Gynecomastia
Which are the most distinguishable attributes of a male breast?
Physiologically, the male breast is composed by the nipple-areolar complex and a small gland, called as mammary gland and is located just behind the nipple. The nipple complex has a diameter of 2-4 cm and is located in the middle of the fourth side, while the mammary gland is small in size. This gland remains atrophic in male breast, since it does not grow at all during puberty in contrast with the female breast.
The mammary gland growth in both men and women is a result of the action of specific female sex hormones, called estrogens giving the special elements of the female sex.
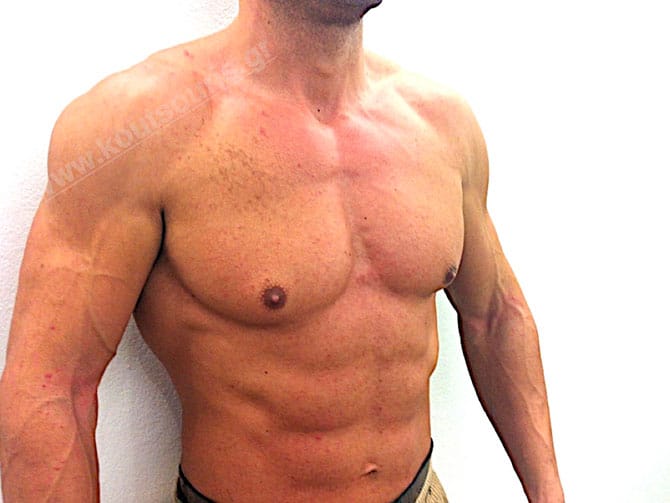
Is gynecomastia a frequent phenomenon of the male population?
Gynecomastia may concern one breast only, but it usually affects both breasts in a male breast.
According to the latest bibliography, gynecomastia is a frequent phenomenon affecting about 35-40% of male population and about 65% of young men.
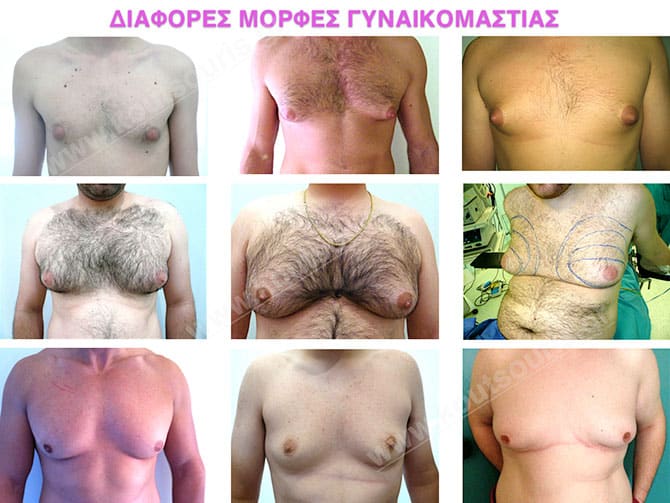
What happens in a male breast under gynecomastia?
Anatomically speaking, when we look at a male breast looking like a female one, we should take under consideration two main reasons:
- The excessive growth of the physiological mammary gland and
- the development of the adipose tissue around the gland
More specifically, gynecomastia is accompanied by the appearance of a hypertrophic mammary gland, which is normally found right behind the nipple. The excessive fat deposition around the gland area is very significant for the overall image of a hypertrophic breast. This situation is called as lipomasty, which is more frequent in overweight or obese people.
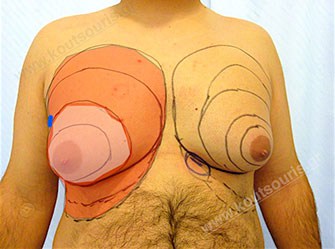
During the clinical check of patient it is very important to measure the rate of gland hypertrophy with respect to the presence of fat in the breast area, since it will help us to provide the best solution for the problem.
What is the reason of gynecomastia in men?
Regarding the explanation of gynecomastia we need to take under consideration that the main factor of the excessive development of mammary gland is the intravenous action of or other substances similar to them or the reduced action of androgens.
