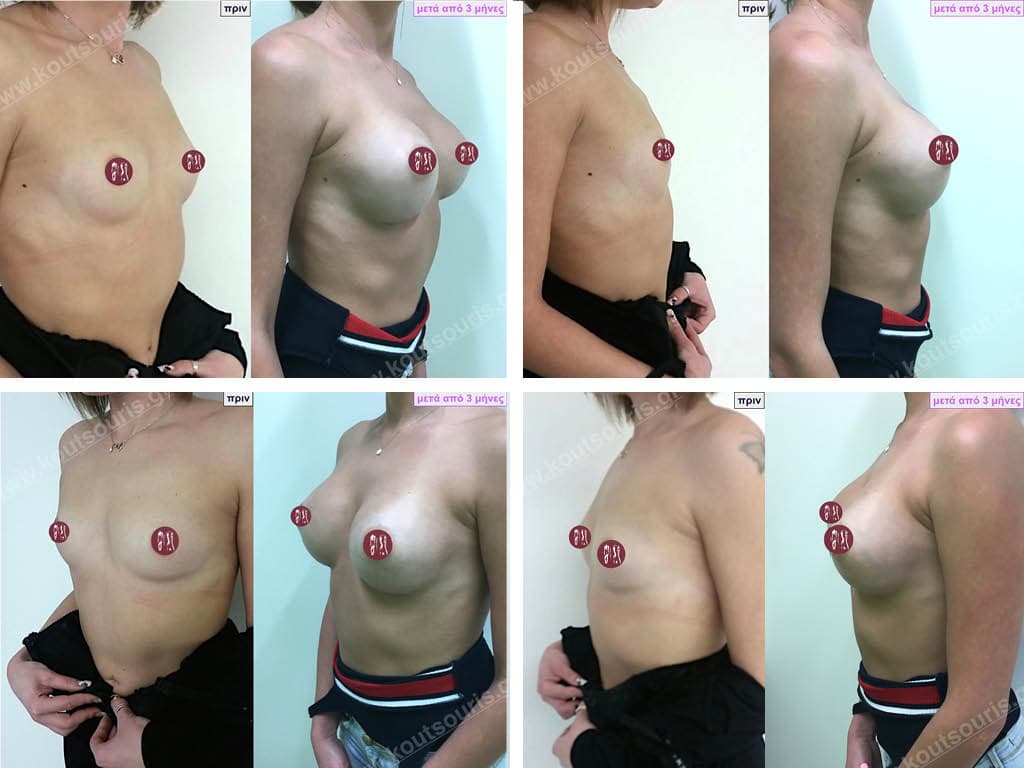
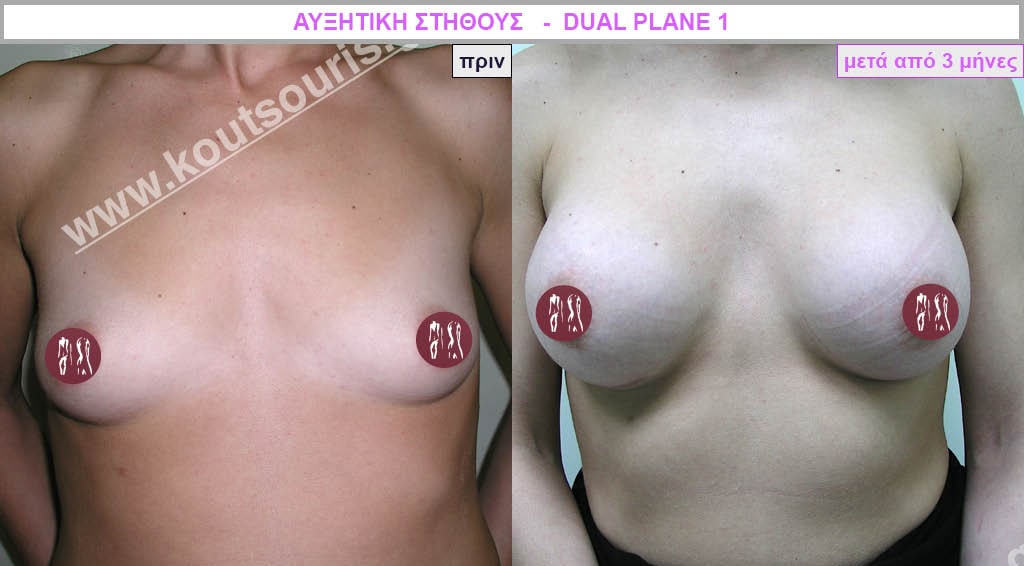
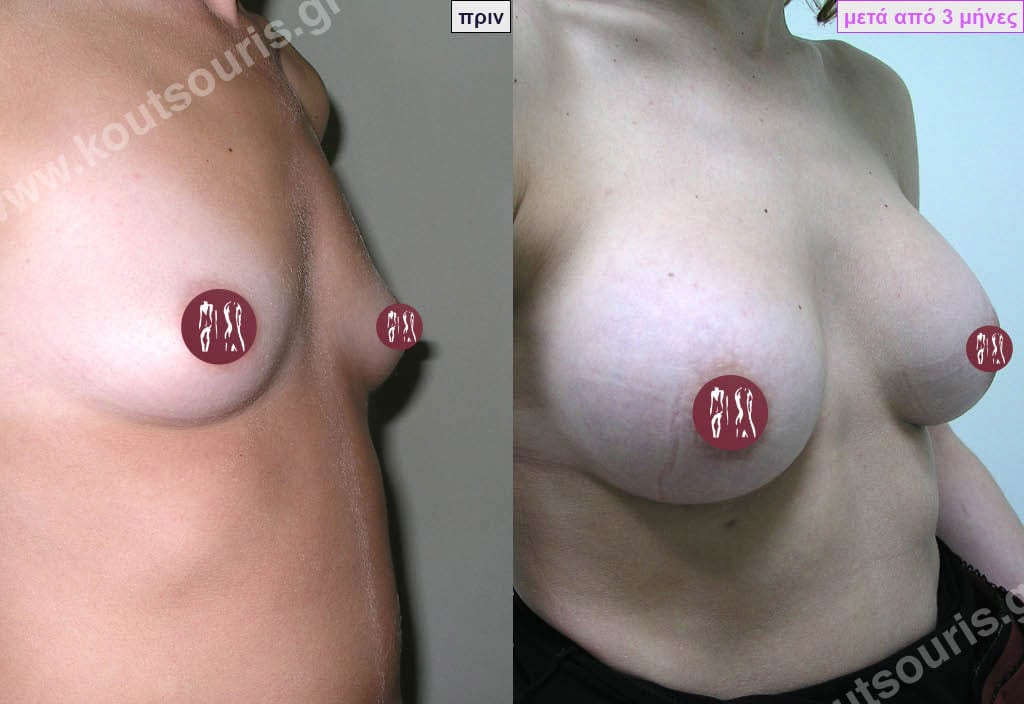
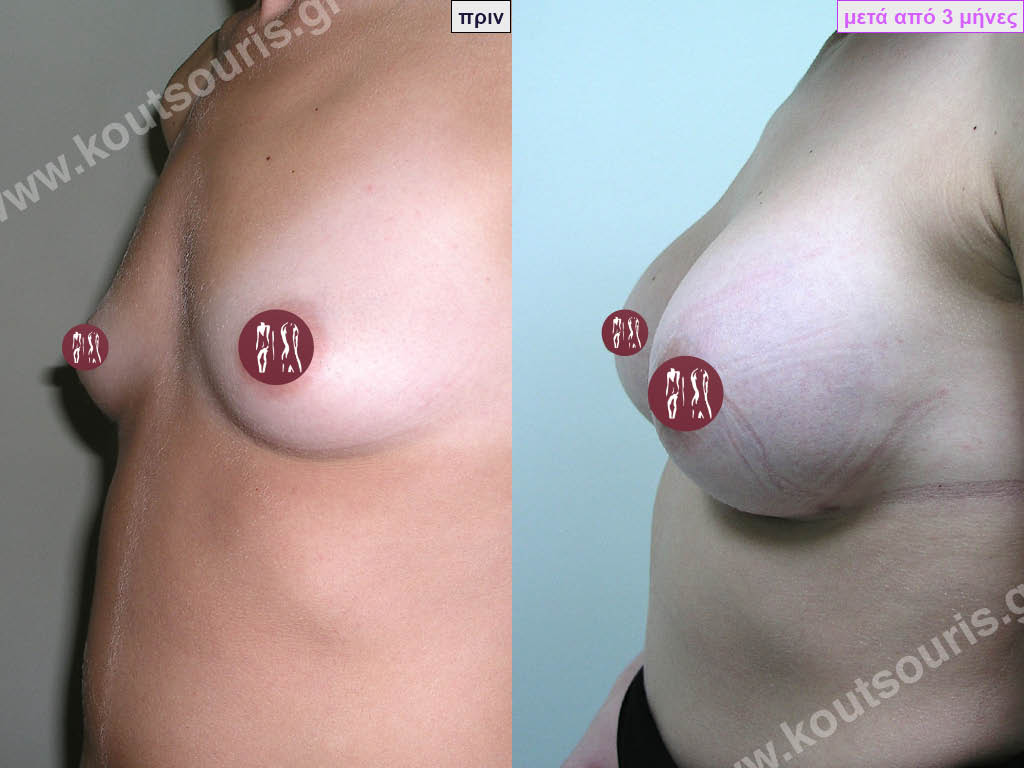
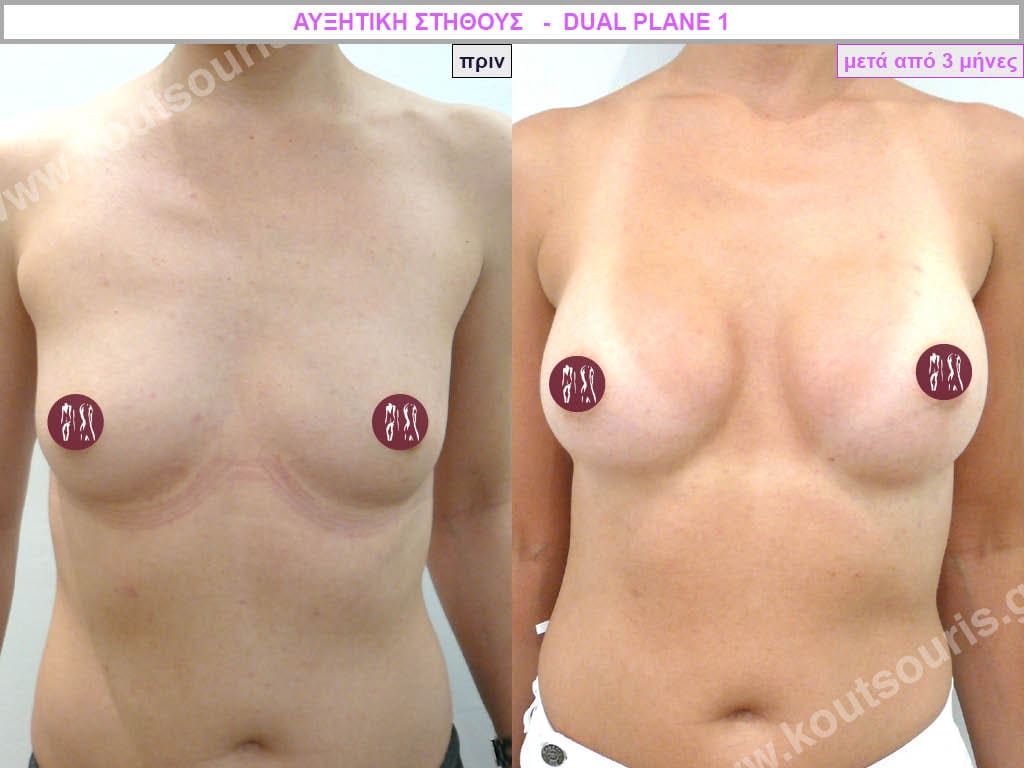
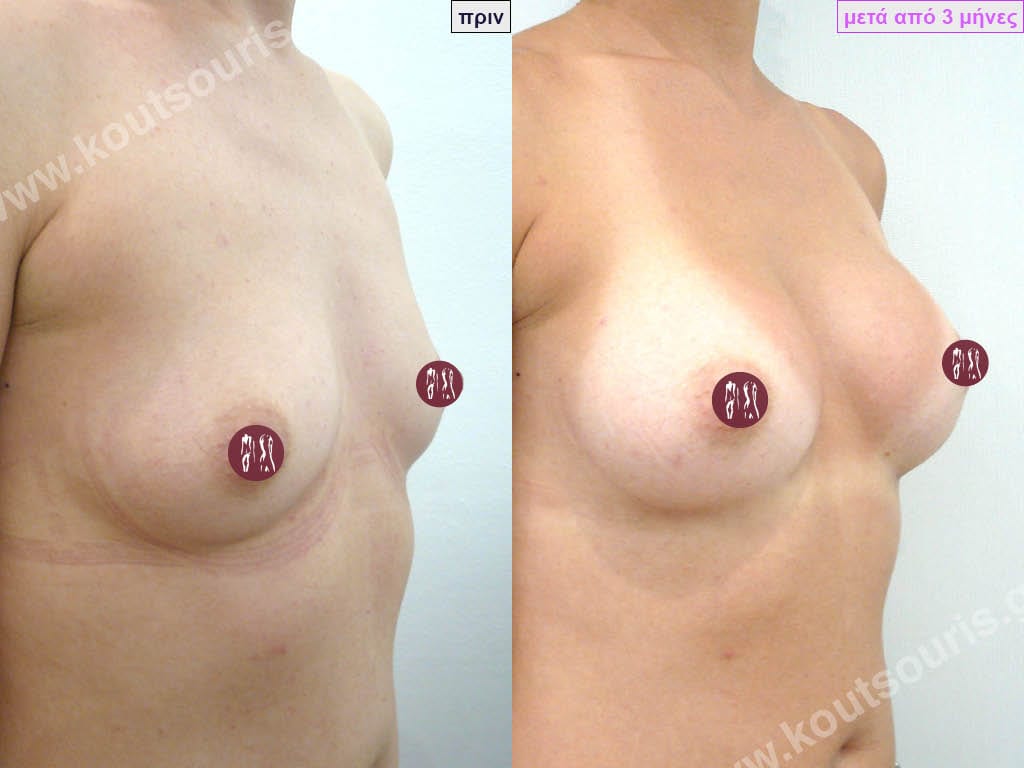
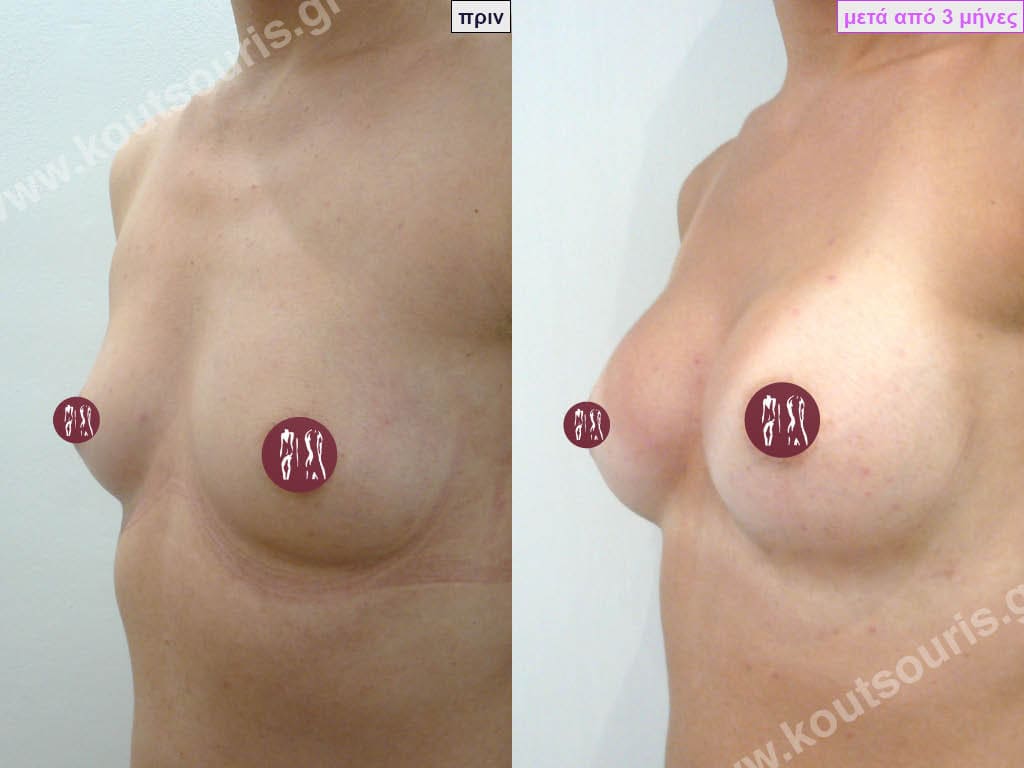
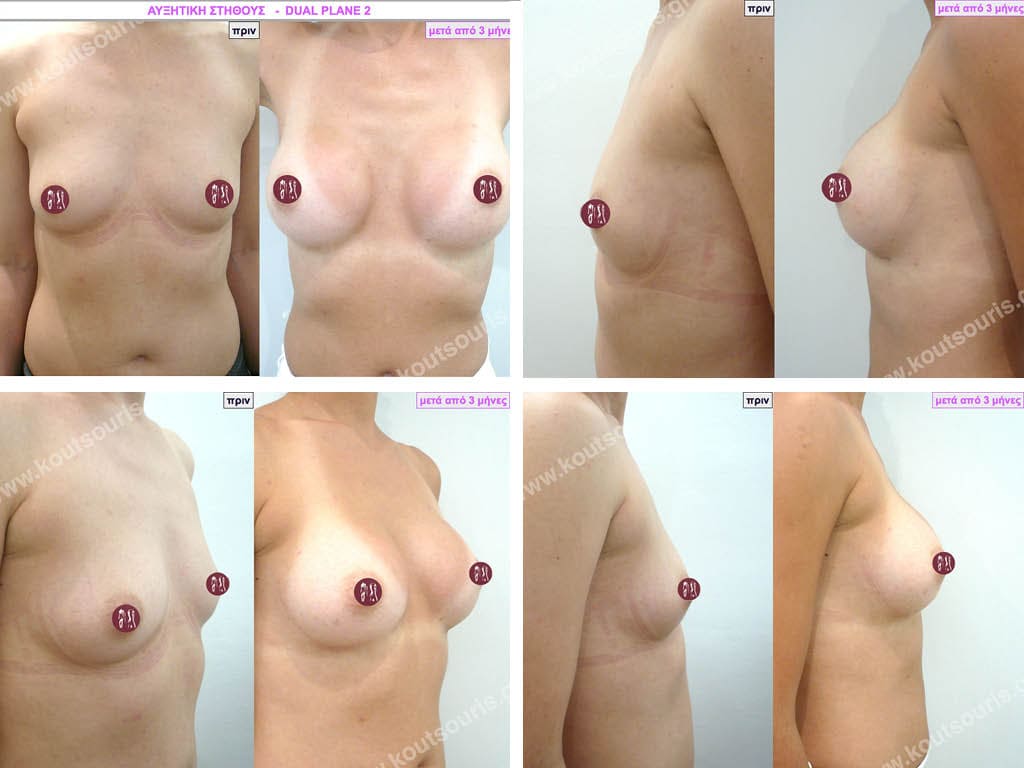
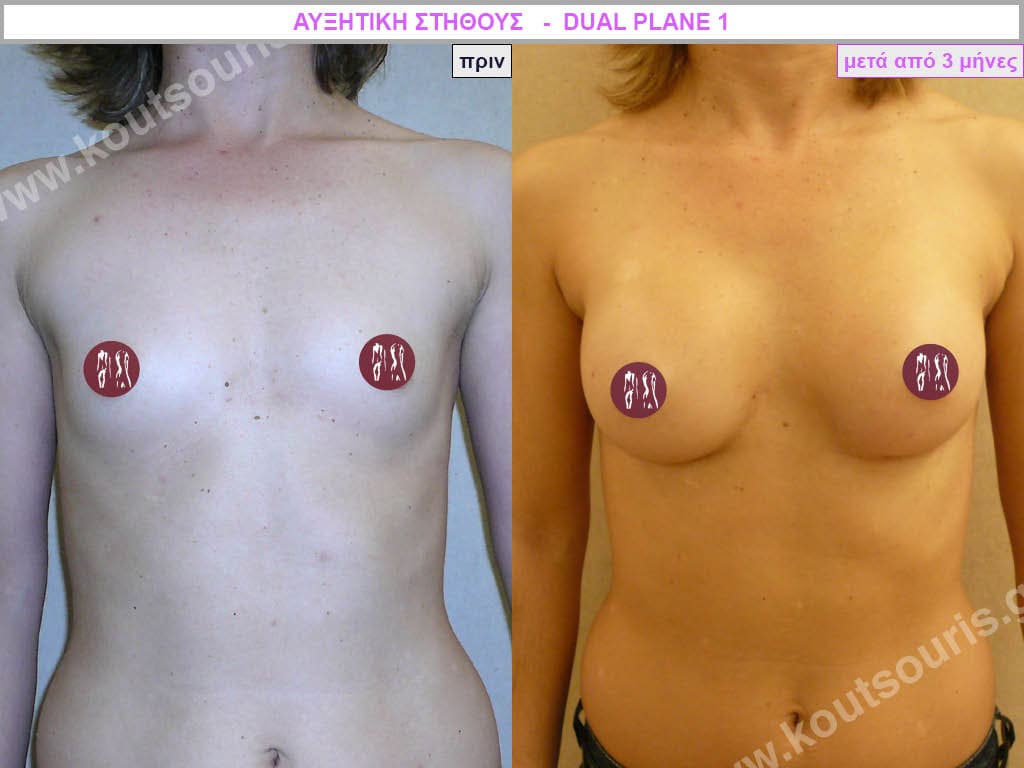
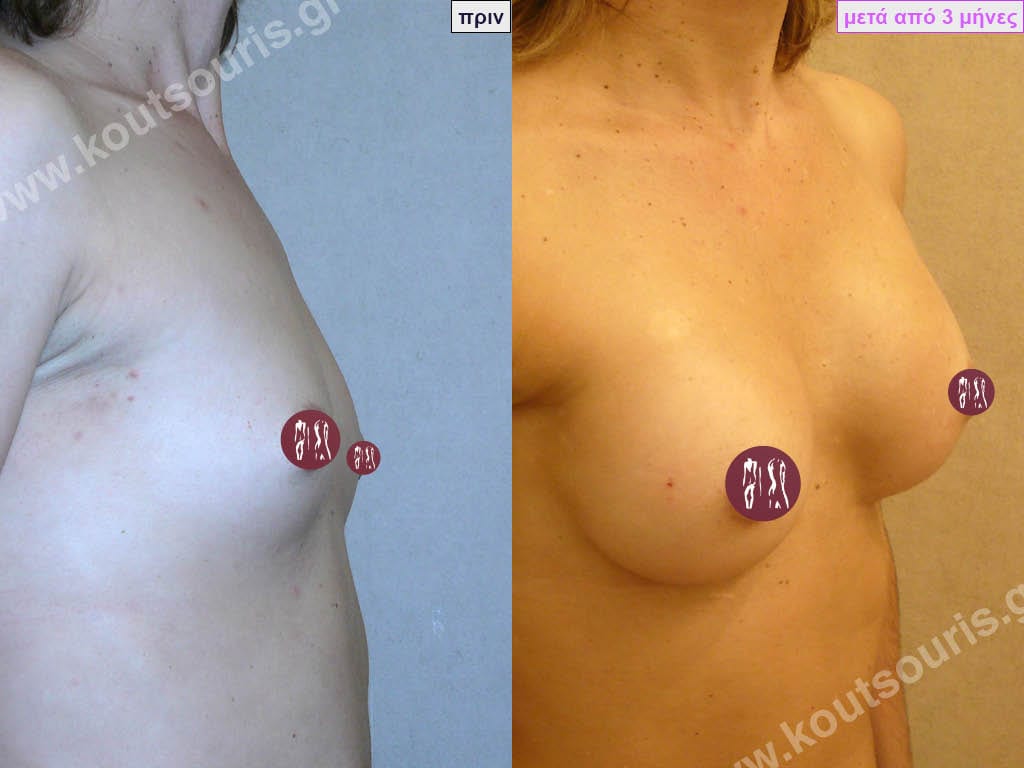
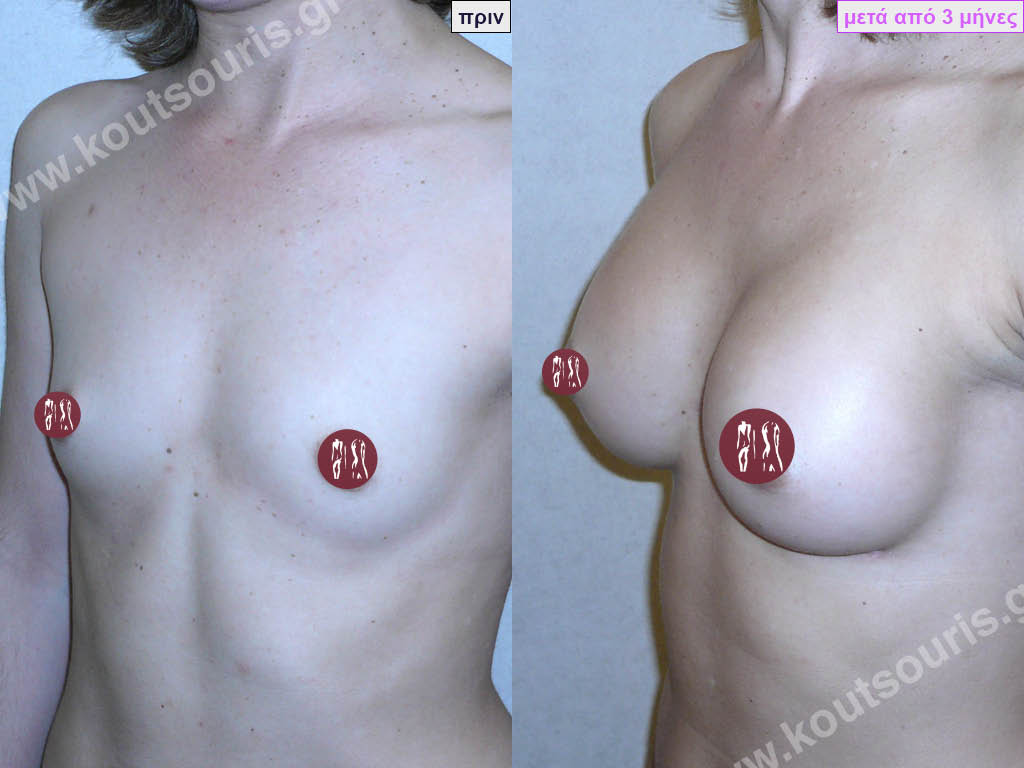
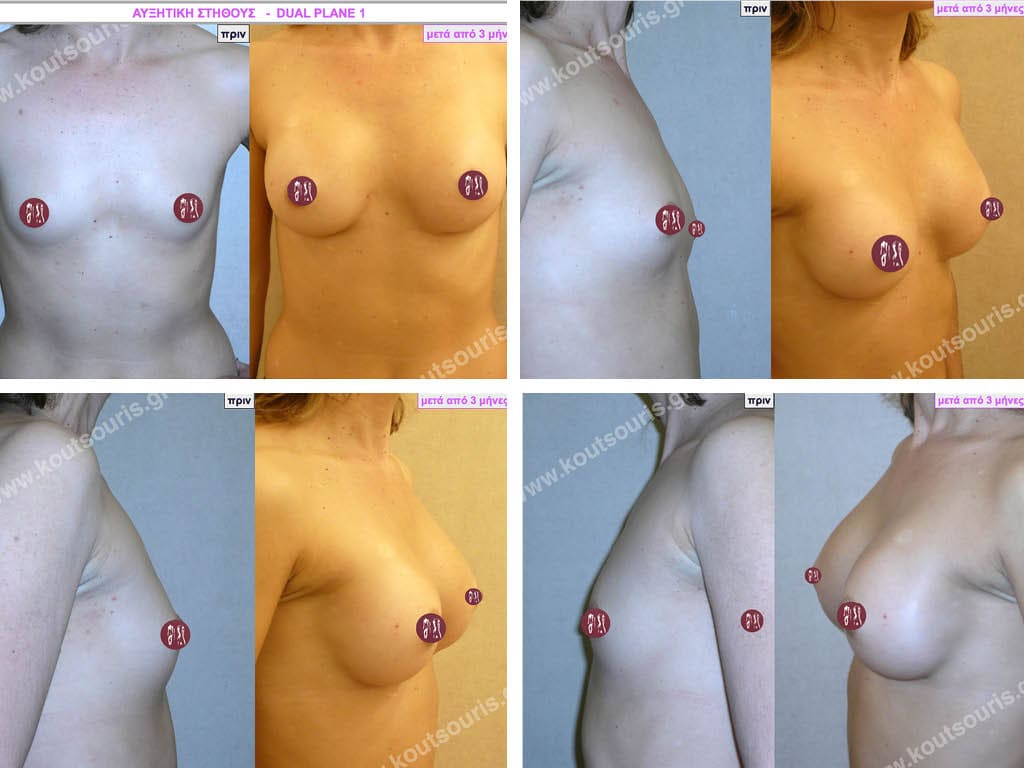
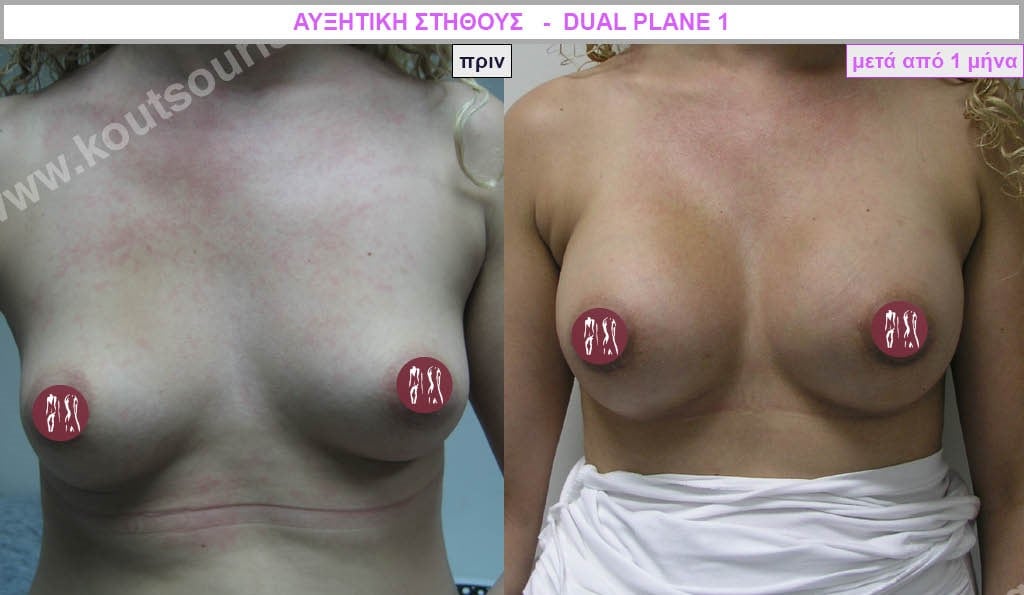
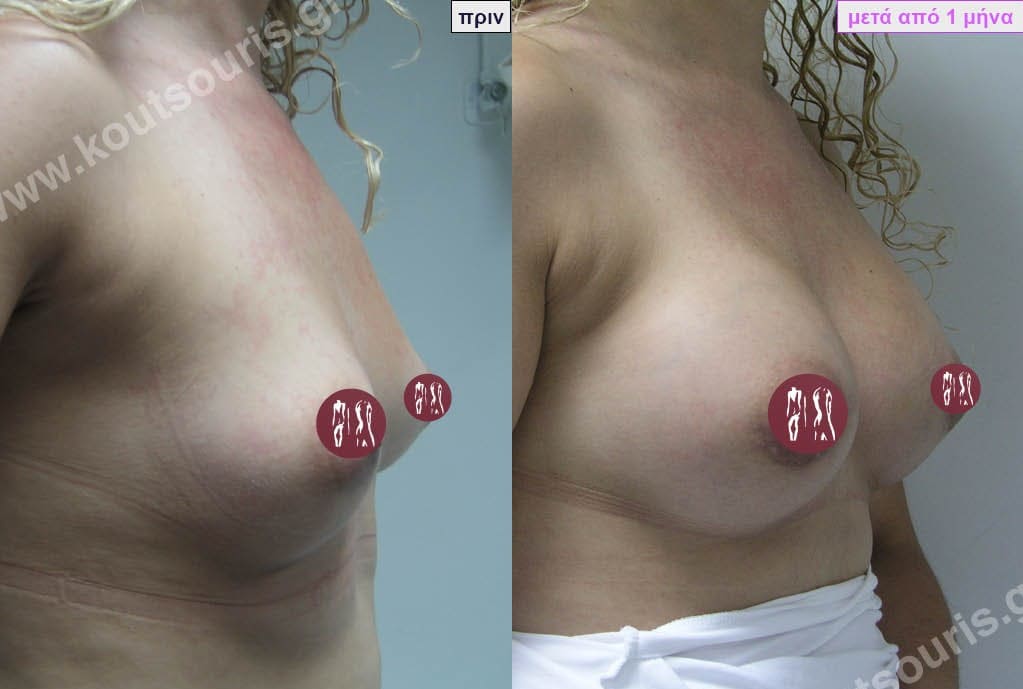
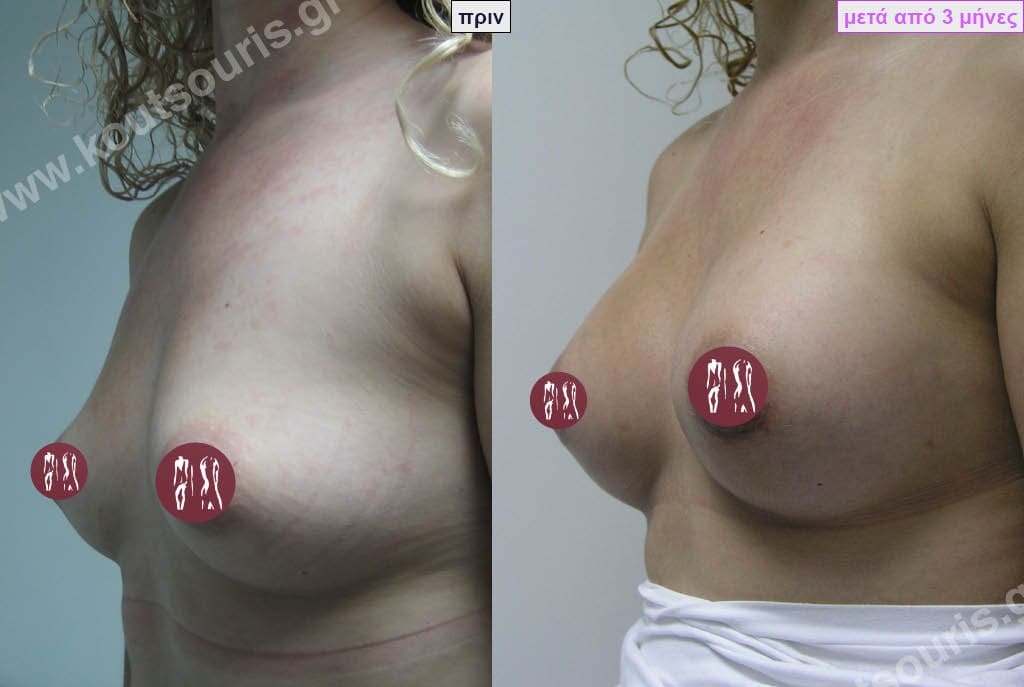
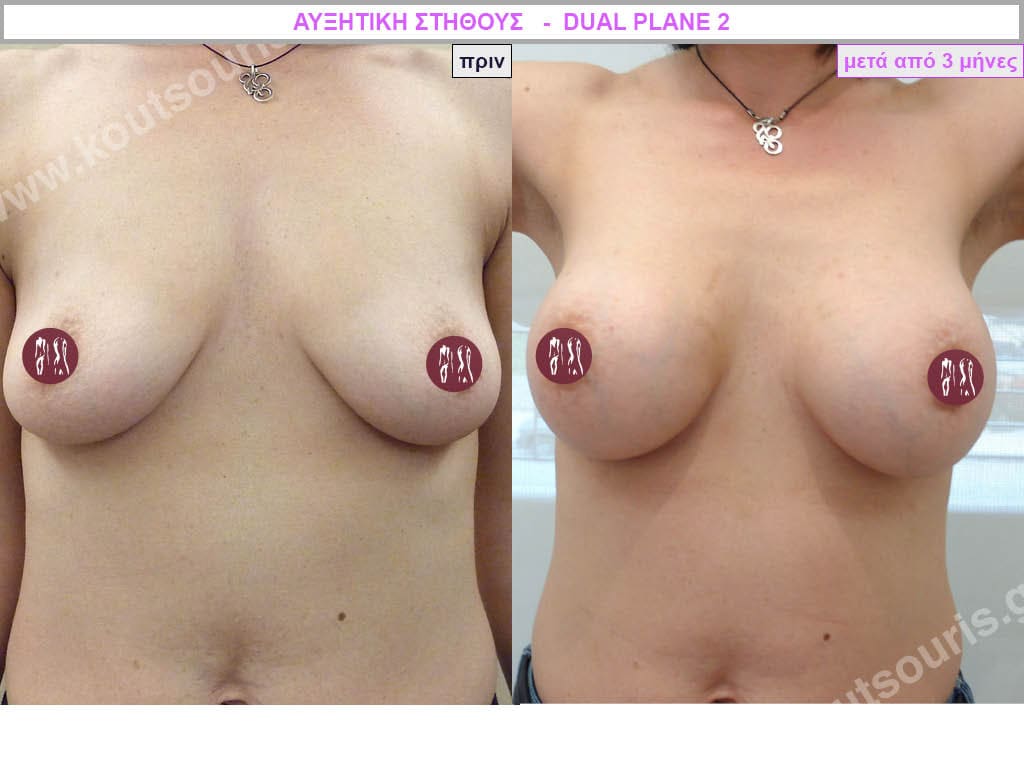
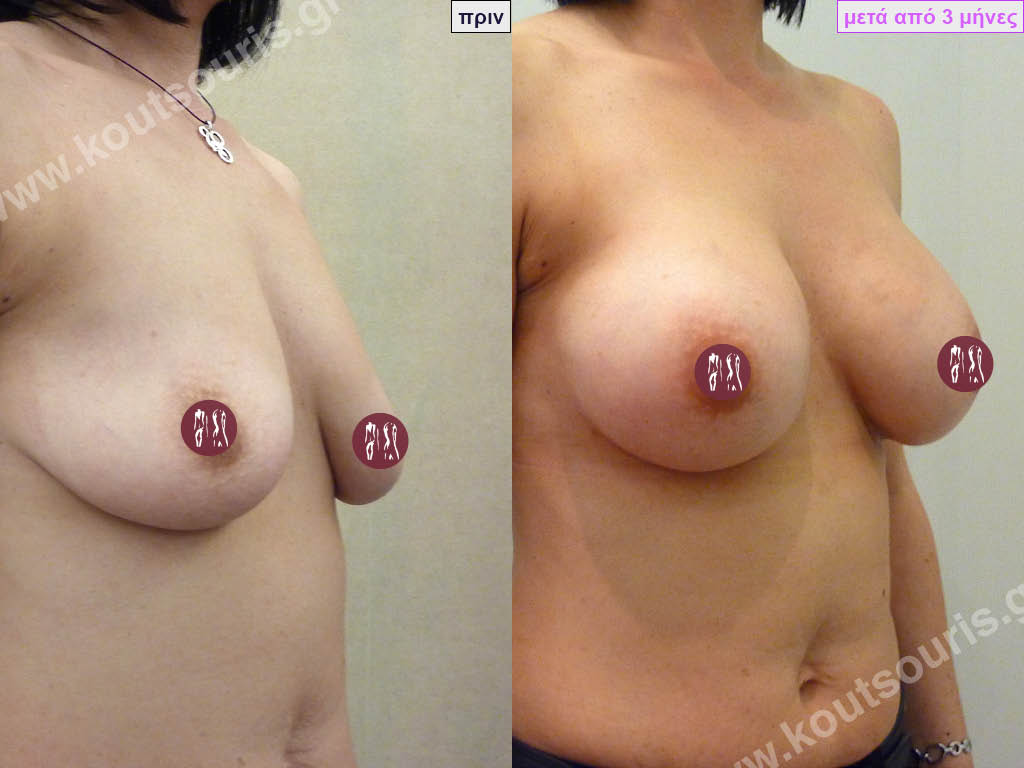
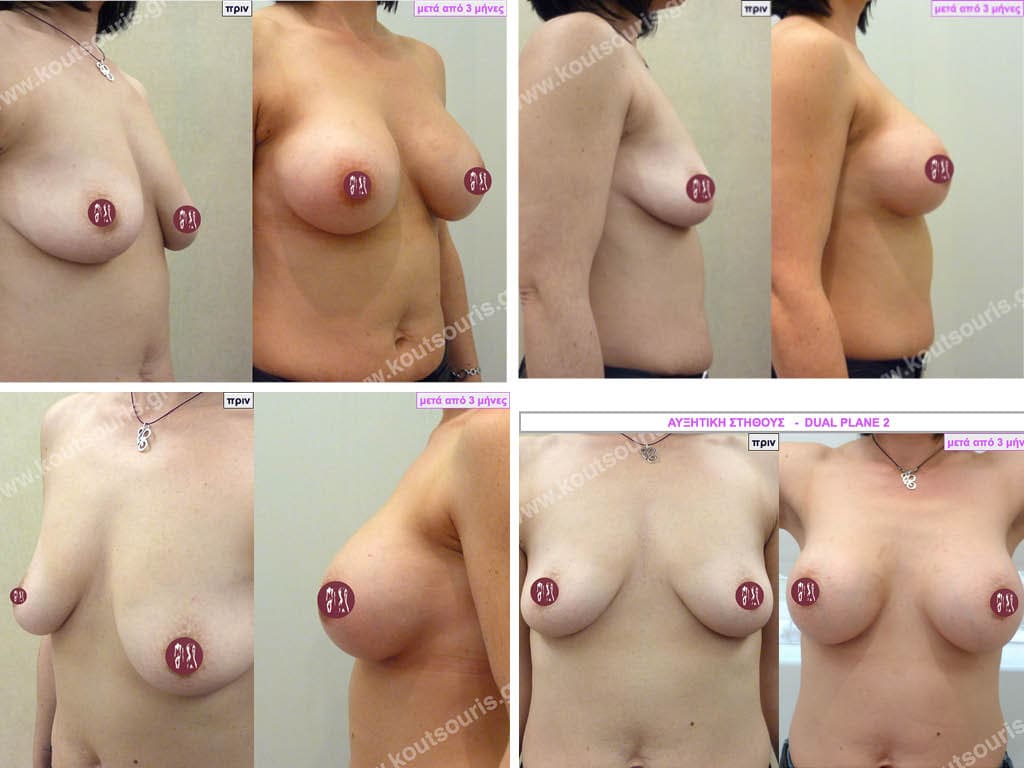
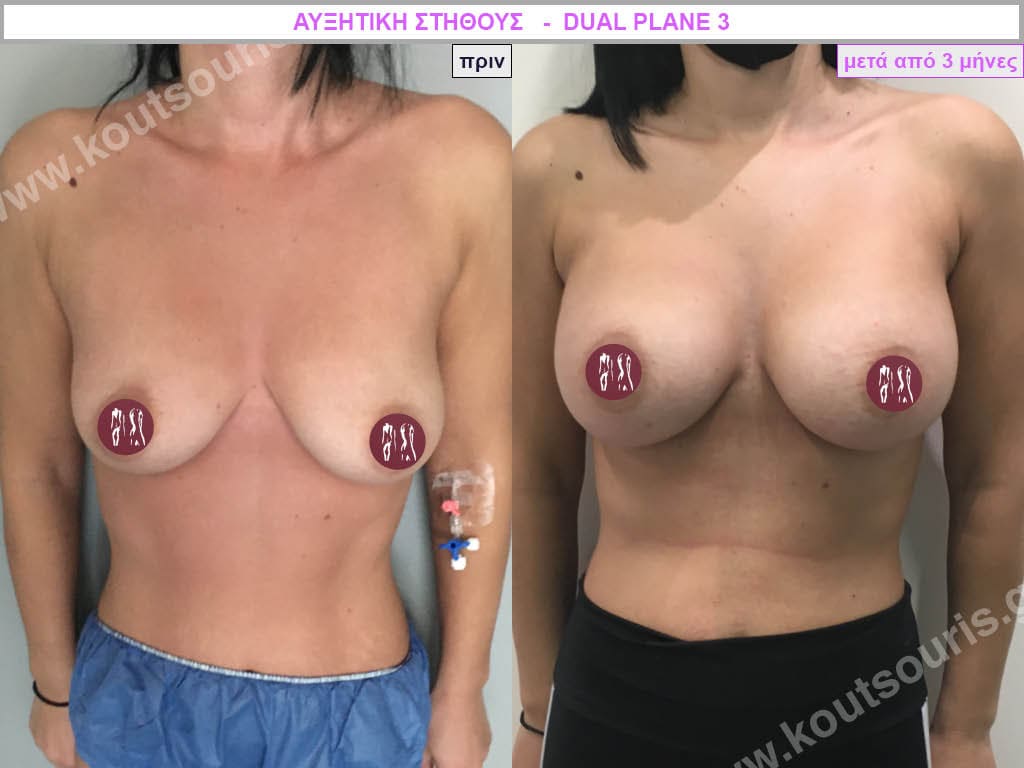
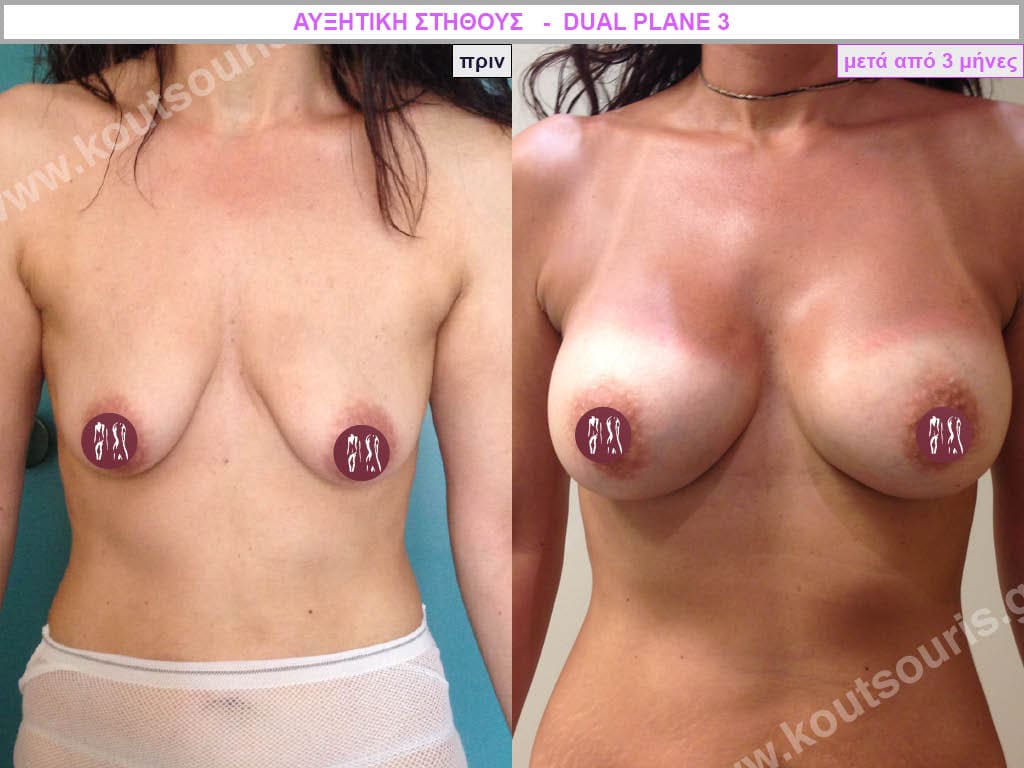
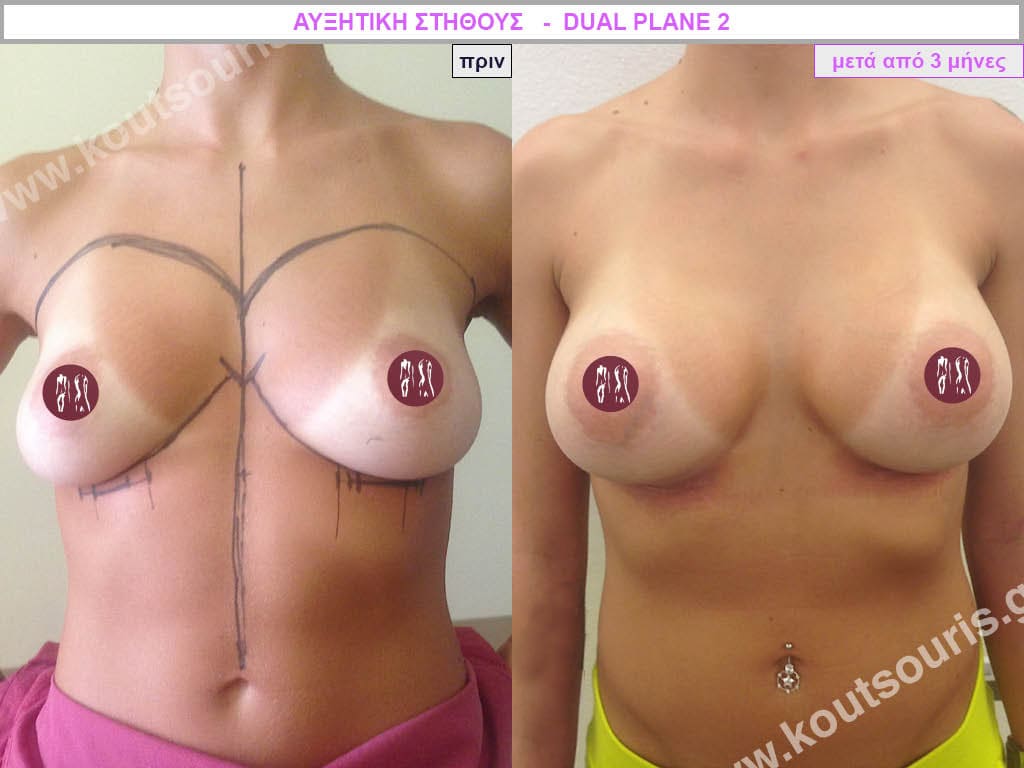
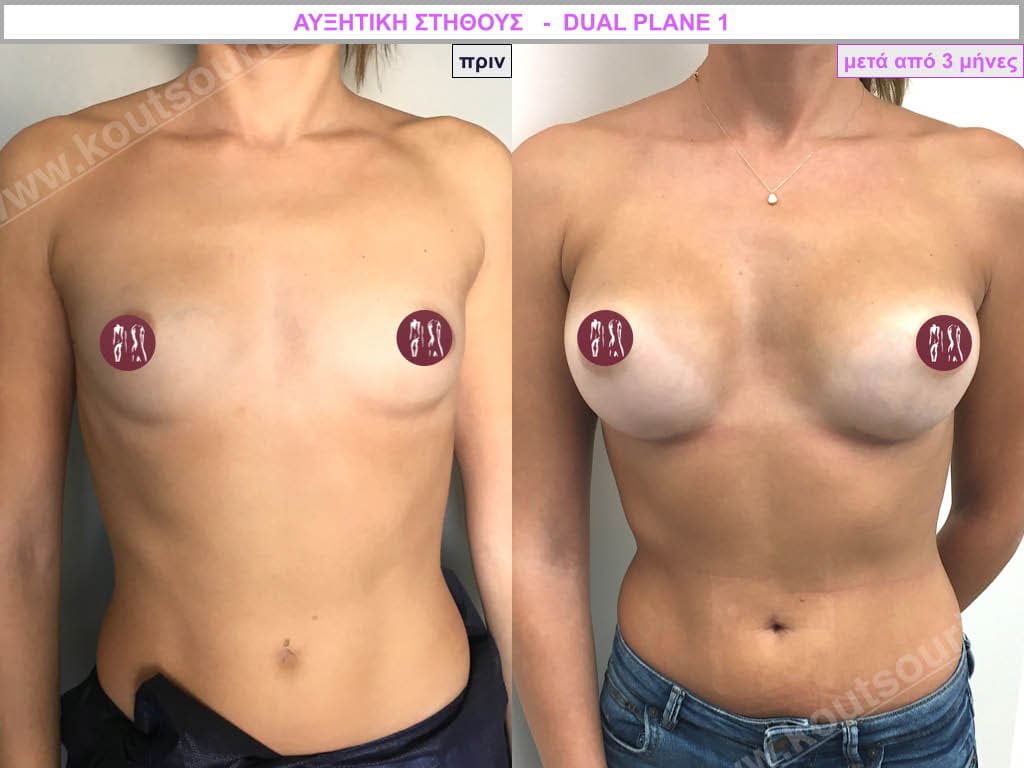
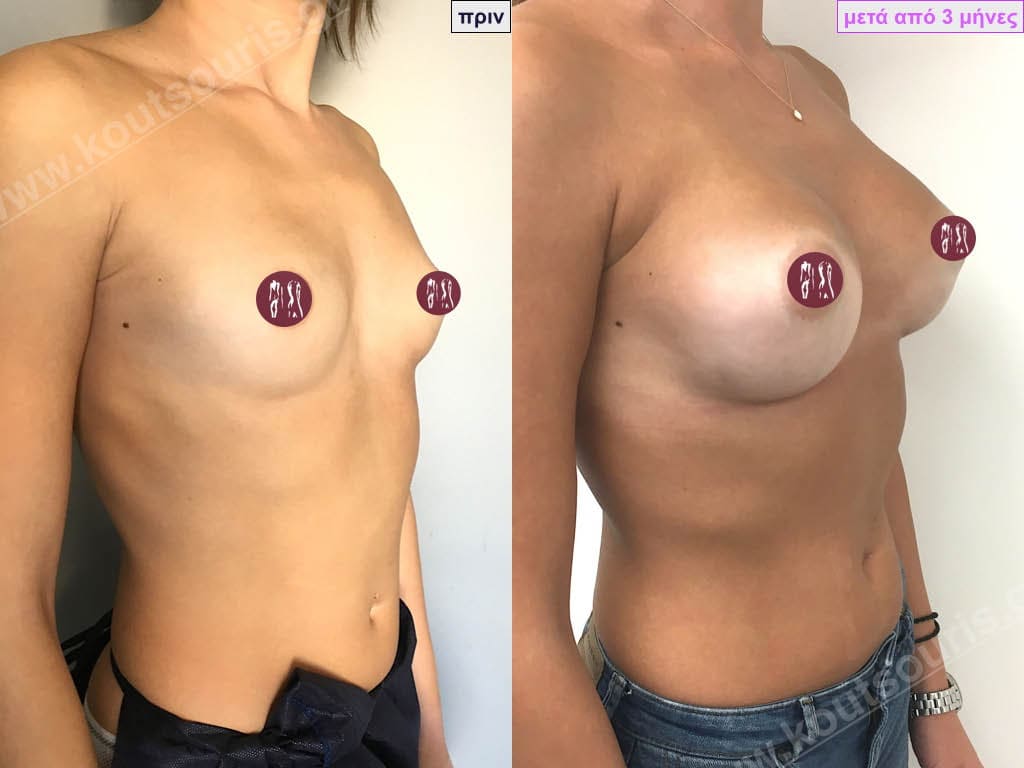
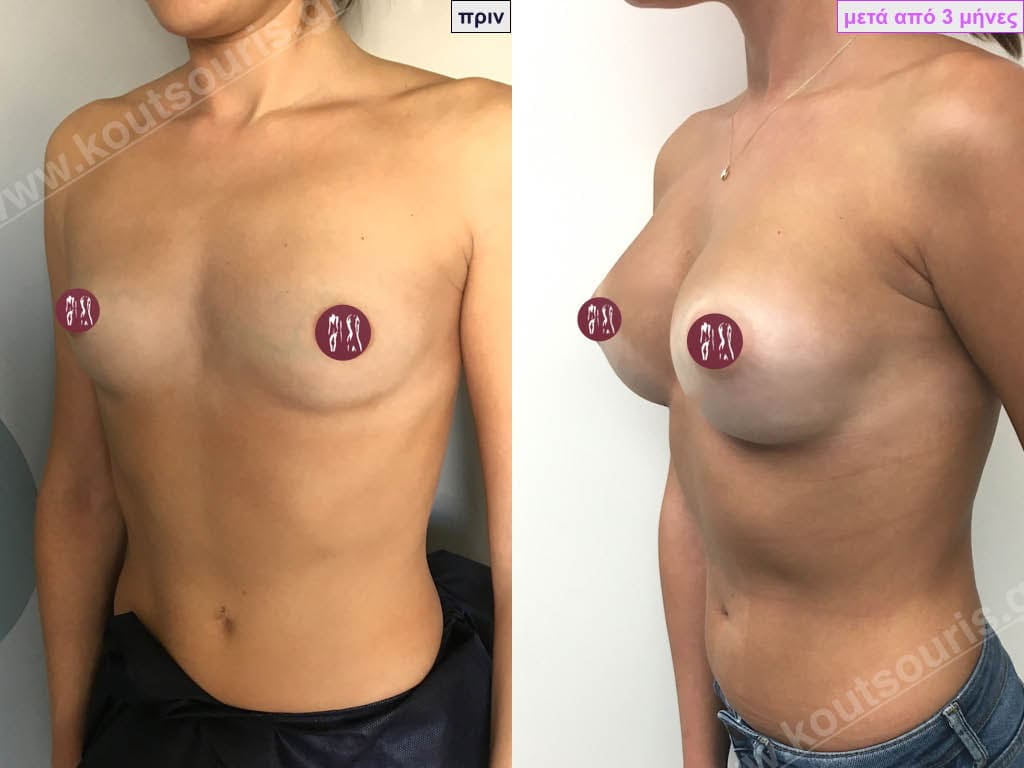
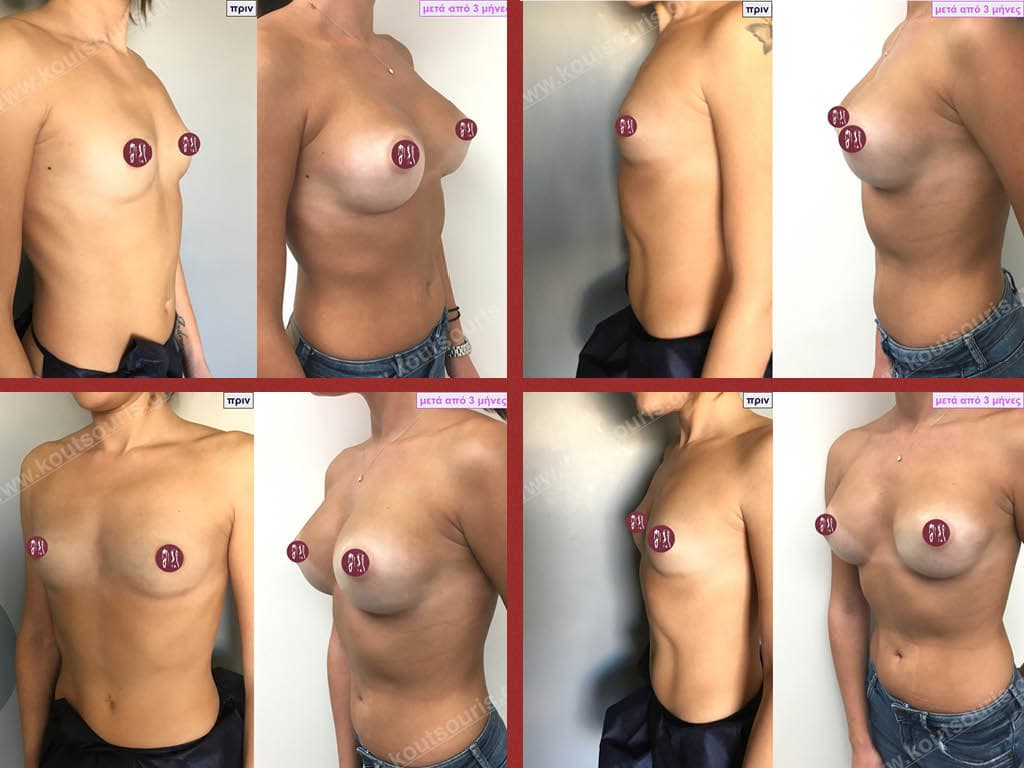
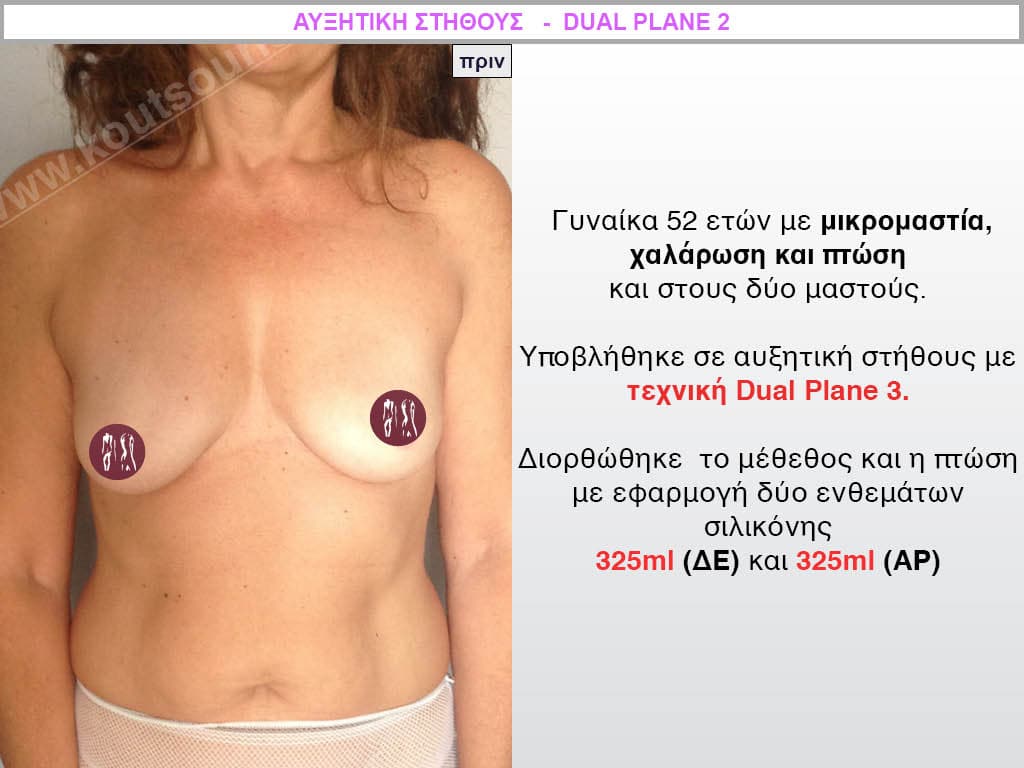
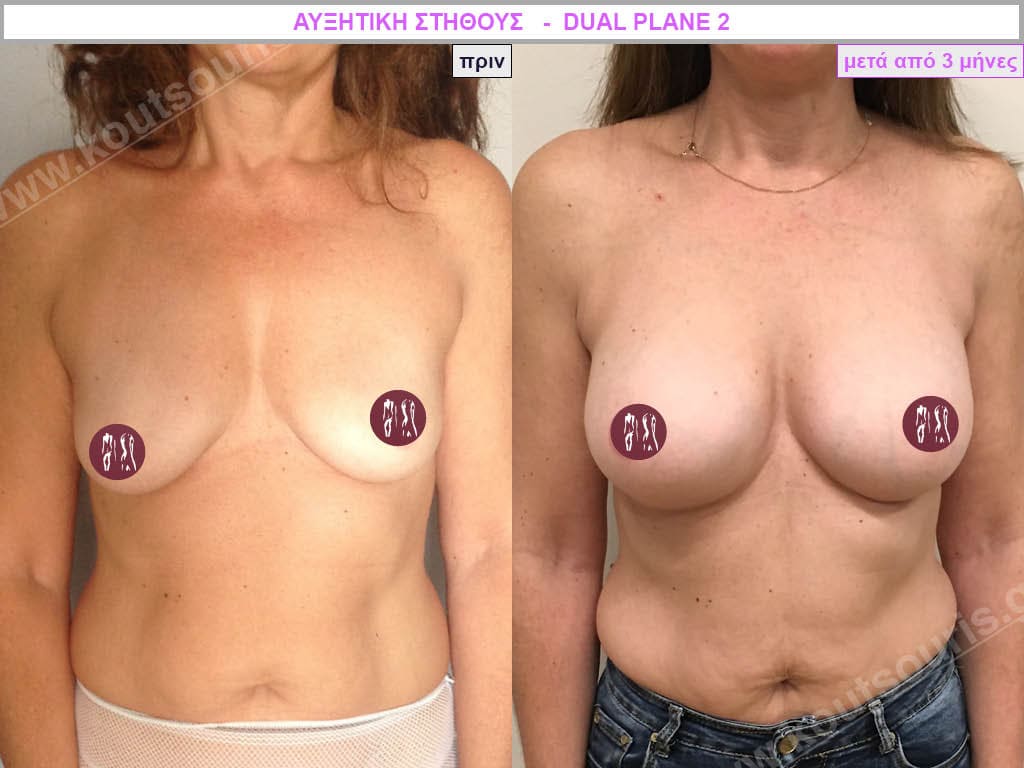
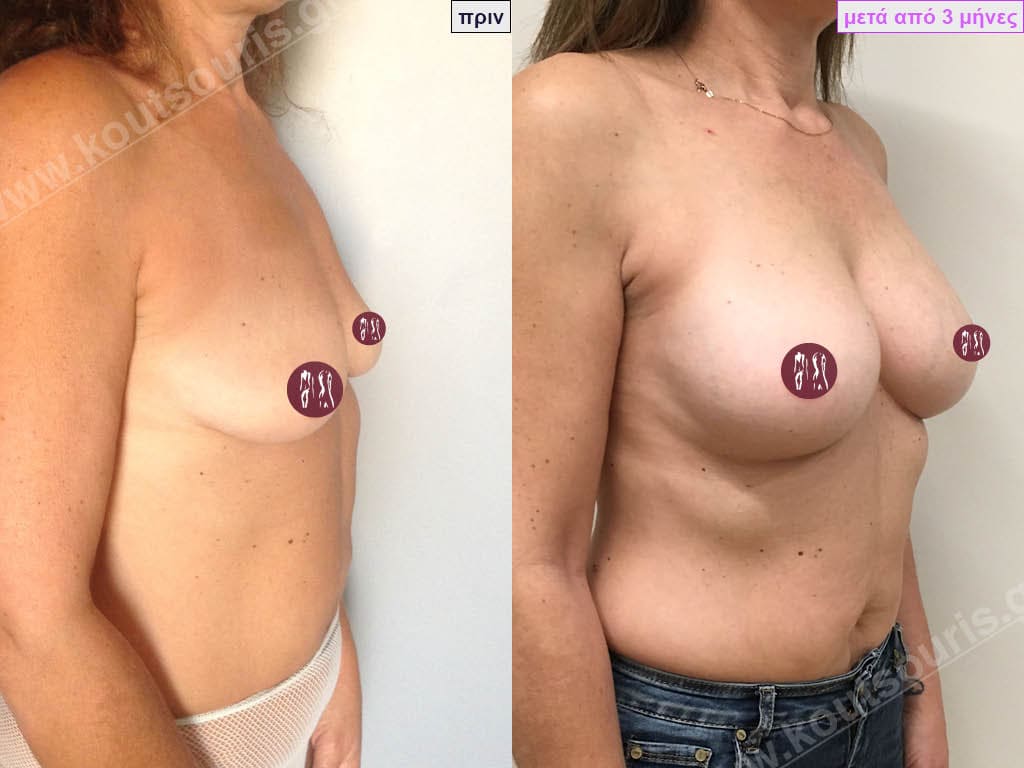
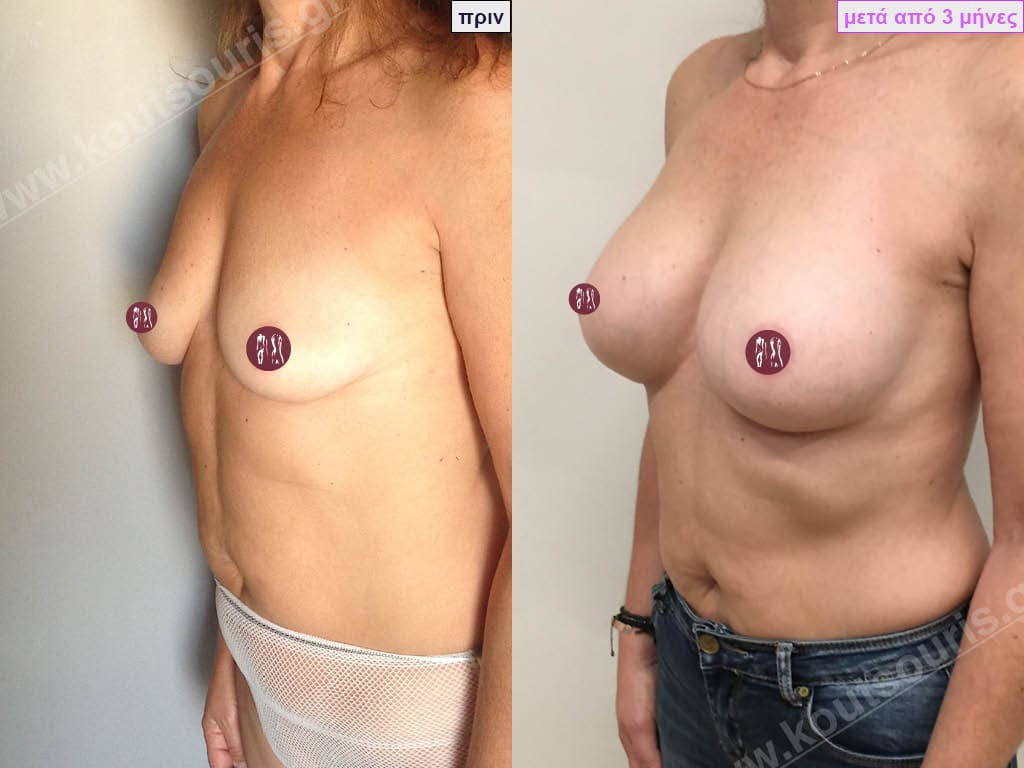
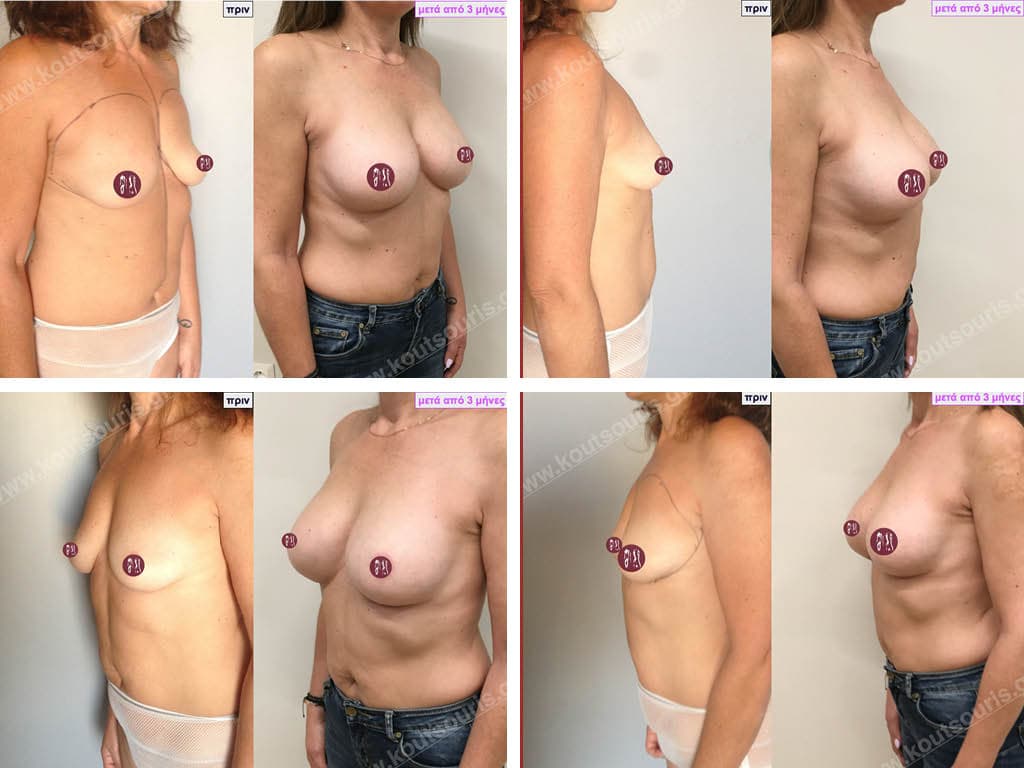
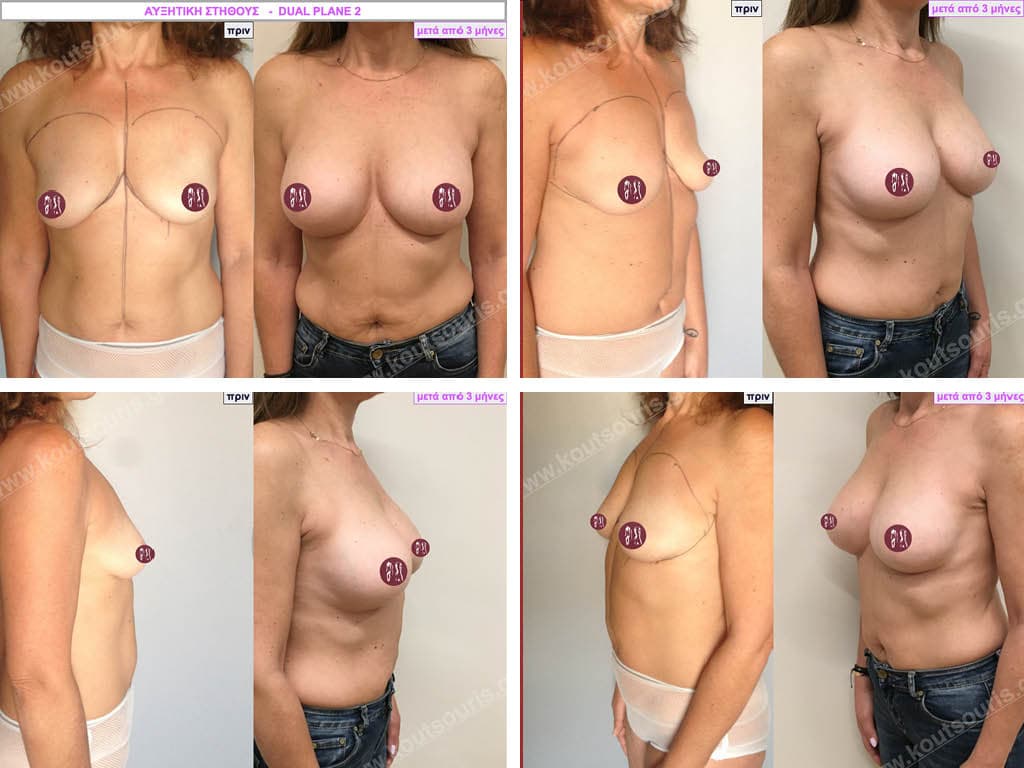
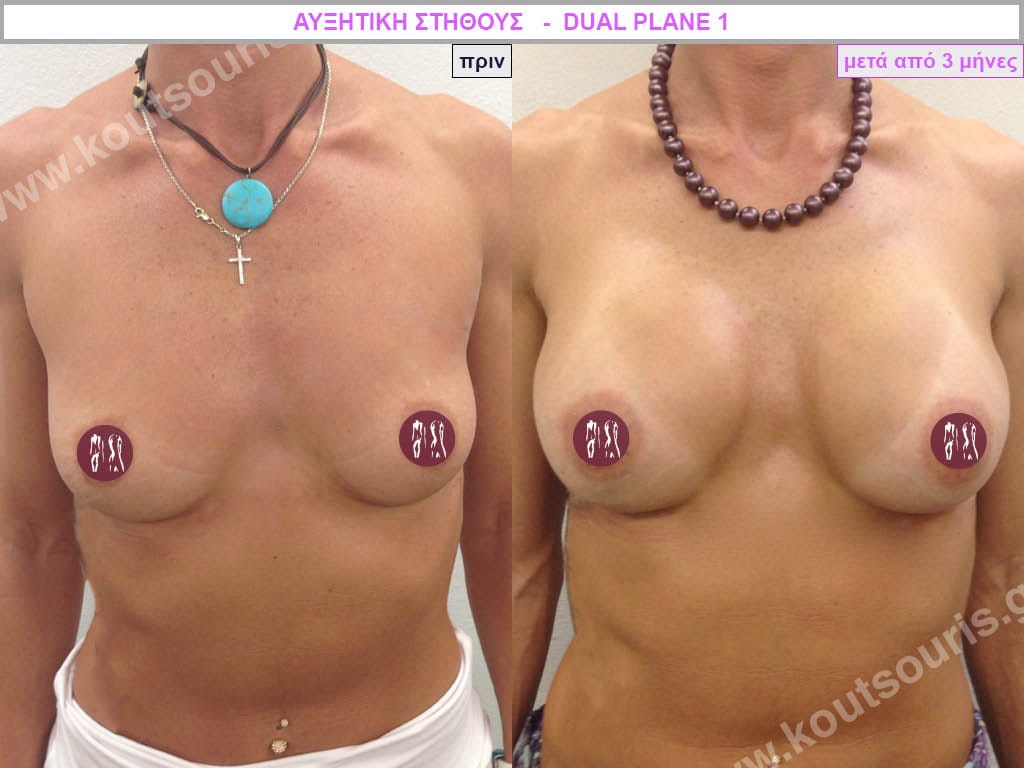
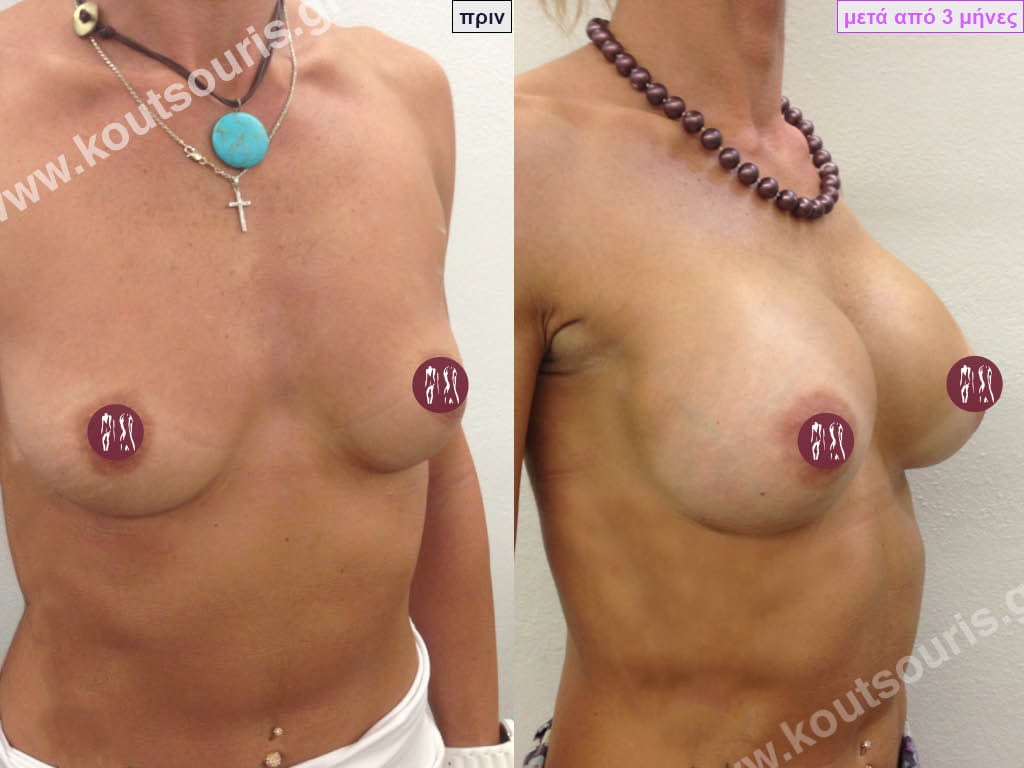
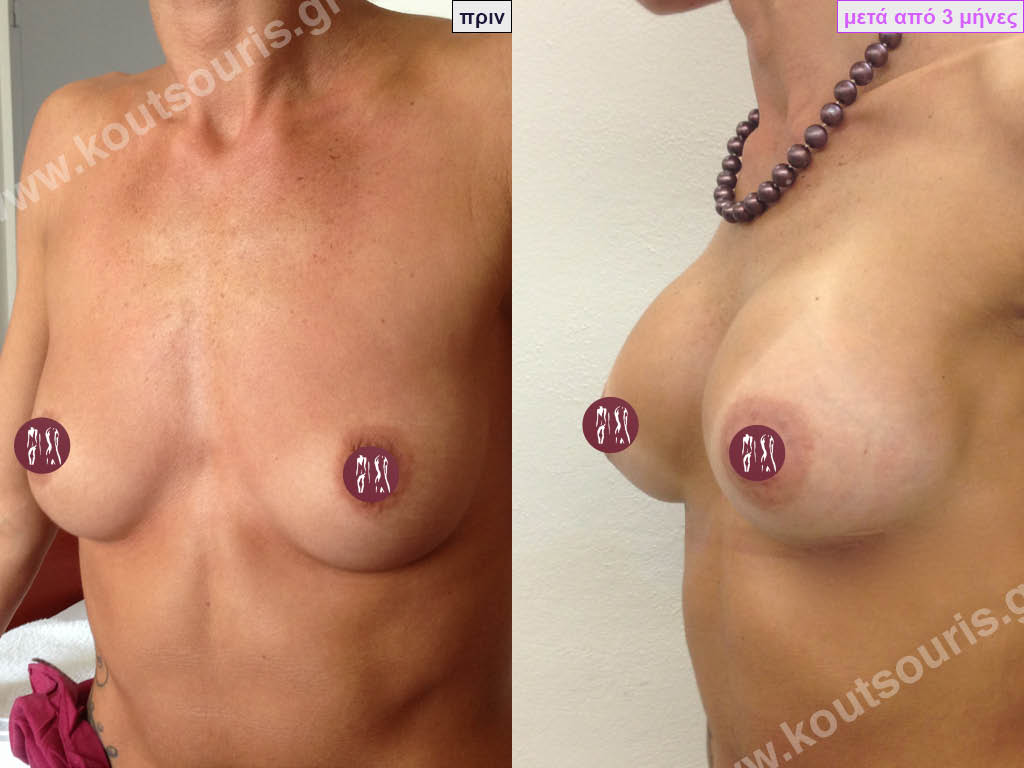
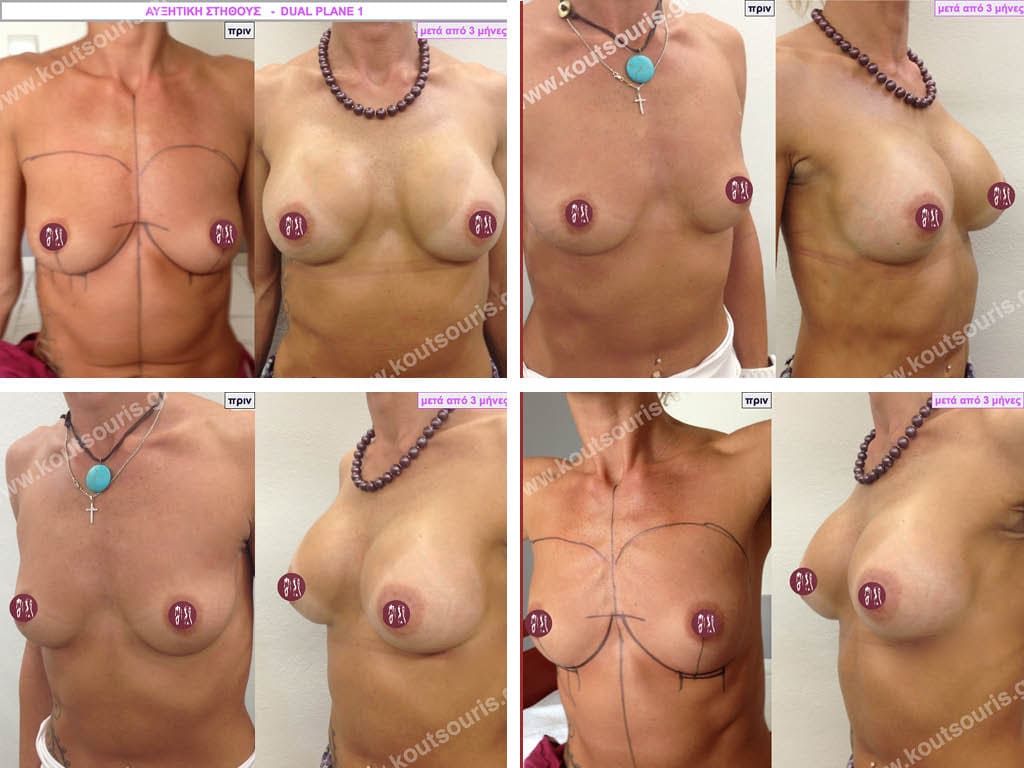
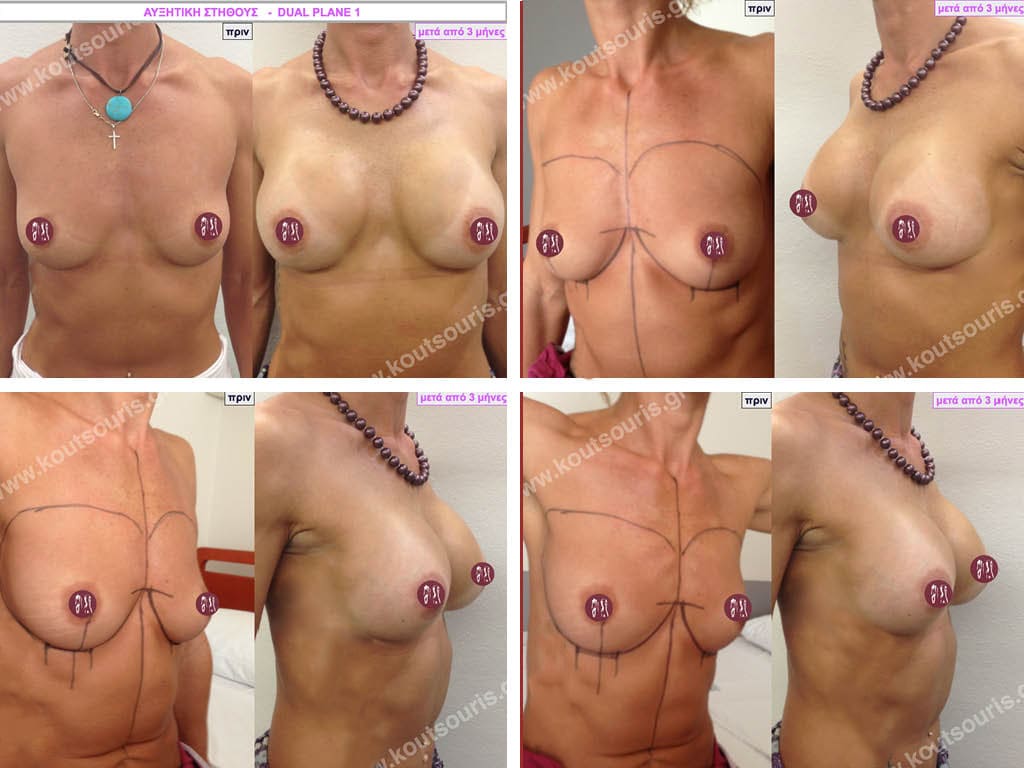
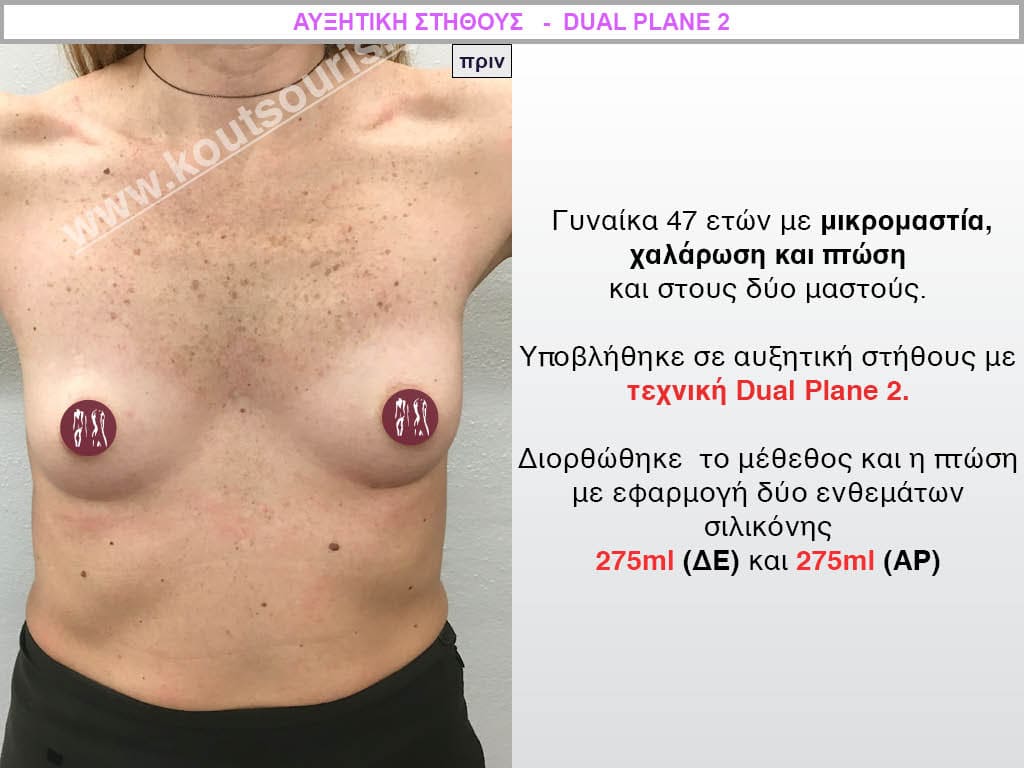
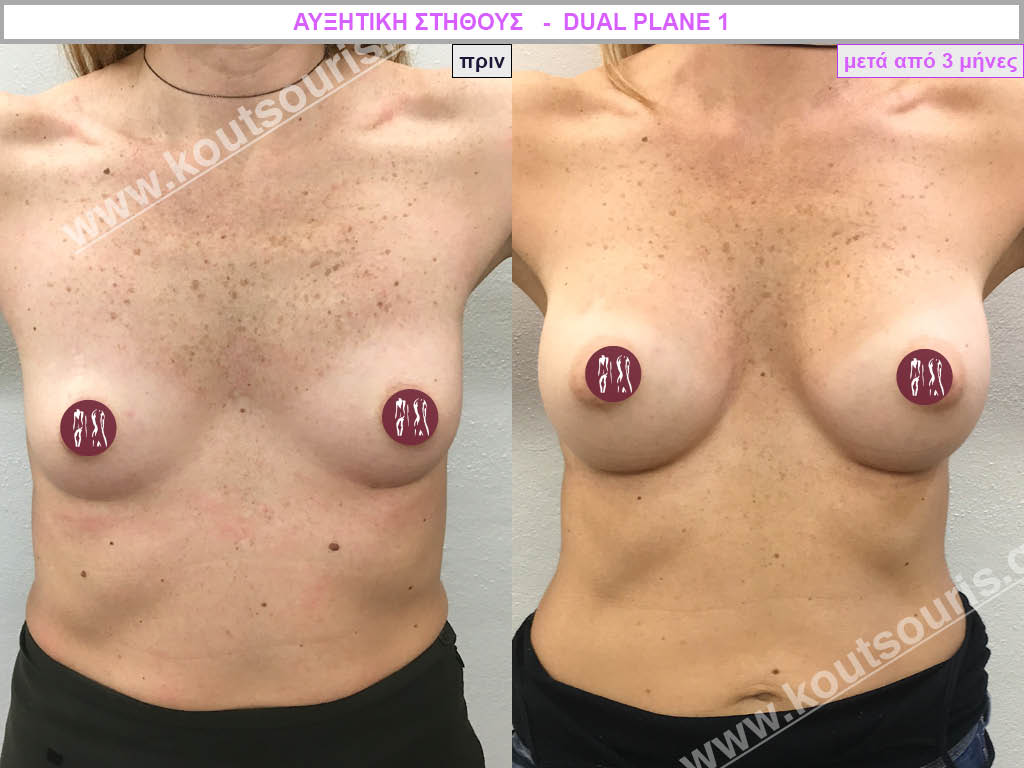
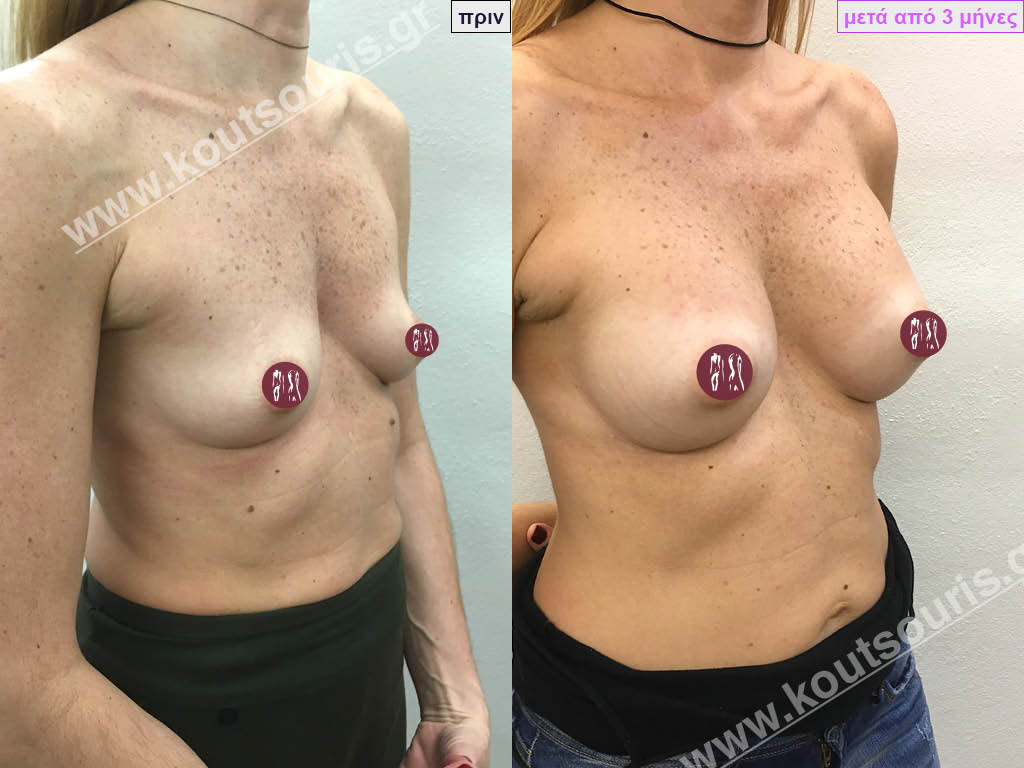
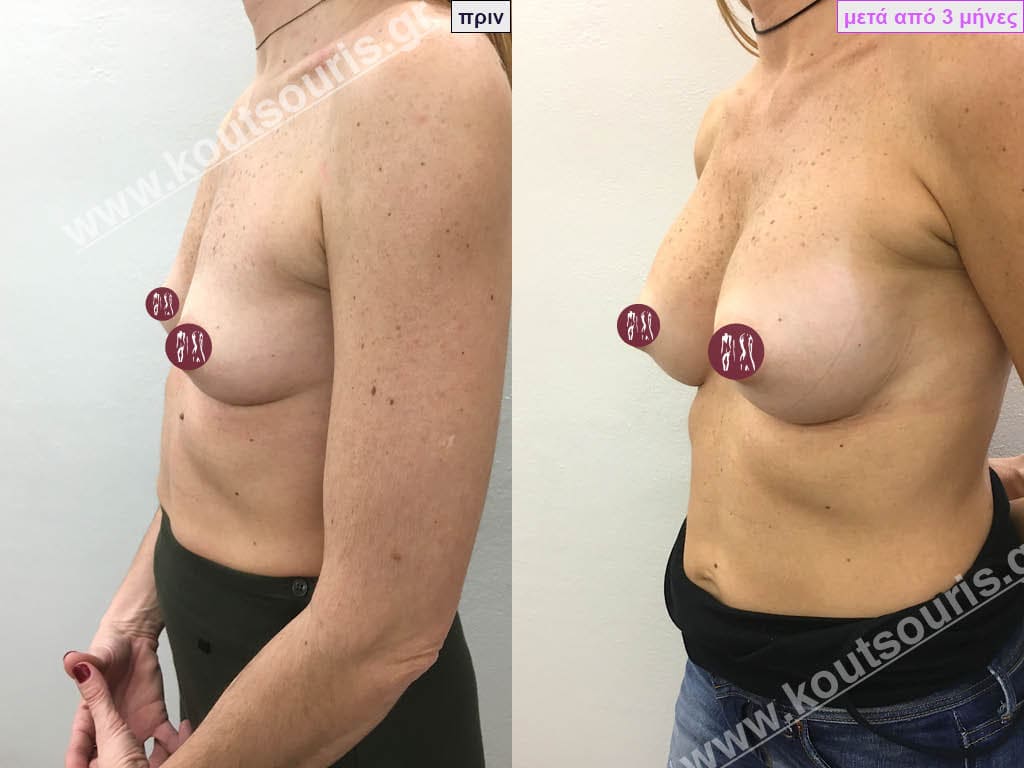
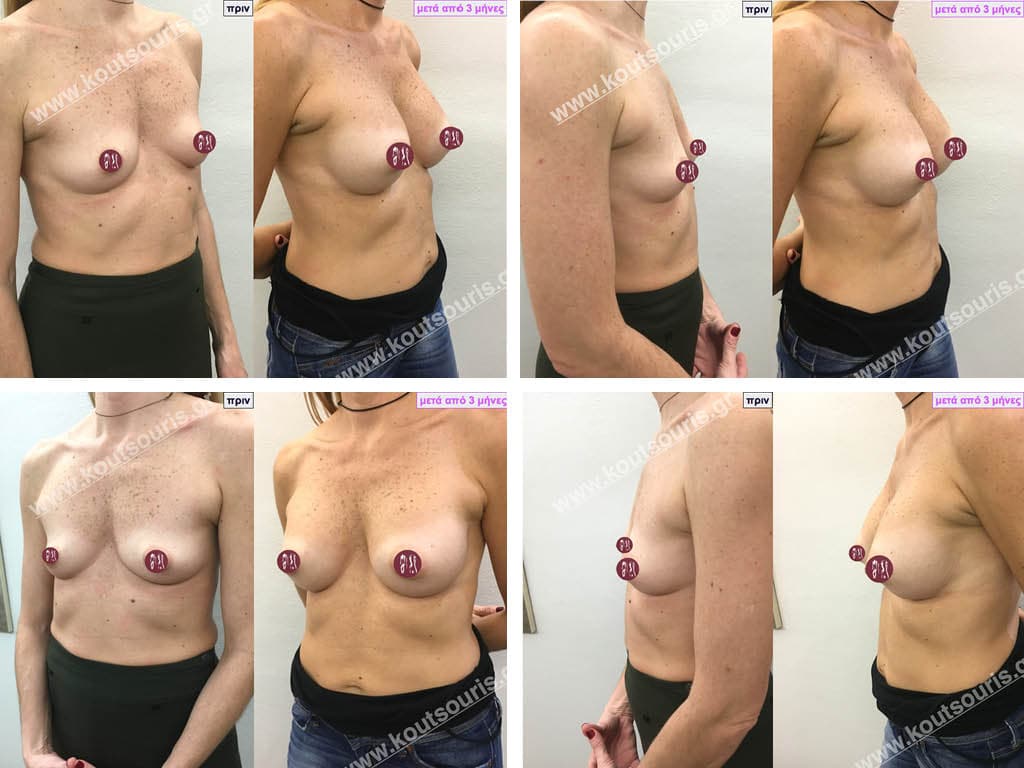
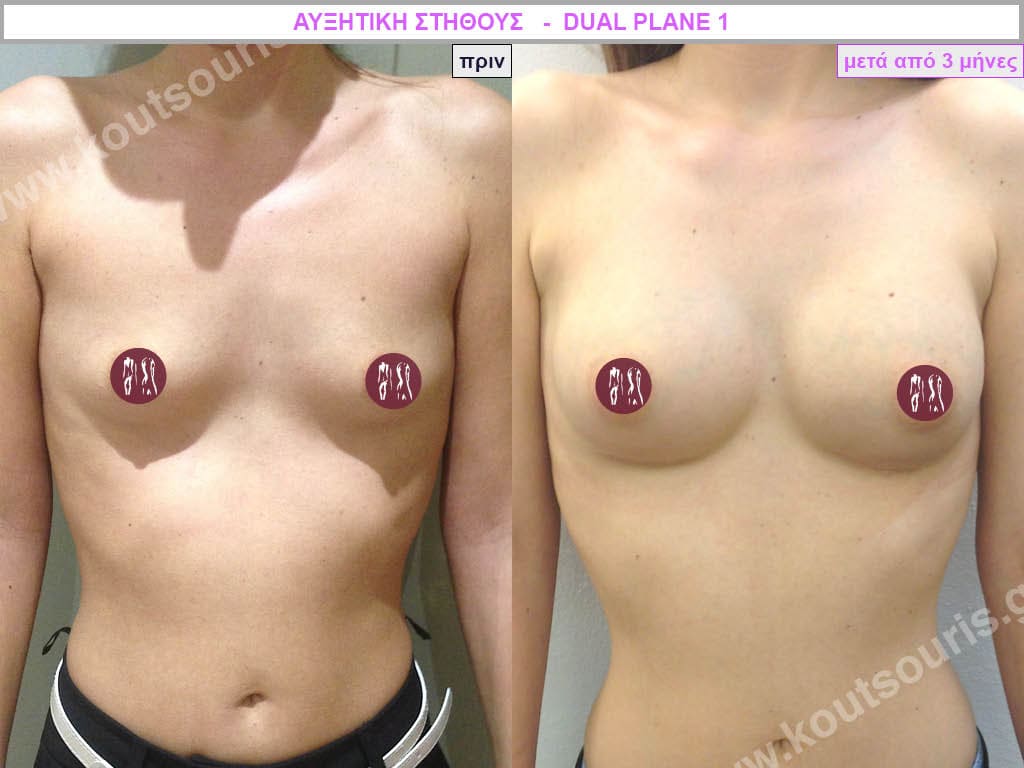
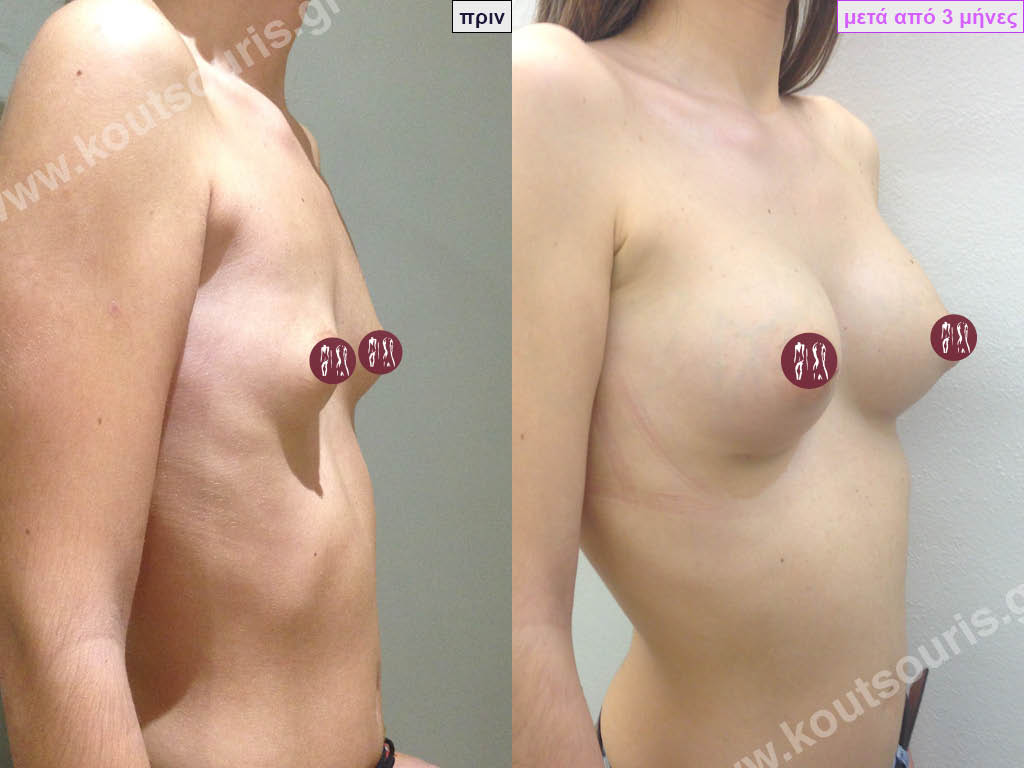
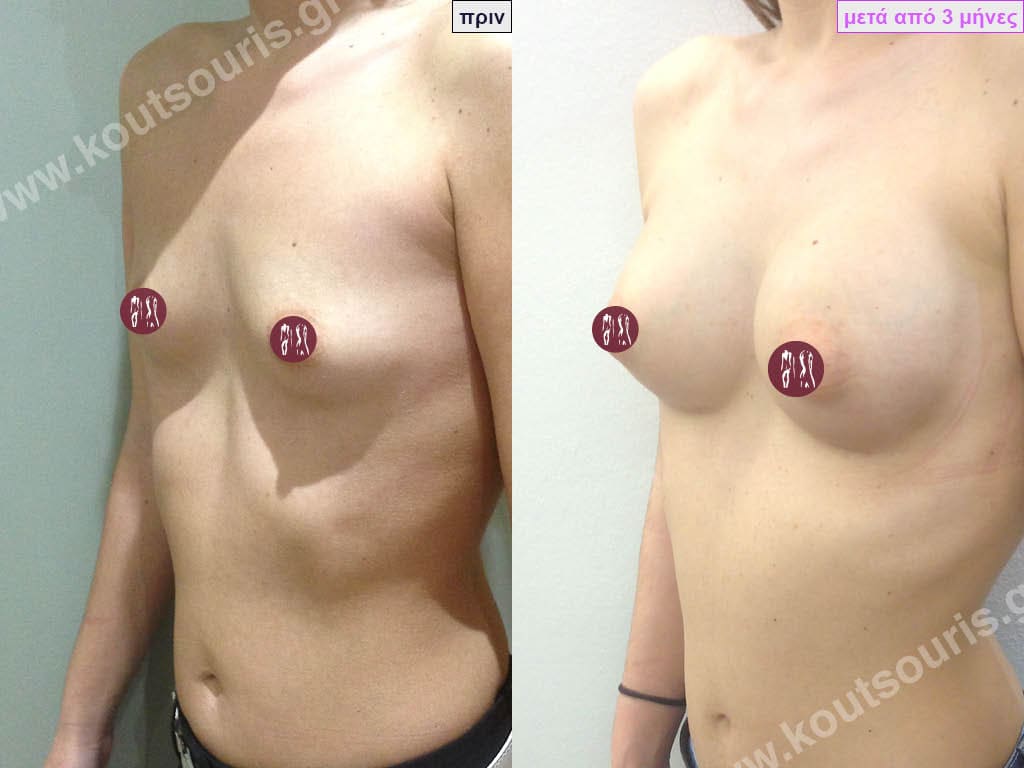