Based on this ascertainment gynecomastia is divided into four categories:
- Physiological
- Pathological
- Pharmaceutical
- Idiopathic
What is the physiological gynecomastia?
The most frequent form of gynecomastia is the physiological, which normally appears during the neonatal, early puberty and adult years (usually after 60-65 years old).
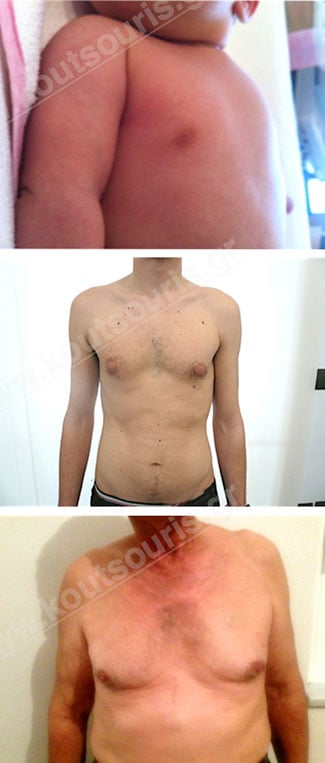
During the neonatal age (0-8 months) the baby’s breast is developed due to mothers’ estrogens, transferred into it through the embryo-placental circulation. The neonatal gynecomastia lasts only a few months and regresses completely over time.
During the early puberty (10-13/14 years old) the feminization of breast is a frequent phenomenon in young boys at a rate up to 65%. This happens due to predominance of estradiol, which (in most cases) regresses completely in comparison with testosterone. If a young teenager develops gynecomastia and the breast remains hypertrophic for at least two years, then gynecomastia is considered as a permanent phenomenon. The only solution for the correction of this problem in such a case is surgery.
During the adult years (more than 60-65 years old) the mammary gland develops in size physiologically. This distension is due to the attenuation of testosterone-estrogens. It is an unpleasant phenomenon but not a pathological one.
2. Pathological gynecomastia
A special category for the explanation of gynecomastia is the administration of medicines such as:
- Testicular tumors
- adrenal glands tumors
- post-renal insufficiency
- post-hepatic insufficiency
- alcoholism
- thyroid diseases
- hypogonadism or
- congenital defects
What is exactly the pathological gynecomastia?
During pathological gynecomastia the distension of mammary gland is due to excessive action of estrogens excreted by testicular or adrenal glands tumors after hepatic or renal insufficiency, alcoholism, thyroid disease or other congenital defects.
If the pathological gynecomastia is not a particularly frequent phenomenon, we always have to be suspicious when it suddenly appears and the breast is growing rapidly at a non-predictable age.
In such cases the disease should be thoroughly and etiologically checked as well as to be treated.
What is the pharmaceutical gynecomastia?
A special category for the etiology of gynecomastia is the administration of medicines. Many cardiovascular medicines such as antihypertensives, diuretics , cardiotonics , antiarrhythmics and gastroprotectives, tuberculostatics antifungal medicines are responsible for the development of gynecomastia.
3. Pharmaceutical Gynecomastia
A special category for the etiology of gynecomastia is the administration of medicines such as:
- cardiovascular medicines, antiarrhythmics, diuretics
- gastroprotectives, tuberculostatics and antifungal medicines
- Antidepressants, anxiolytics and generally neurological drugs
- Marijuana, amphetamines, heroin, methadone
- Doping substances
A large group of young adults who visit a plastic surgeon and ask for a solution to the problem of gynecomastia are individuals who use doping substances in order to improve their muscle power. The doping substances used for the growth and strengthening of muscle tissue are “flavored” in the cells of mammary gland, have as a side effect the excessive gland growth and the anti-aesthetical distension and falling of breast. In such case gynecomastia is usually at stage II, pure and is rarely accompanied by the appearance of lipomasty.
4. Idiopathic gynecomastia
It concerns about 25% of cases of gynecomastia.
It is a very frequent phenomenon for which we do not have any etiological explanation.This is the reason why it is called idiopathic.
What is idiopathic gynecomastia?
Another great category for the etiology of gynecomastia is the idiopathic gynecomastia, affecting about 25% of cases. It is about the excessive growth of feminine breast in men, which is not related to the cases above. It is a frequent phenomenon for which we do not have any etiological explanation and this why it is called “idiopathic”.