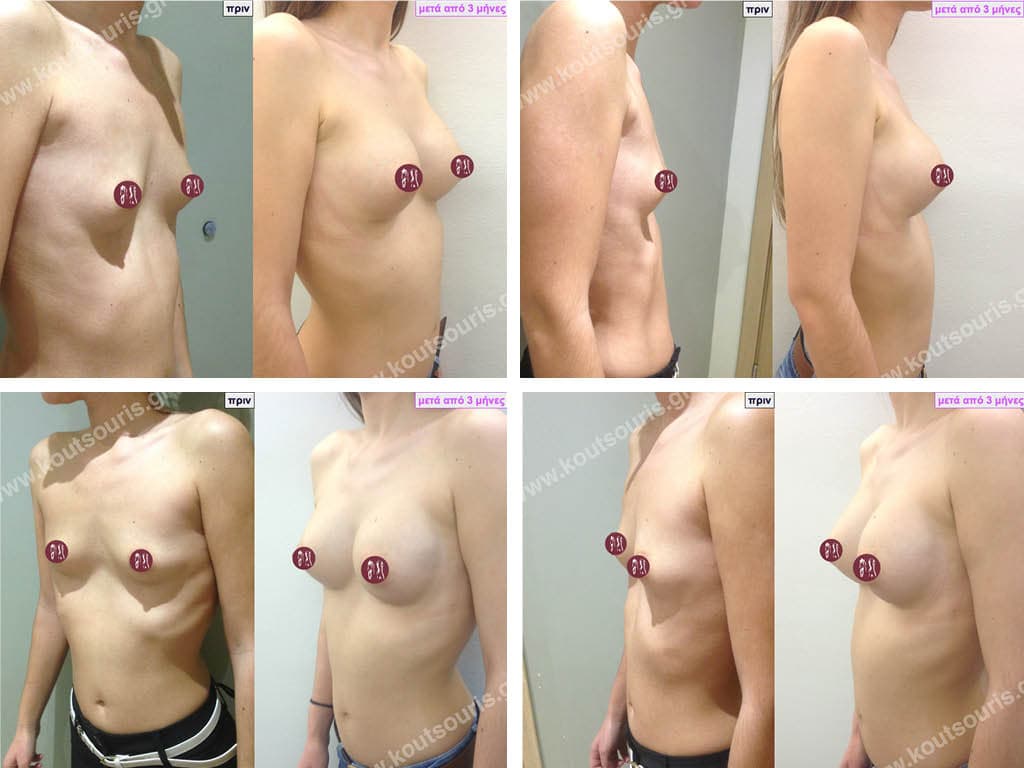
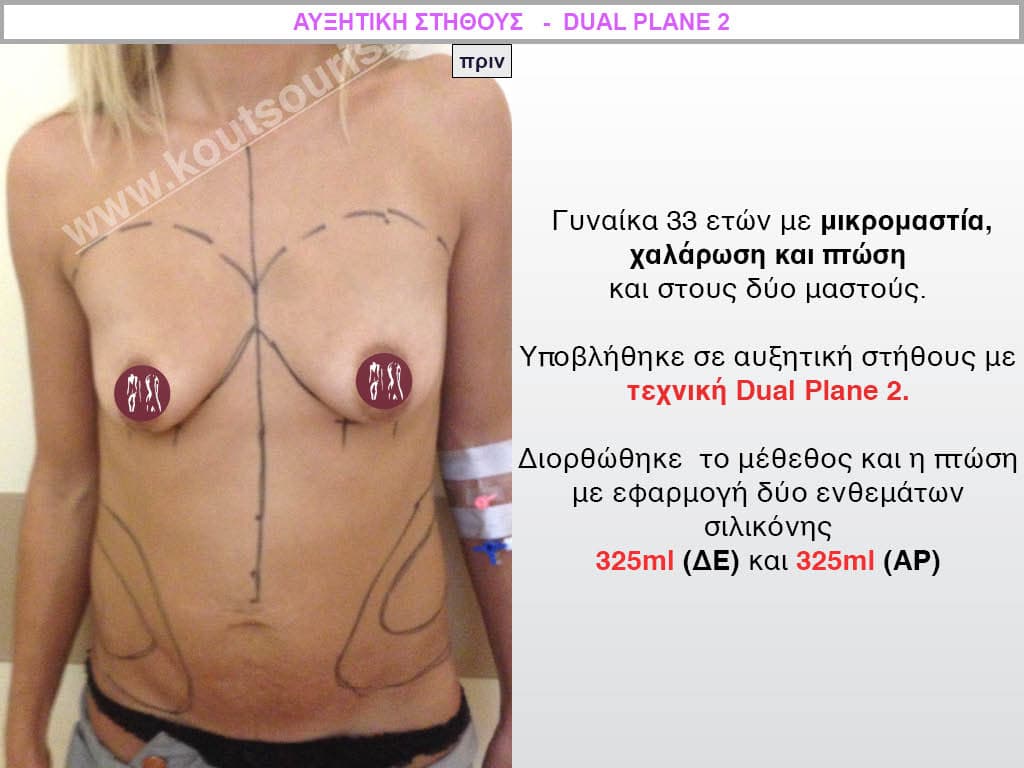
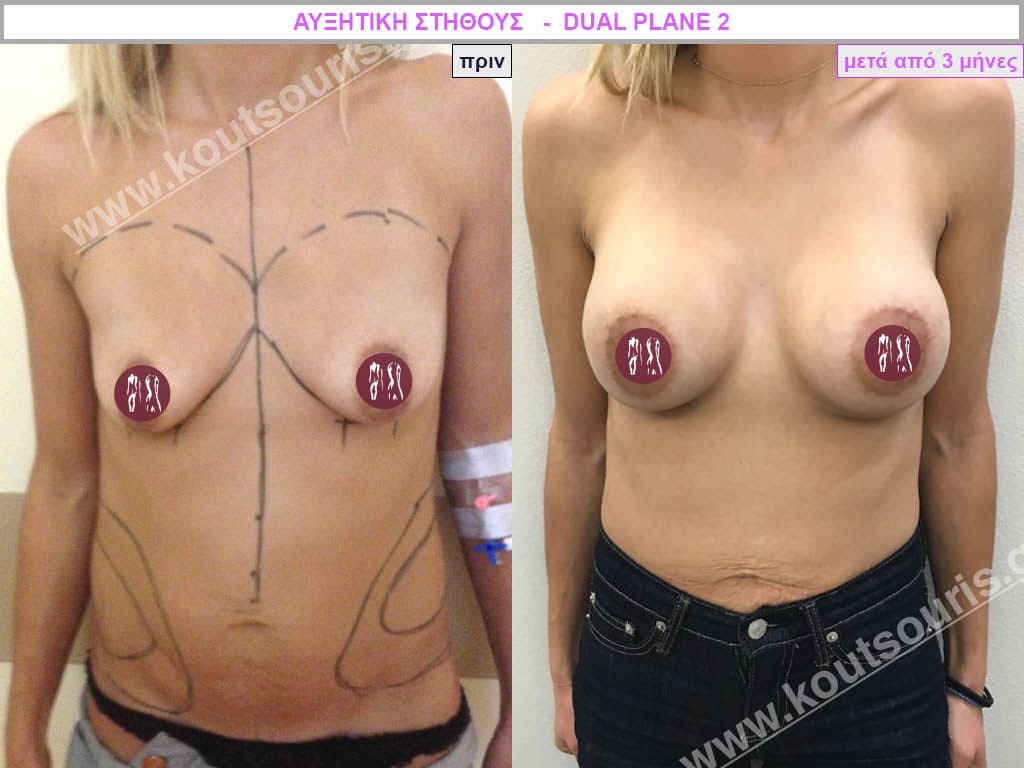
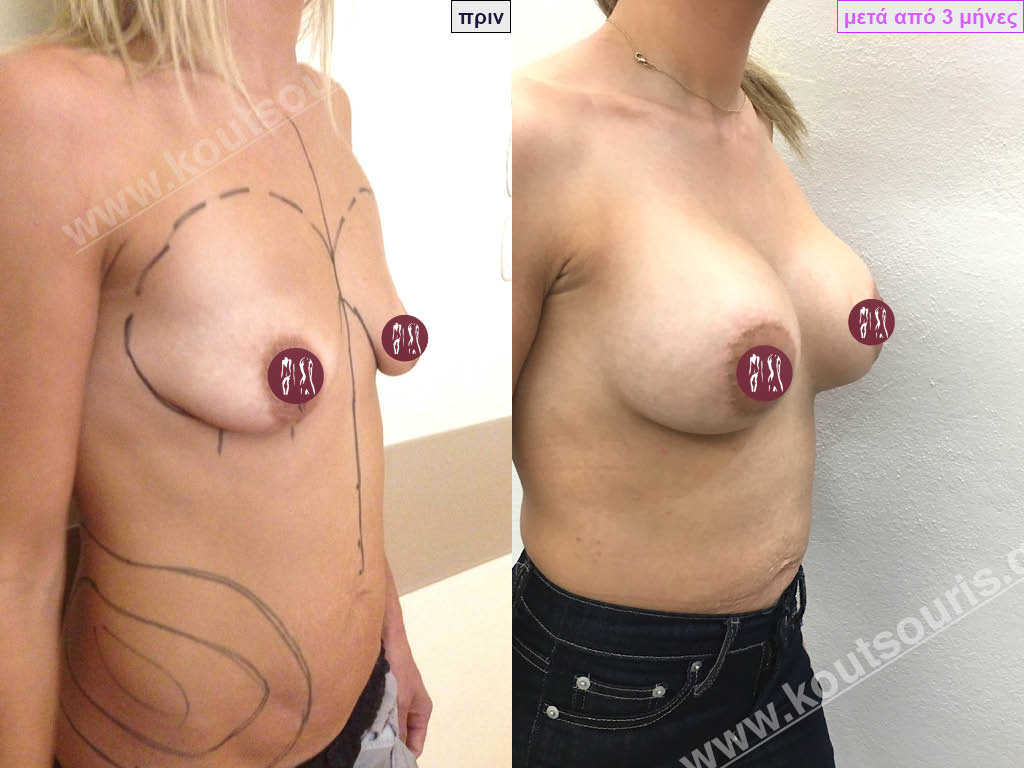
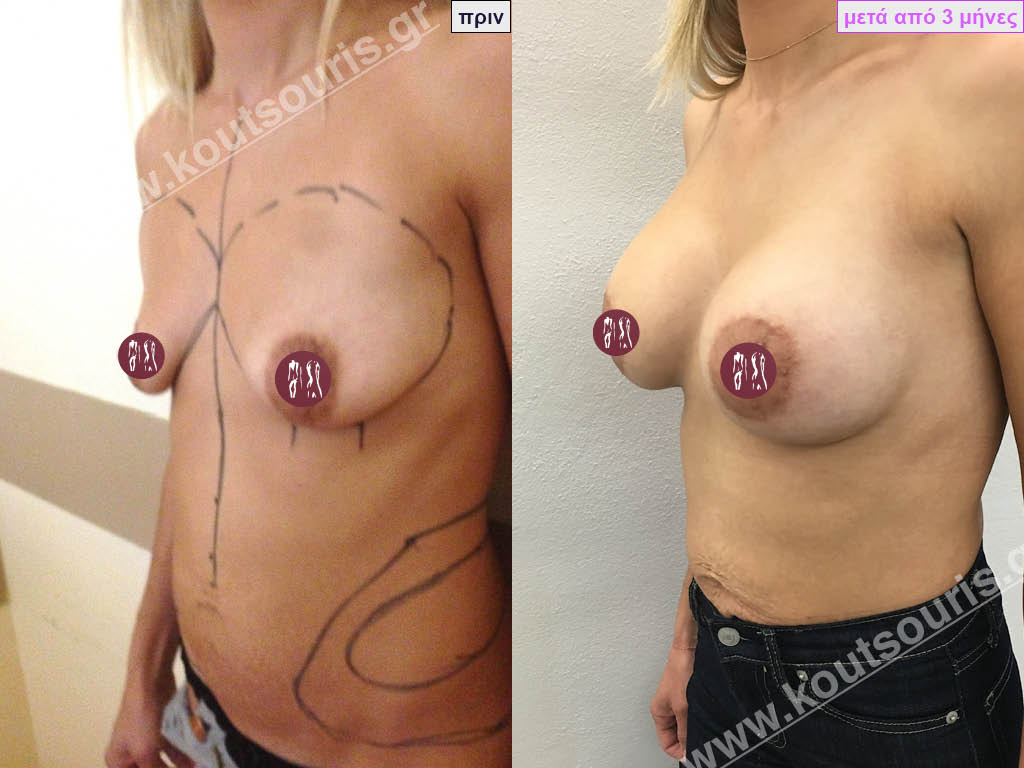
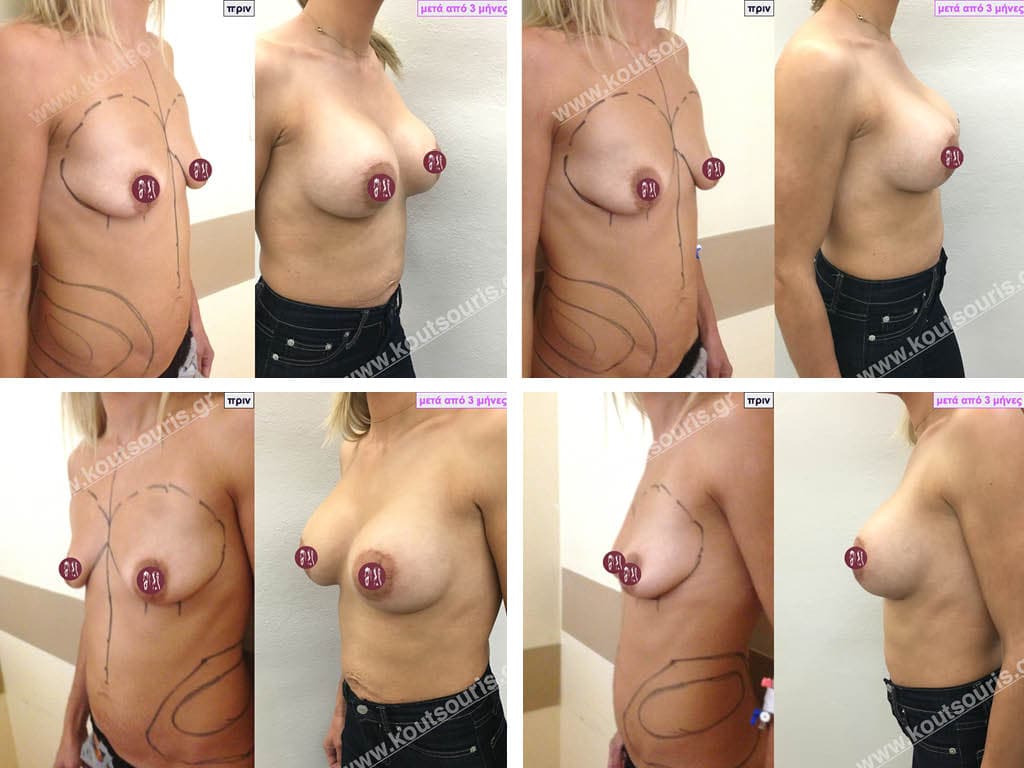
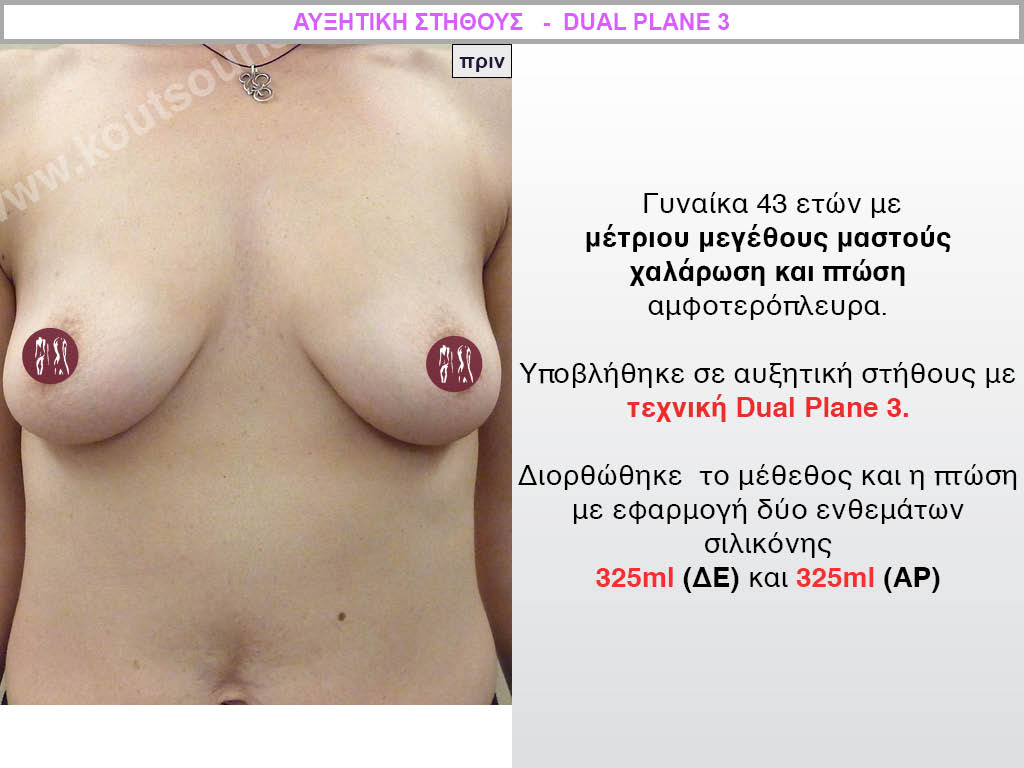
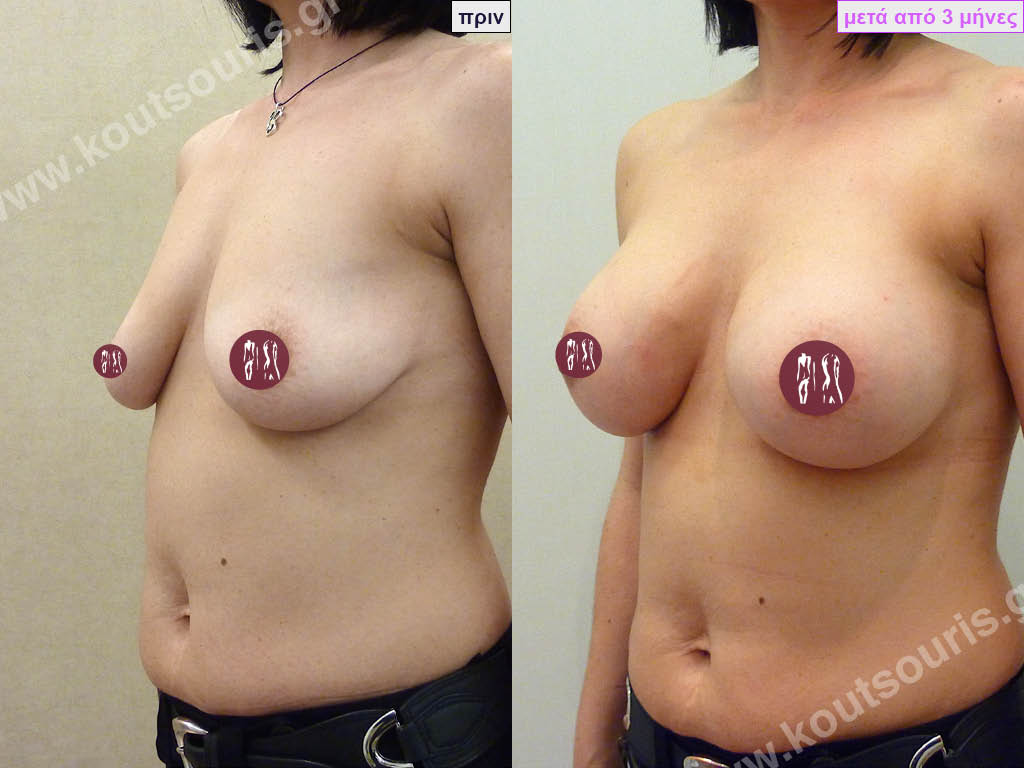
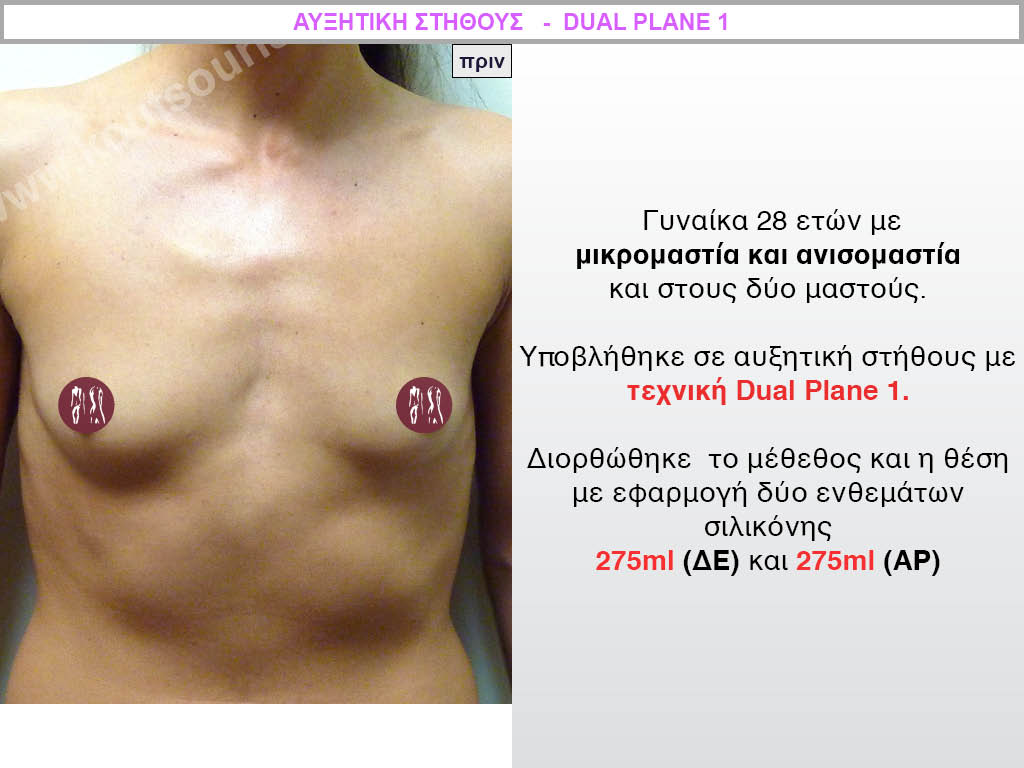
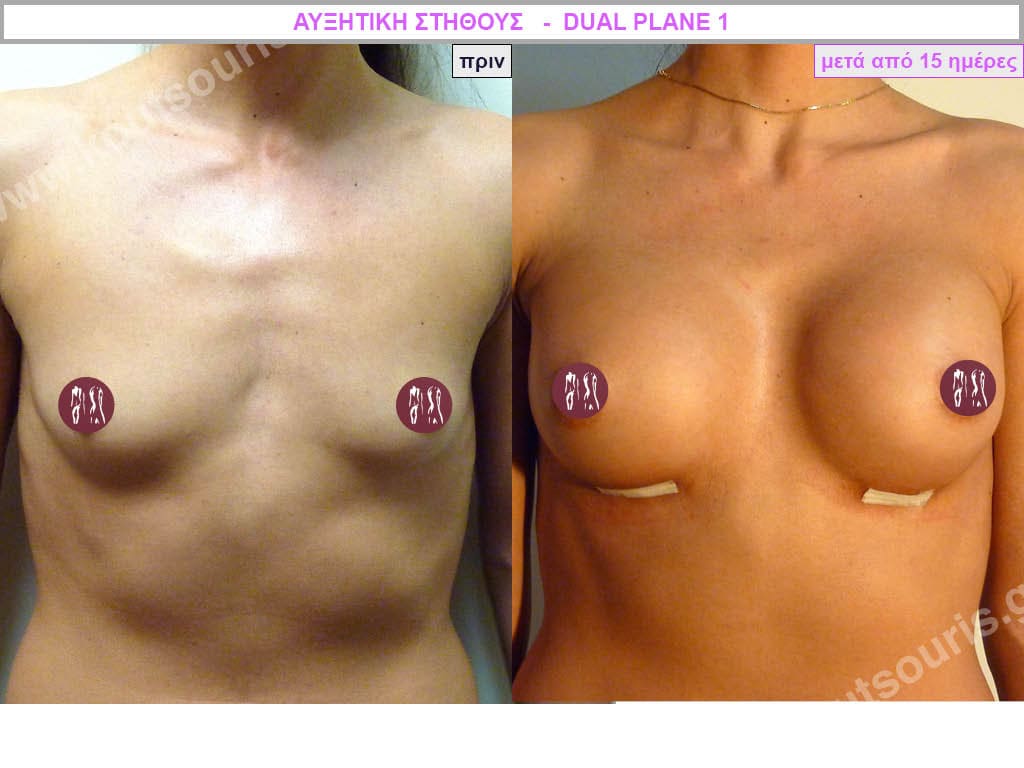
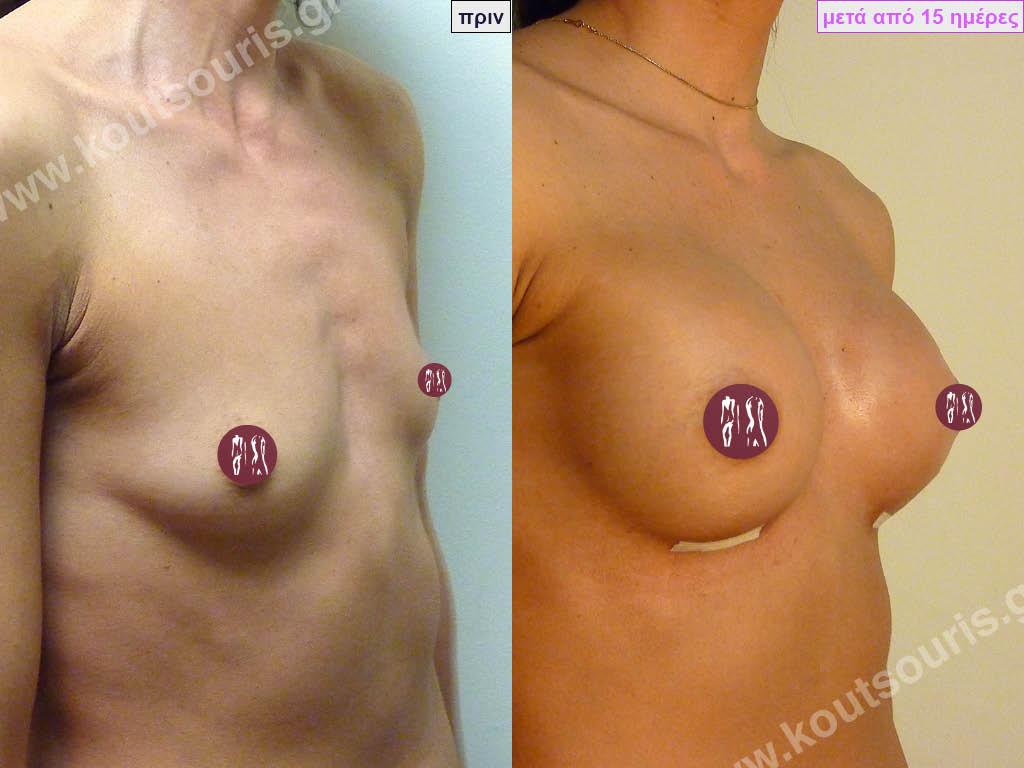
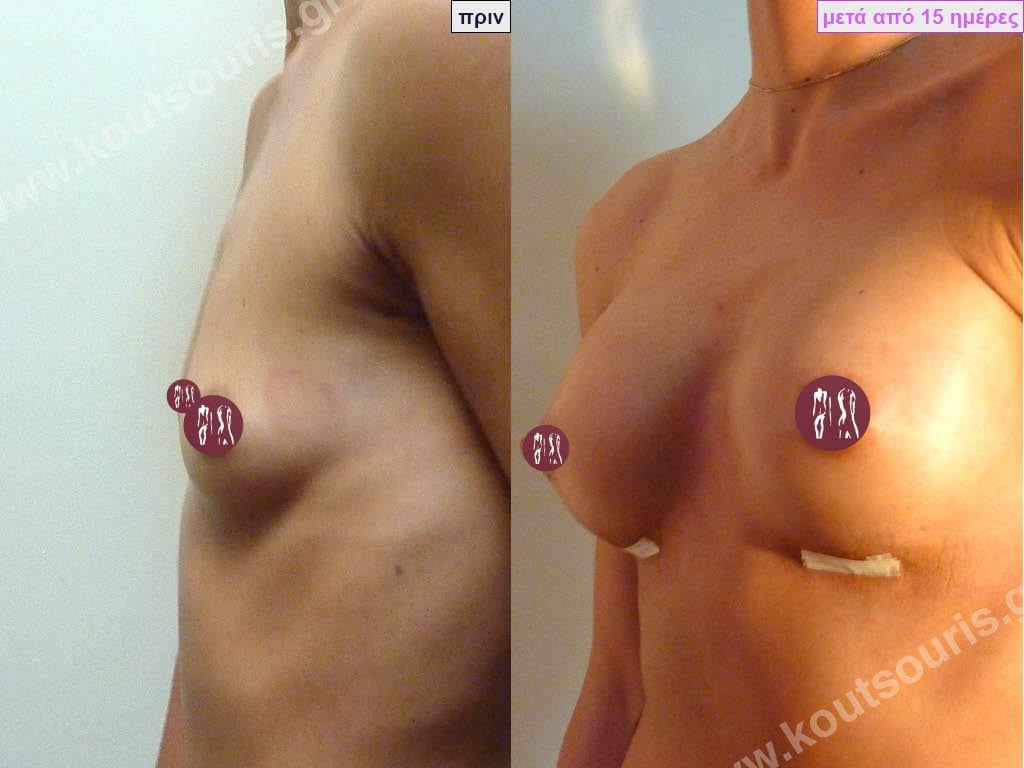
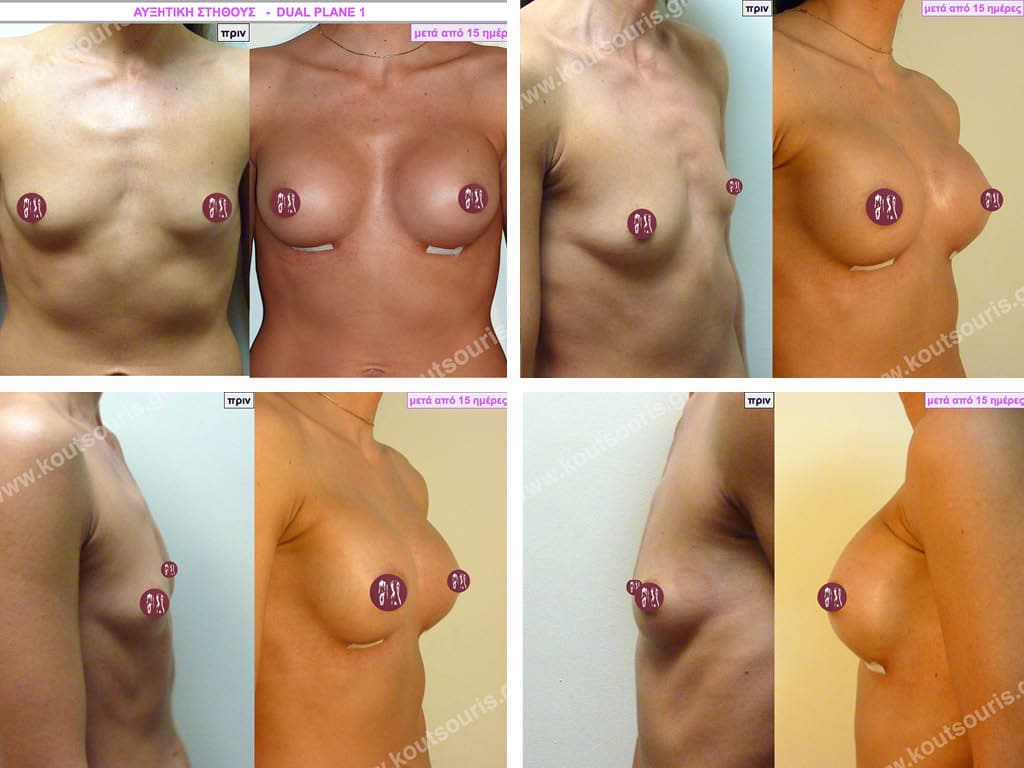
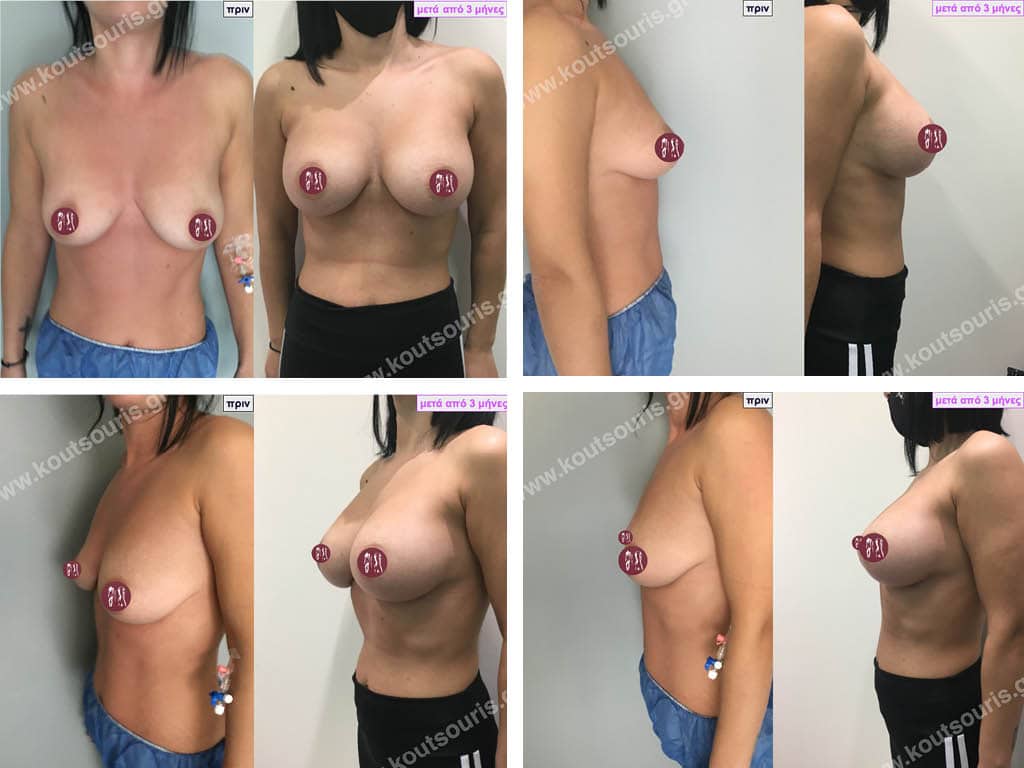
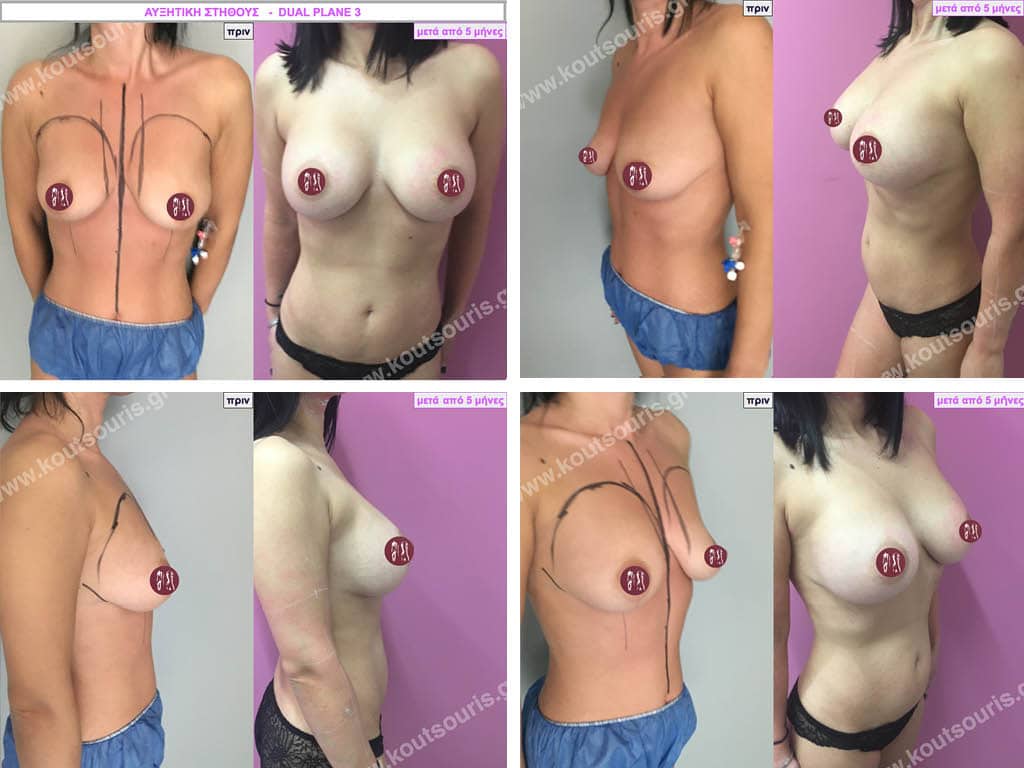
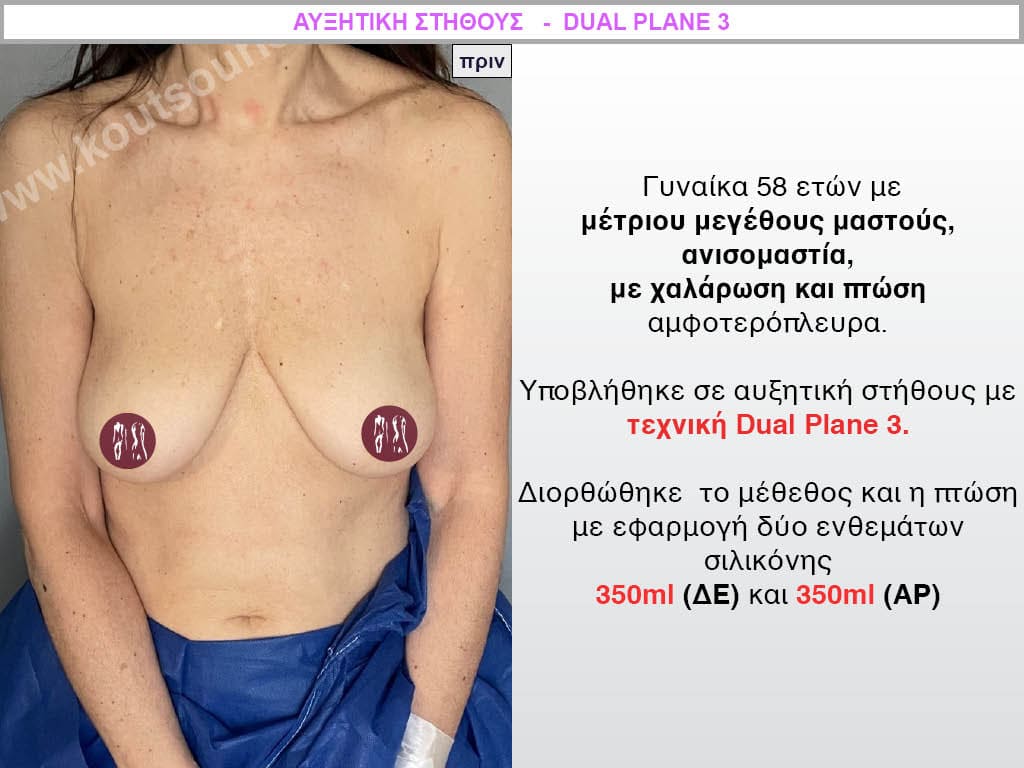
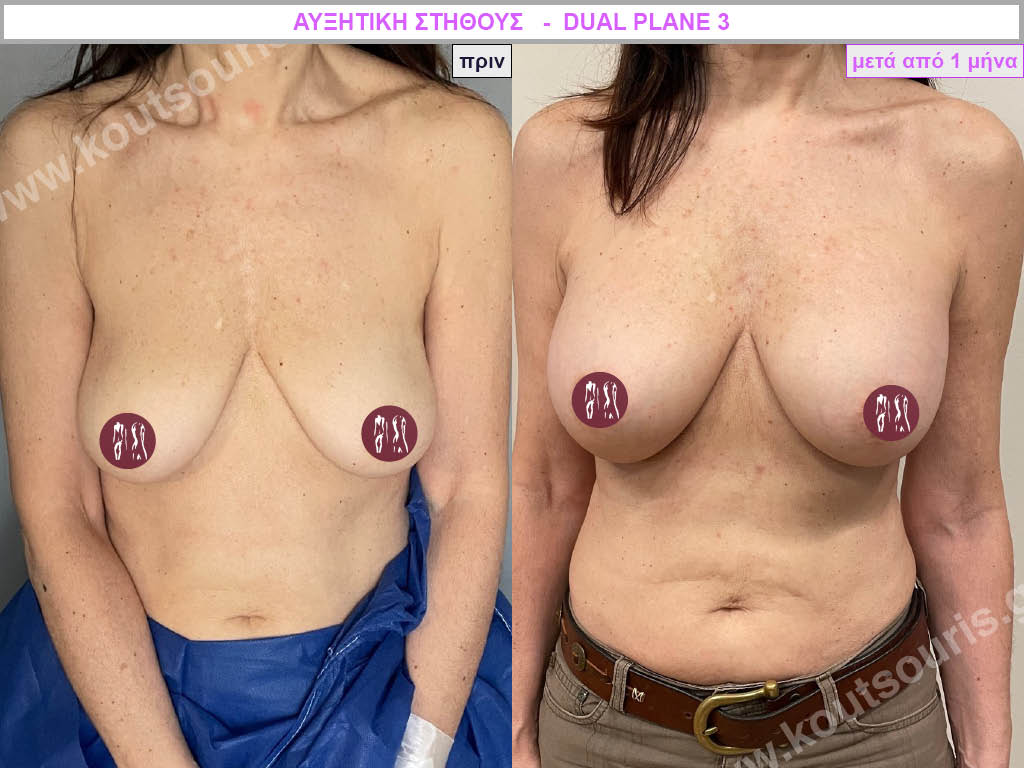
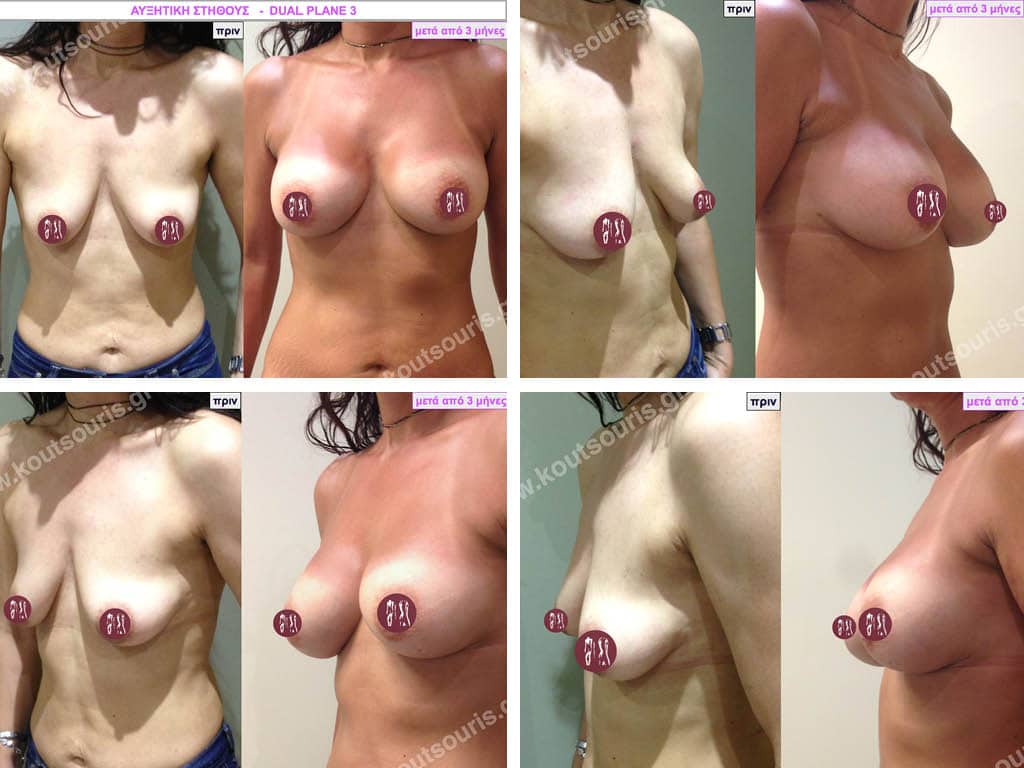
Dual Plane silicone insert placement
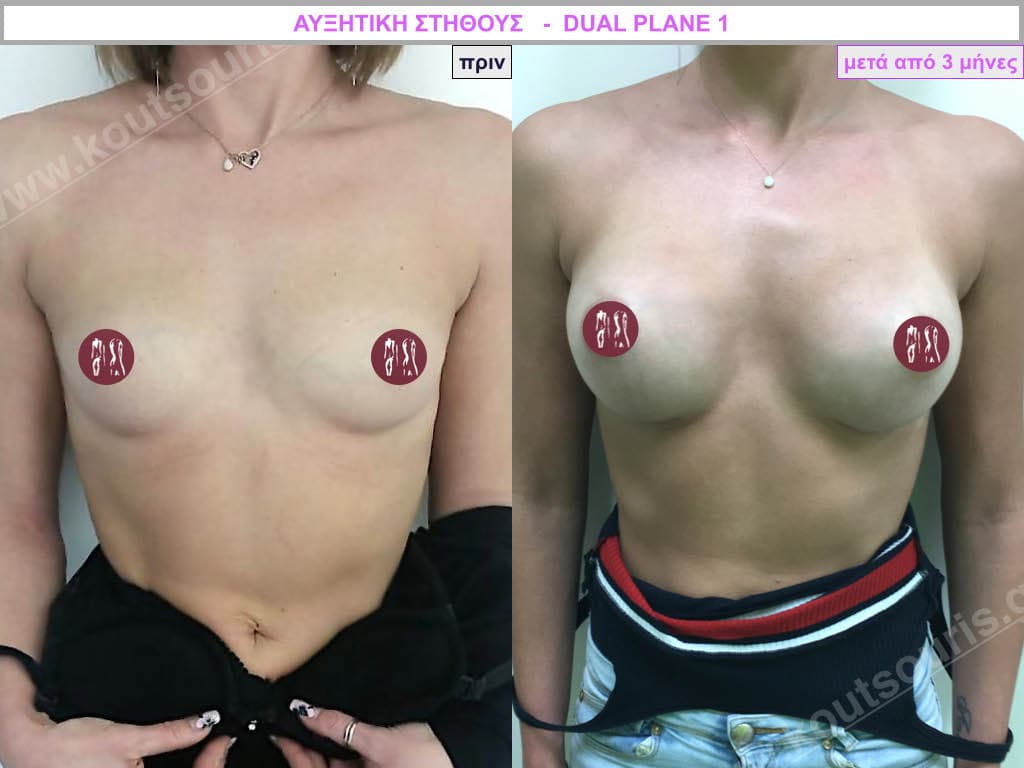
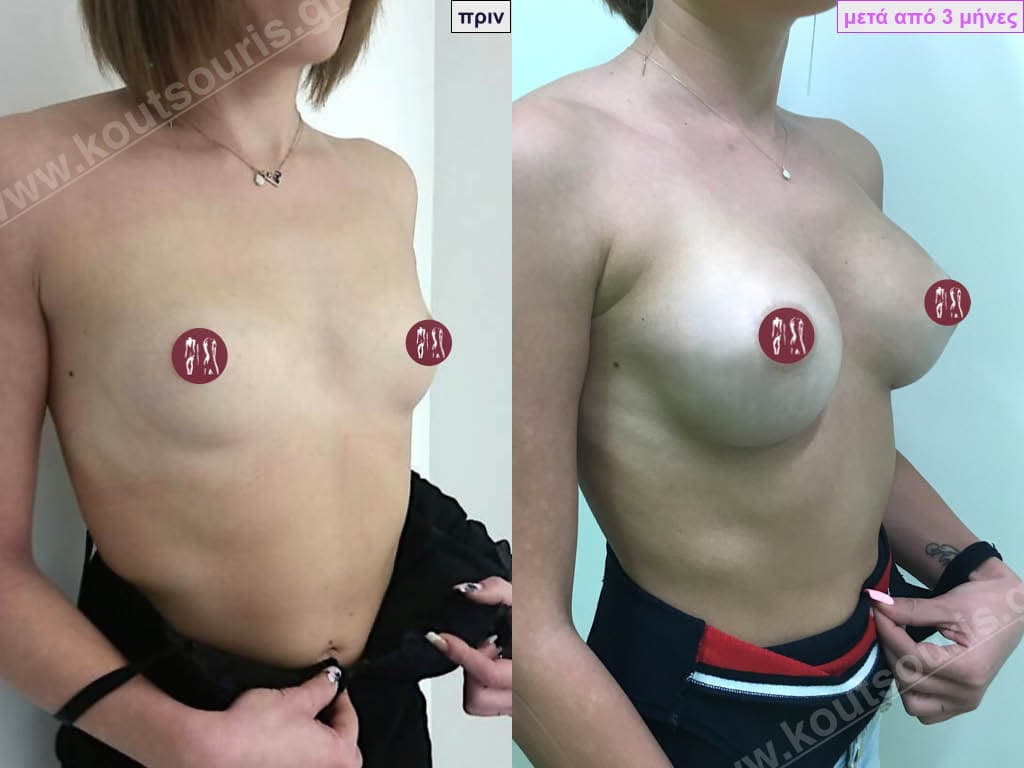
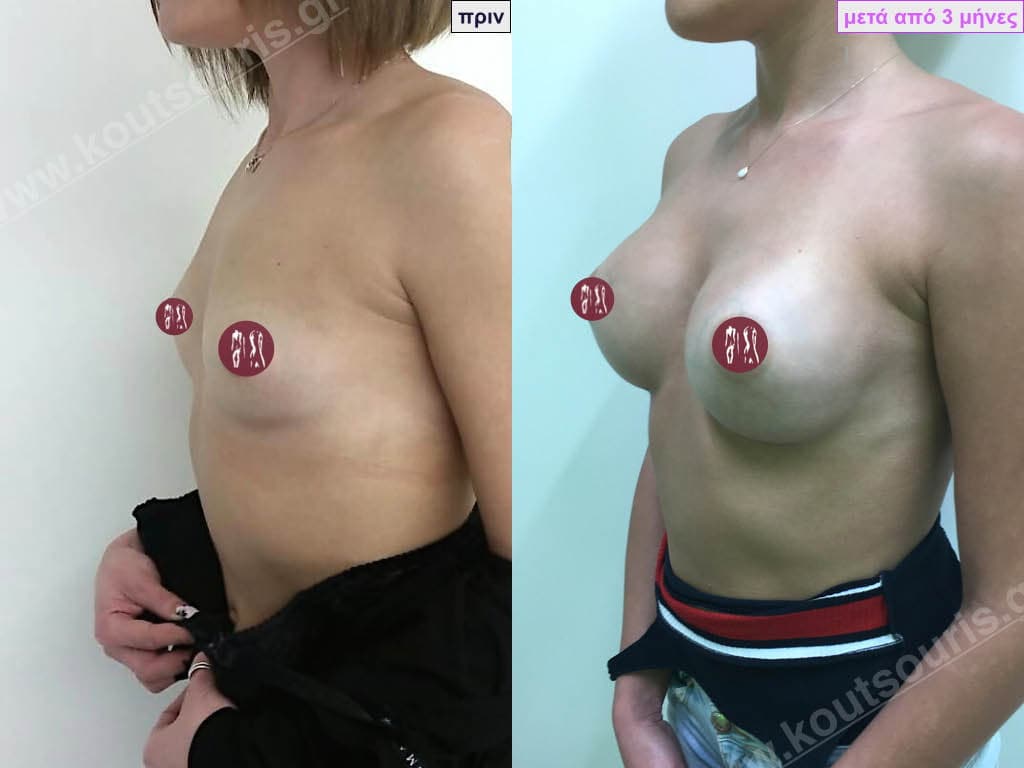
The Dual Plane technique is the method of choice for most cases of breast augmentation with silicone The reason is that it is an extremely safe and predictable technique with a very natural result and a low rate of complications since the implant is very well protected by the overlying tissues.
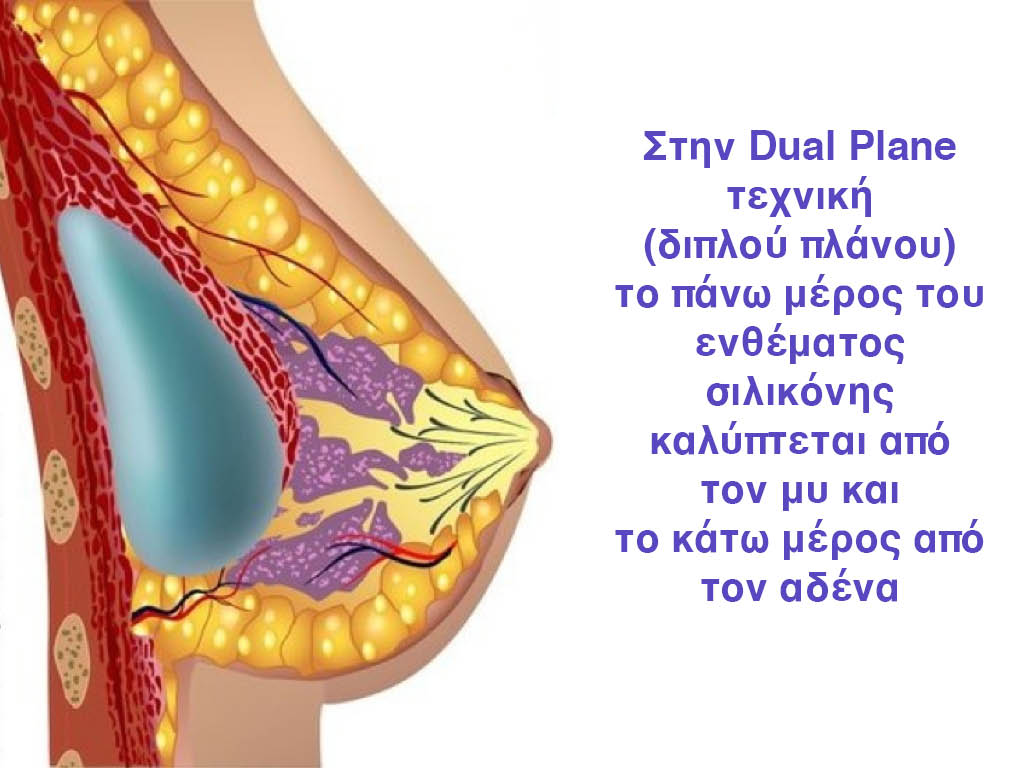
In the placement of the insert with the Dual Plane technique, half of the insert is inserted under the muscle and the other half under the gland.
The upper pole of the insert is perfectly covered by the pectoralis major muscle so that the silicone is not visible at all under the skin (on top of it) no matter how many years pass.
The lower pole of the insert is protected by the natural mass gland and gives a beautiful view of the entire breast.
This is an excellent technique for all women and all breasts that need augmentation. However, it is absolutely indicated for thin women with small breasts or for athletes with trained muscles and it gives us a safe solution for a very natural result since the upper part of the insert is perfectly covered by the major pectoral muscle.
With the Dual Plane method, the risk of systolic capsule formation is greatly reduced (it can form at a rate of 1%). Also, because the implant is smoothly held by the muscle and the natural gland of the breast, the result of the operation lasts a long time.
The Dual Plane technique is an excellent technique with amazing, natural results. However, it is a very demanding technique because the Plastic Surgeon must have knowledge, perception, experience and expertise.

Aseptic – Bloodless – Traumatic – No touch
Non Touch Technique
The potential complications of any surgery are:
- inflammation – infection,
- bleeding – hematoma,
- tissue injury – poor healing,
- formation of a sagging capsule.
To minimize the possibility of these complications ie:
For the operation to be Aseptic:
We use a special antiseptic protocol specific for breast augmentation operations which starts three days before the operation with a trunk bath with a specialized antiseptic solution. In the morning just before the operation, the patient takes a bath again in the clinic, while directly pre-operatively a targeted antibiotic is administered for pathogenic skin microbes. In this way we have extremely low rates of post-operative infections.
For the operation to be Bloodless:
At the beginning of the operation, along with the general anesthesia, we administer locally in the chest area a solution that causes vasospasm and additional local anesthesia. This results in the tissues not bleeding at all and the operation being completely painless and completely bloodless.
For the operation to be Traumatic:
We use very fine specialized surgical instruments in conjunction with an endoscope to create the surgical field and design the implant case. Applying delicate surgical manipulations, the operation is absolutely precise. Because the tissues are not injured, there is no postoperative pain, or if there is, it is minimal.
For the operation to be a Non Touch technique:
When we have completed the creation of the case and before placing the silicone insert on the breast, we perform thorough hemostasis so that our operation is absolutely bloodless.
To place the insert in its case – inside and under the breast tissues – we do not grasp the silicone with our hands. Instead we use a specially shaped conical structure (Keller funnel device) in which we put the insert under aseptic conditions.
Through this special construction we push the silicone into place without touching it at all with our hands (Non Touch Technique).
This happens :
- in order not to press the insert with our hands and not to cause a traumatic rupture of it,
- in order not to abuse the tissues during insertion of the insert,
- to be completely invulnerable,
- to be completely sterile.
How long does breast augmentation surgery take?
Breast augmentation surgery lasts from 50′ usually up to 90′ in the most difficult cases.
How will I feel afterwards?
Most patients right after they wake up from surgery are very well and have no pain or only a little discomfort. What they usually describe is a feeling of pressure or weight but not pain.
There is often a swelling, that is, a swelling in the breast which then turns into a mild “pulling” and subsides completely within about ten to fifteen days.
The breast may initially feel a little numb to the touch, but sensation returns fully within six to eight weeks usually.
What do I do with incisions, stitches, drains, bra?
We place special waterproof tapes to protect our incisions so patients can bathe from the very first day.
The stitches are absorbable so they do not need to be removed as they fall out on their own after two to three weeks usually.
We almost never use drains since our procedure is non-traumatic. In very rare cases if we put drains then we remove them the next day.
Immediately after the operation, we put on a light, loose bandage for a few hours to gently hold the breast. In the afternoon of the same day or the next day, we remove the bandage and wear a sports bra (not a bra with reinforcements or underwire). We recommend a soft sports bra that opens and closes in front of the chest, not in the back. This makes hand movement much easier.
Should I take antibiotics or painkillers?
After breast augmentation surgery, we administer antibiotics and simple oral painkillers. If we use large inserts on small breasts then there can be a discomfort towards the sides of the breast usually. If there is discomfort it occurs when raising the arms for the first three to four days.
In most cases the operation is not painful at all.
When do I leave the clinic?
Most patients are very well and do not need to stay in the clinic for more than a few hours. They usually stay until afternoon hospitalization. In only a few cases they may need to stay overnight.
When do I go back to work?
You usually return to work after a few days and you should avoid very intense physical exercise for about three to four weeks.
When can I drive?
While not immediately prohibited we recommend driving after 4 to 5 days or so. You should be careful because you may feel some discomfort in sudden movements and this will affect your reflexes.
What should I do after breast augmentation?
After seven to ten days we recommend massaging the breast daily for 10 to 15 minutes. By making circular massaging movements, the breast becomes softer to the touch, while the numbness that could be present recedes much faster. For one to one and a half months, we recommend sleeping on your side or back so that the breast is not pressed. This way the swelling and the feeling of heaviness will subside more quickly. Then you can sleep as you wish.
When will I get the final result of breast augmentation?
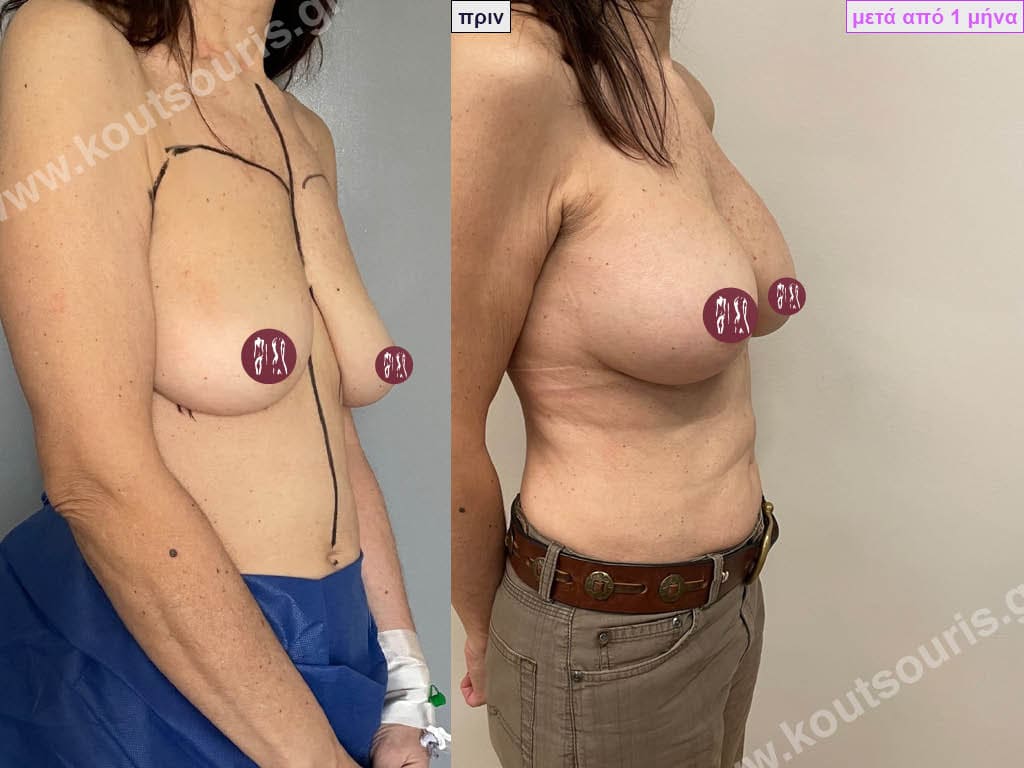
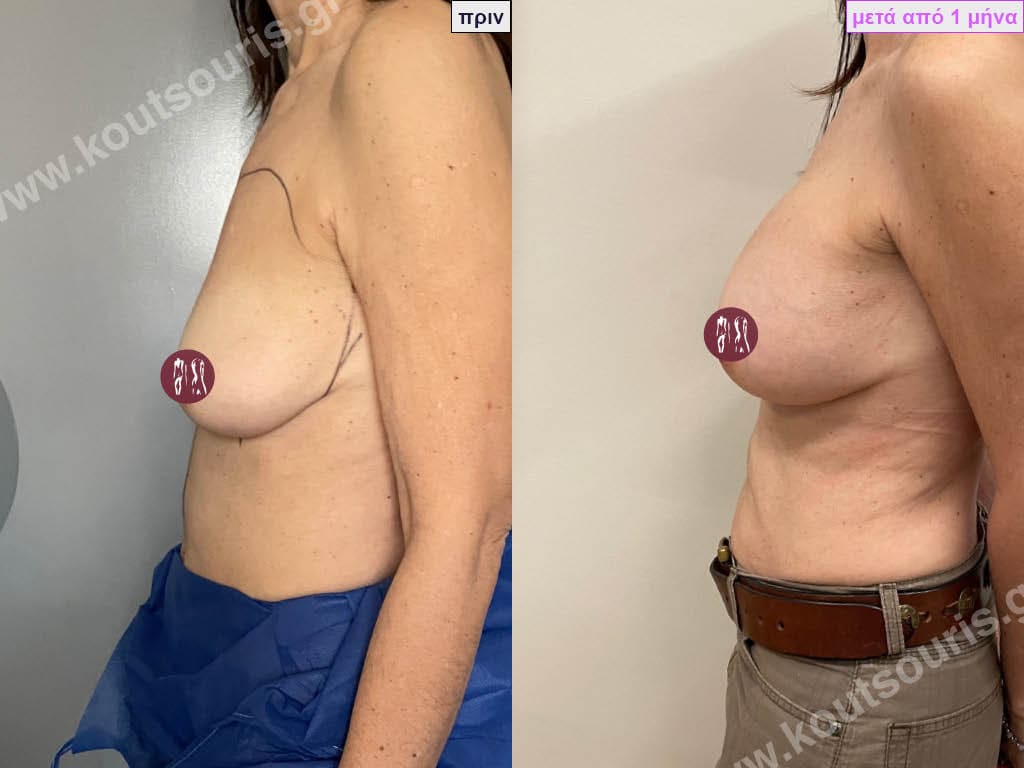
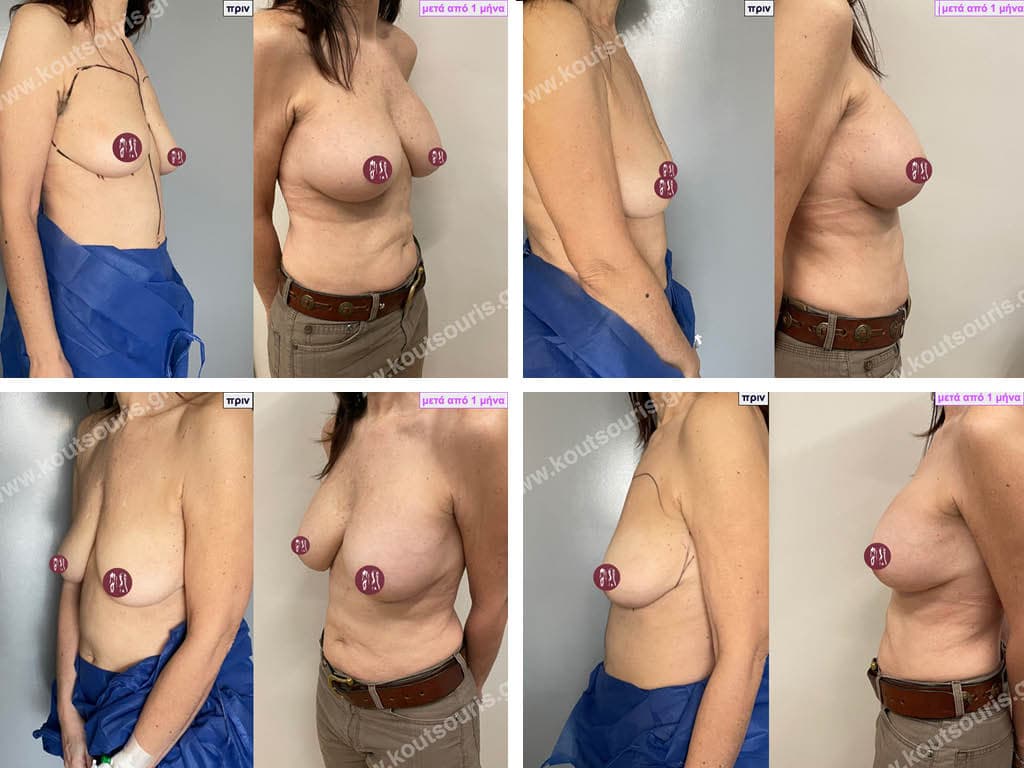
The result of breast augmentation is immediately visible, however, it becomes even better after 8 to 10 months when the swelling subsides and the implants “sit” better.
The marks from the incisions are a little more pronounced at first, but after 8 to 10 months they will look like two almost imperceptible lines.
When is sexual intercourse allowed after breast augmentation?
Initially there may be a feeling of heaviness in the breast area and the woman is usually afraid to have sex in case it hurts. Sexual intercourse is allowed immediately, usually after 3 to 5 days, but you should be careful not to press too hard on the breast to avoid injury.
How do we check the breast after breast augmentation?
The most basic and simplest way to check the breast after augmentation is by breast self-examination. Palpation should be done every month, between the 15th and 20th day from the start of the cycle. New nodules or suspicious lesions (inflammations) should be evaluated.
The presence of breast implants may improve the detection of tumors through self-examination (palpation).
Once a year, the breast should be checked by a mammologist or gynecologist, or a general practitioner or a plastic surgeon, also by palpation.
Further inspection of both the breasts and the silicone implants after the augmentation is done:
- with Magnetic Tomography (MRI),
- with Breast Ultrasound (U/S) and
- with digital mammography.
MRI is the most reliable and accurate test to check the breast and implant after augmentation and is the recommended test.
Breast ultrasound is a fairly quick, safe and effective examination, but it is not absolutely accurate.
During digital mammography the insert can make the examination difficult as it is pressed by the X-ray machine and there is a risk of rupture. Also some shots are more difficult to take.
With these tests we can make sure of the good condition of the implant as well as the shape and composition of the breast and rule out damage to the implant or lumps of the gland. Breast screening with ultrasound every year and MRI every 3 to 5 years (if the ultrasound is normal) is recommended.
If a suspicious lesion is found during the clinical examination or the imaging test of the breast with mammography, ultrasound or MRI, then it should definitely be evaluated by doing a biopsy. During the biopsy it is very important not to puncture the insert.
Complications after breast augmentation with silicone and how they are solved
All surgical procedures carry the risk of complications. Although not very common, possible complications after silicone breast augmentation are hematoma, seroma, pain, hypersensitivity or hypoesthesia of the nipples, inflammation, infection, capsule formation, healing disorders, wrinkling, microcalcifications, rupture or debulking (in saline inserts) of the insert, ALCL.
Hematoma or seroma (serum). This is a collection of blood or serum in the area of the pouch. They are extremely rare complications and usually occur immediately postoperatively or in the following days. The hematoma or seroma is manifested by swelling and tenderness of the breast. If the amount of serum or hematoma is small then we do not need to do anything. If the hematoma or oozing is large then drainage is needed.
Pain. It is usually mild and more like a muscle cramp, heaviness or pulling sensation than pain. It subsides immediately with simple painkillers and stops completely within the next few days or weeks.
Hypertrophic scars – keloids. They are extremely rare and relatively easily treated with a corticosteroid injection and silicone patches.
Disturbances in nipple sensation. Rarely, hypoesthesia or hyperesthesia of the nipple may occur after augmentation surgery. This is more common after periammary access. It usually subsides within the next few months. In very few cases it may persist for a long time.
Formation of a capsule (capsular contraction). After the silicone insert is placed in the pouch under the breast tissues, a strong cohesive membrane is naturally formed to hold the insert in place. This membrane is called a capsule. In some cases the capsule can collapse and compress the insert which is called capsular contracture or capsulitis.
There are 4 stages of Baker’s capsule. Symptoms vary from hardness, mild discomfort and simple pressure to pain, deformity and displacement of the implant. The capsule may appear unilaterally, bilaterally or asymmetrically. In subglandular or subfascial placement the possibility of creating a pathological capsule is approximately 17-20%, while in the submuscular or dual plane technique it is less than 1%. This is another reason we prefer dual plane mounting. If the capsule is painful or causes breast deformation, then we will have to surgically remove it, change the plan and place new implants under the muscle. The possibility of recurrence after replacement of implants is small.
Closed capsectomy, i.e. the crushing of the fibrous capsule around the insert in order to relax the capsular contracture, is not recommended because, on the one hand, it is very painful and, on the other hand, it can lead to a hematoma or rupture of the insert. The cause of the prolapsed capsule is unknown.
Wrinkles – Asymmetry. They can occur in thin breasts with moderate or severe sagging, usually when subglandular or subfascial placement is performed. It is corrected by changing the implants or by fat grafting.
Microcalcifications – microcalcifications. They may appear on the breast after months or years, most commonly after periammillary placement. While they are benign formations they can be confused for the development of malignancy. Thorough imaging and exclusion of malignancy by biopsy should be performed.
Atrophy of breast tissue. Large implants can cause atrophy of breast tissue. This happens in thin breasts usually. Thinning and shrinking of the breast is a result of pressure and can occur when the implants are left in place but is worse if they are removed without being replaced with new ones.
Insert infection. It is a rare complication (less than 1%) and is due to infection of the implant by a microbe. Although we apply all the rules of asepsis (bath with antiseptic solution in the previous days, intravenous antibiotics preoperatively and postoperatively, aseptic covering of the nipples, atraumatic technique) the possibility of infection of an implant may occur. It manifests itself with sensitivity, heat, pain, redness in the area of the insert or with discharge of fluid from the incision and often causes a fever. It can happen after a few days or even weeks after the operation. If the infection does not respond to local manipulations and antibiotic treatment then the implant should be removed and replaced with a new implant which is usually done after a few months.
Rupture or debulking (in saline inserts) of the insert.
It is usually subclinical, goes unnoticed (“silent” tear) and is detected after Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Ultrasound (U/S). When the rupture of the insert is large then it can worry us because it is palpable and creates a strange, abnormal projection of the breast. It can occur after excessive stress on the insert, injury to the casing, or as a result of natural wear and tear. After rupture of the insert, there is no substantial problem for the body since the silicone is cohesive and remains locked inside the insert’s capsule. If a rupture or swelling of the insert is detected, then a replacement operation will have to be performed. Most companies today cover the replacement of ruptured inserts for life.
ALCL
In an extremely small percentage – about one in eighty to one hundred thousand cases – the appearance of ALMC (anaplastic large cell lymphoma) in the tissue of the capsule or in serous effusion around the implant has been described. ALMC is not breast cancer but a very rare form of lymphoma which is however very treatable. ALMK on average can appear after eight years of breast augmentation usually in tracheal surface implants and it is believed that its occurrence may be the result of chronic inflammation or genetic predisposition. It manifests as serous discharge, pain, induration or swelling around the implant and is diagnosed by cytology and biopsy. As of mid-2019, 573 cases of ALMC have been described in millions of breast augmentations with silicone implants. This is a very rare phenomenon and as a result, due to the very small number of cases worldwide, treatment is individualized with a variety of treatment protocols.
Breast cancer
Silicone breast augmentation is not associated with the development of breast cancer.μαστού.
Analytical multicenter studies have shown that women with breast augmentation with silicone implants have the same rates of developing breast malignancy as women without silicone.
Because of frequent breast screening if a woman develops breast malignancy the diagnosis is faster and more timely in women with augmentation than in women in the general population.
Collagen – connective tissue diseases
Breast augmentation with silicone is not related to the development of autoimmune connective tissue diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, lupus, etc. Large epidemiological studies in women with and without silicone breast implants have shown that collagen diseases are not more common in women with silicone breast augmentation.
What should I worry about in the following days after breast augmentation?
If in the following days after breast augmentation you experience:
fever, heat, redness, edema, pain or fluid leaking from the incision area or the breast in general, you should talk to your surgeon immediately.
Will I be able to breastfeed after breast augmentation with silicone implants?
Yes. Chances are you will be able to breastfeed.
Breast augmentation when done from the inframammary fold or from the armpit has the least effect on the function of the mammary gland so breastfeeding is not affected or is minimally affected. However if the operation is done from the nipple then you are likely to have less milk production for breastfeeding.
Of course, we should take into account that women with hypoplastic or aplastic breasts have a lower milk production capacity anyway compared to those with adequate or large breasts.
The European Committee on Quality Assurance and Medical Devices in Plastic Surgery (ECQAM) concluded that silicone gel breast implants do not cause unwanted effects on pregnancy, fetal development, breastfeeding or the health of the nursing child. The American Academy of Pediatrics maintains that there is no reason for a woman with implants to refrain from breastfeeding.
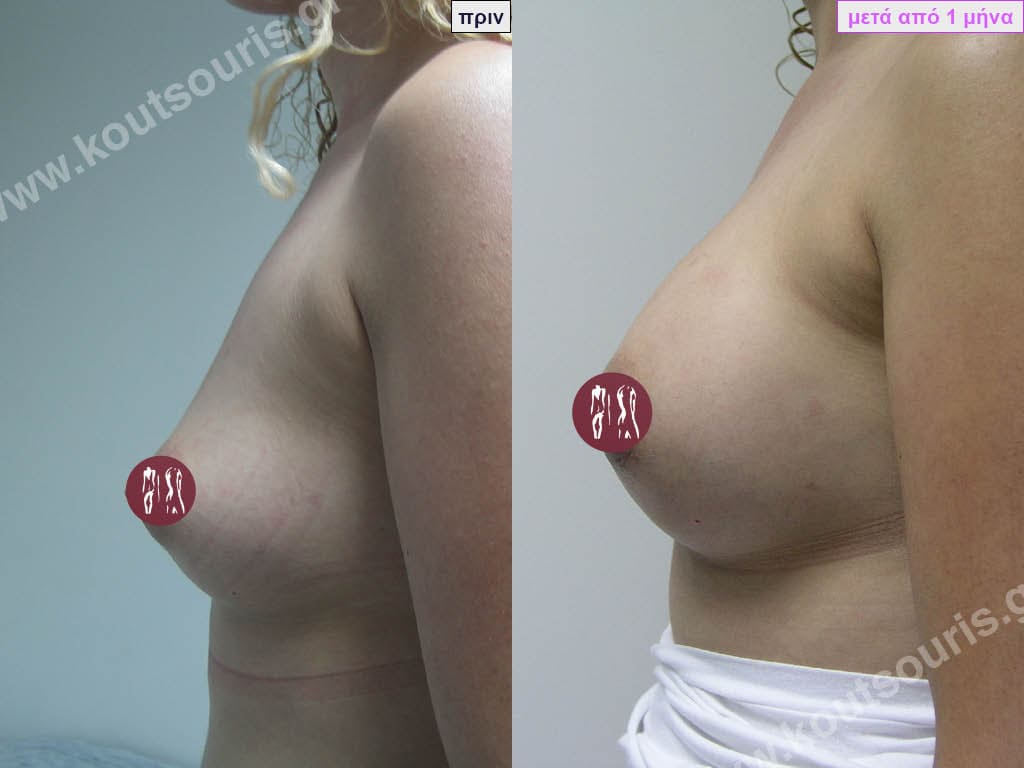
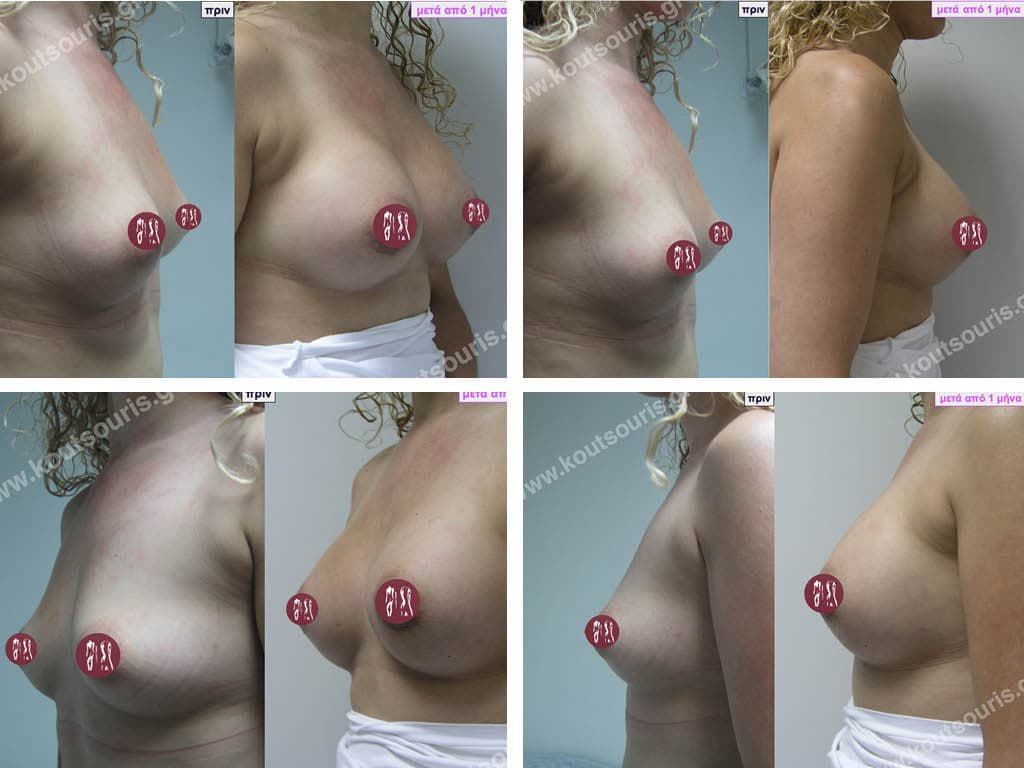
What will the breast look like if I choose to remove the implants without replacing them?
If the silicone implants are removed without their replacement then we will have thin, atrophic breasts with sagging equal to or greater than the one that existed before the implants were placed. The only solution to obtain a satisfactory aesthetic result without replacing the implants is the transplantation of autologous fat into the breast.
How long do silicone breast implants last?
The silicone breast implants we use today are predicted to last a lifetime, meaning they do not need to be replaced after a certain period of time.
However, if after some years a problem occurs either in the insert such as rupture or displacement or in the breast itself, such as sagging or falling, then a reconstructive operation is needed.
Today, most companies producing silicone inserts give a lifetime guarantee, while in case of rupture they cover the free replacement of the insert.
STATUS/LEGAL STATUS OF BREAST IMPLANTS FOR PATIENTS FROM EUROPE
All breast implants sold in the European Community are subject to the Medical Devices Directive (93/42/EEC) and are Class III devices according to Commission Directive 2003/12/EC of 3 February 2003.
Up to what age can a woman have silicone breast augmentation?
Breast augmentation with silicone implants can be done at any age after 18 years. In fact, there is no upper age limit for which silicone breast augmentation is not indicated.









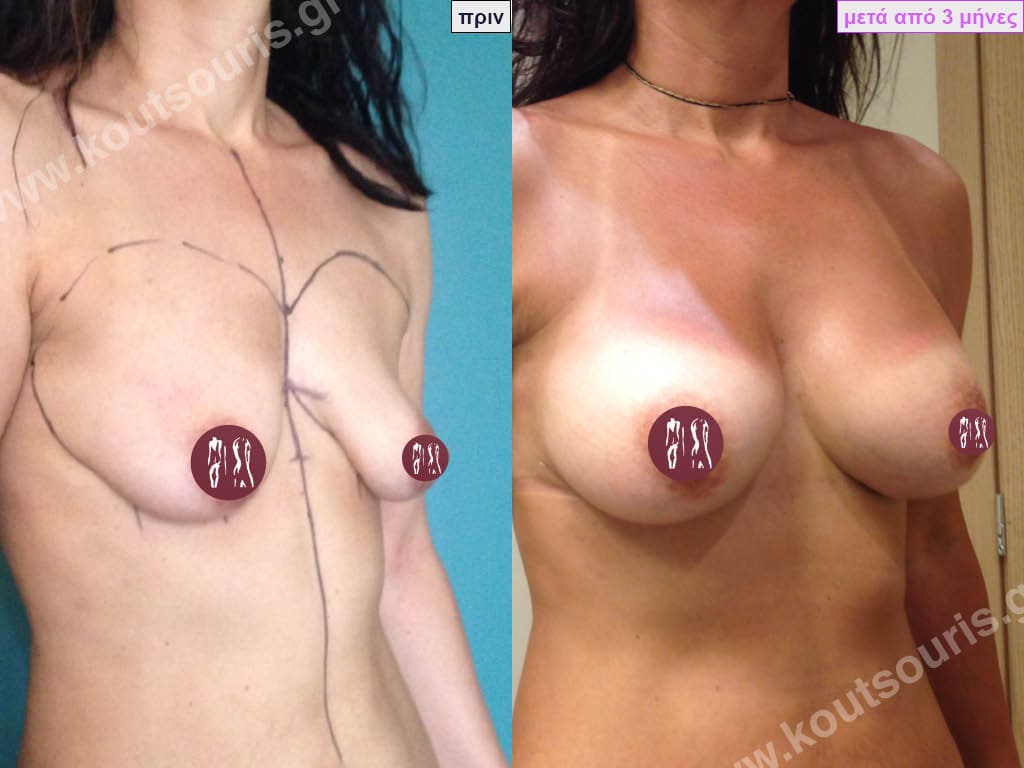
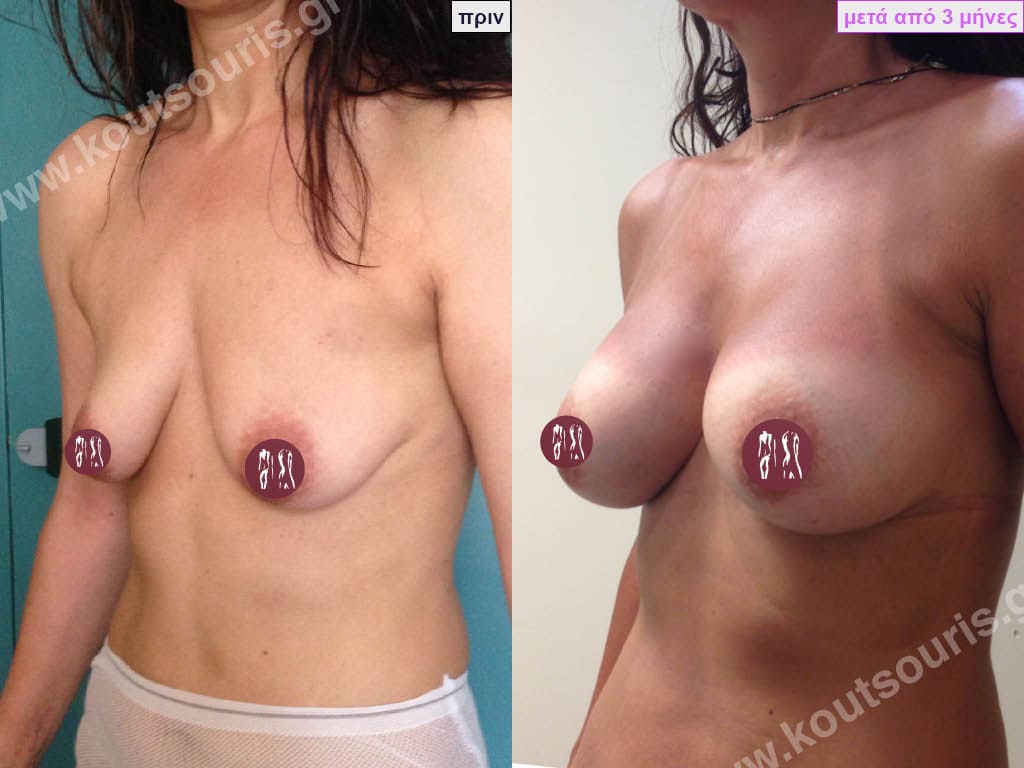
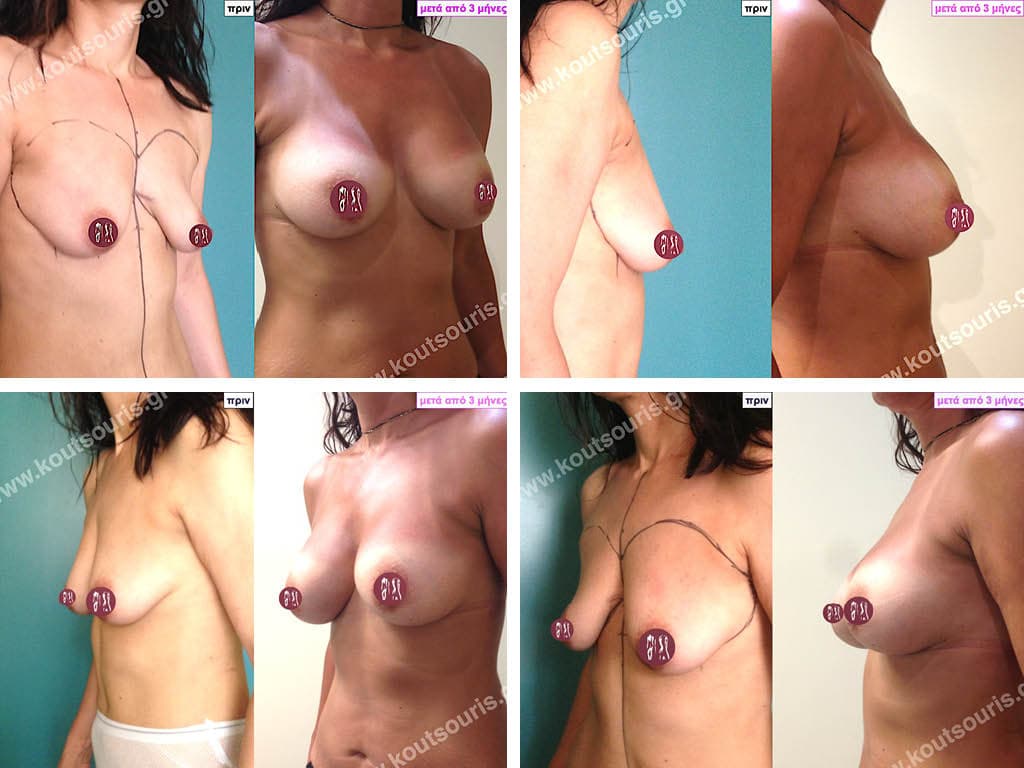


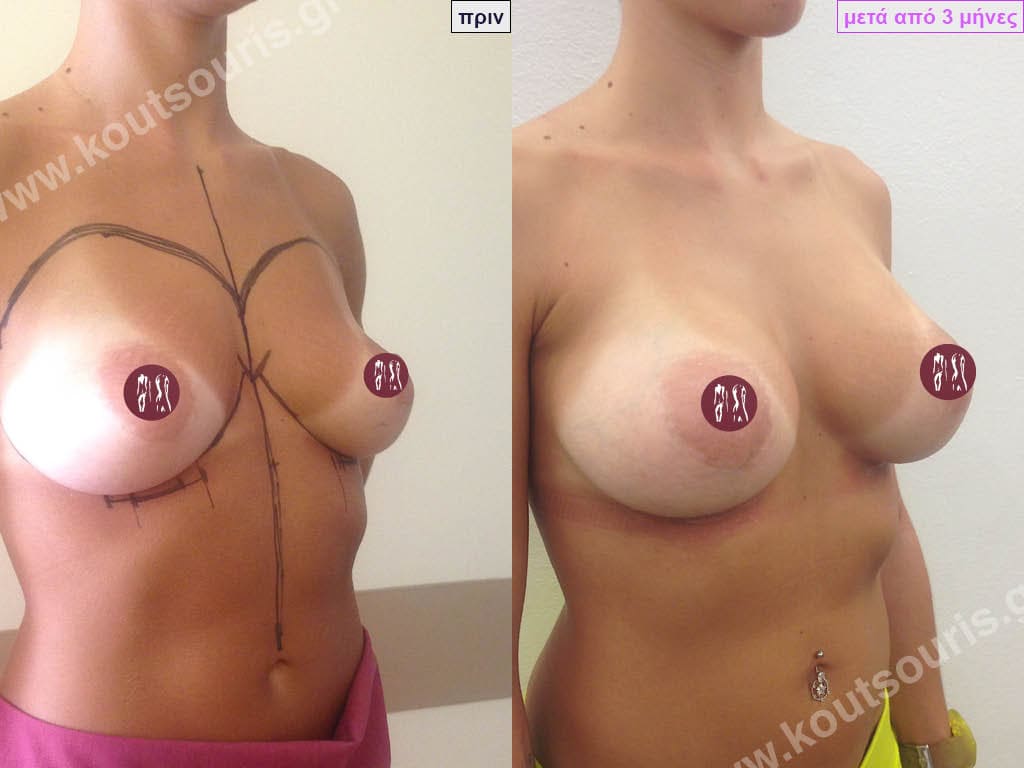
BREAST AUGMENTATION WITH FAT
Another technique to do breast augmentation in a woman is with Fat Grafting. In very simple words after doing Another technique to do breast augmentation in a woman is with Fat Grafting. In very simple words, after doing liposuction and removing fat from different areas of the body instead of throwing it away, we transplant it into the breast of the person who has a problem. When we talk about Fat Transplantation, we always mean Autologous Transplantation, i.e. the transfer of fat FROM A DONOR AREA TO A RECIPIENT AREA OF THE SAME PERSON.
Which women can undergo breast augmentation with fat grafting?
The transplant candidate should have a sufficient amount of fat in her body so that we can get the necessary amount of fat that we need to transplant. Women who are underweight or too thin are excluded from candidates. Also, if a woman has a history of breast malignancy in her family or has herself undergone a related operation, a very careful check and thorough investigation should be done pre-operatively, and if there are reasons to exclude her from being a candidate.
How is breast augmentation done with fat grafting?
The anesthesia we use is general anesthesia. When we perform Fat Transplantation in the breast we use special cannulas and place the fat deep, close to the surface of the pectoralis major muscle as well as subcutaneously, about 1 to 1.5 cm under the skin. Since a percentage of approximately 50 to 70% of the transplanted fat is absorbed within three months after the operation, in each lipotransfer operation we should take and transplant twice or three times the amount of the desired increase. Usually we transplant 250 to 450ml in each breast so the benefit of the intervention amounts to about 150-300cc per breast.
What complications can there be when we do breast augmentation with fat grafting?
The most common occurrence after breast fat grafting is ecchymosis (bruising) and edema (swelling) which gradually disappear within 2 to 3 weeks.
Hematoma and inflammation or infection of the DONATION or LIPTRIA area are also rare complications which are managed with drainage and antibiotic coverage respectively.
Often there is numbness, i.e. numbness in the entire area of the anterior chest wall, which gradually recedes and is fully restored in a period of usually one to two months.
After usually several months of breast fat grafting, small fatty cysts may appear within the breast mass due to melting of fat which may resemble a malignant transformation. In any such case, a diagnosis and a surgical solution are required, which is usually done with a diagnostic puncture.
One of the most common problems with fat grafting is that because we don’t know in advance how much of the fat we transplant will be absorbed, we usually transplant double or triple the amount of fat. This, as a fact, creates a technical issue by itself: a. if more fat is absorbed than desired then I will have to repeat the operation in a second year (usually after 3 to 4 months). b. if less fat is absorbed than desired then a deformity may be created in the area like a “bloat” or like a small egg. In this case, we will have to re-operate the patient by performing liposuction.
Another complication of breast fat transplantation is that the process of placing the fat with the microcannulas injures the gland in various places. This results – often after years – in the formation of calcifications or microcalcifications within the mass of the gland due to the organization of microhematomas and a differential diagnosis is required to rule out the development of malignancy in the breast since an indication of malignancy is microcalcifications.
How is the breast checked in women who have undergone fat grafting to their breasts?
After the operation of augmentation or correction of the shape of the breast with Fat Transplantation, a regular check of the breast is required by the woman herself through bimanual palpation on a monthly basis. Every woman must undergo a regular radiological check-up through: a. Digital Mammography b. Ultrasound or c. Magnetic Tomography. Breast augmentation with fat transplantation is a modern technique which, although it has several difficulties, could provide a solution in several cases where we want to increase the size of the breast without using silicone inserts. In summary, we can conclude that breast augmentation with silicone inserts is today the most popular and most functional technique for increasing the size and shape of the breast.