Is there any classification scale of gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is divided into four stages according to the hypertrophic growth and falling rate of the mammary gland:
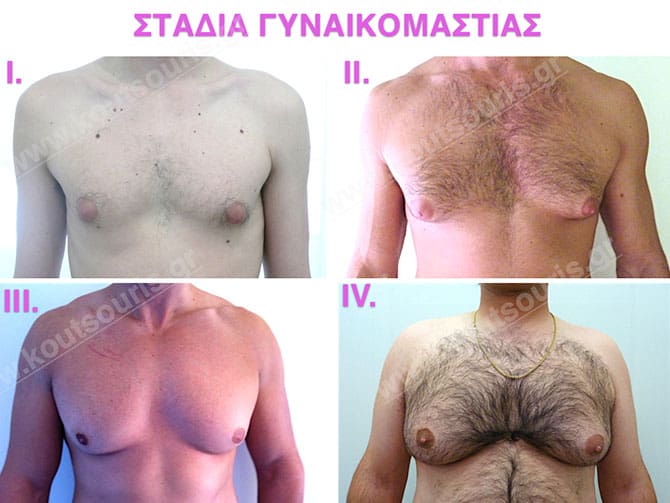
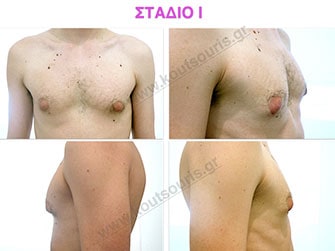
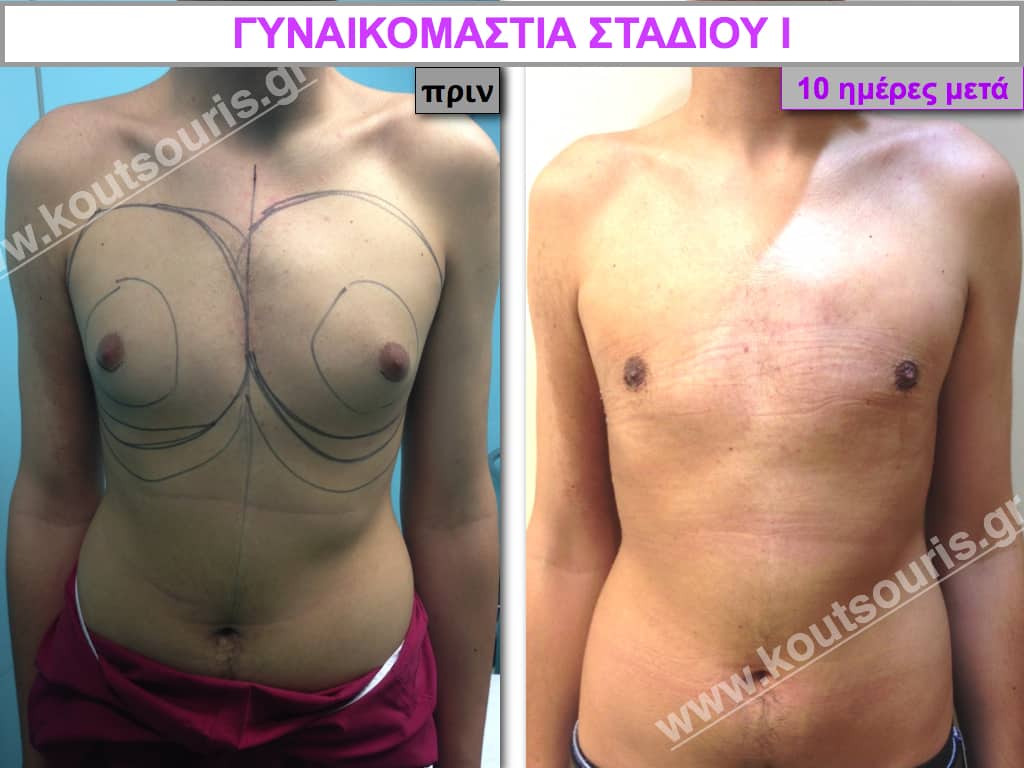
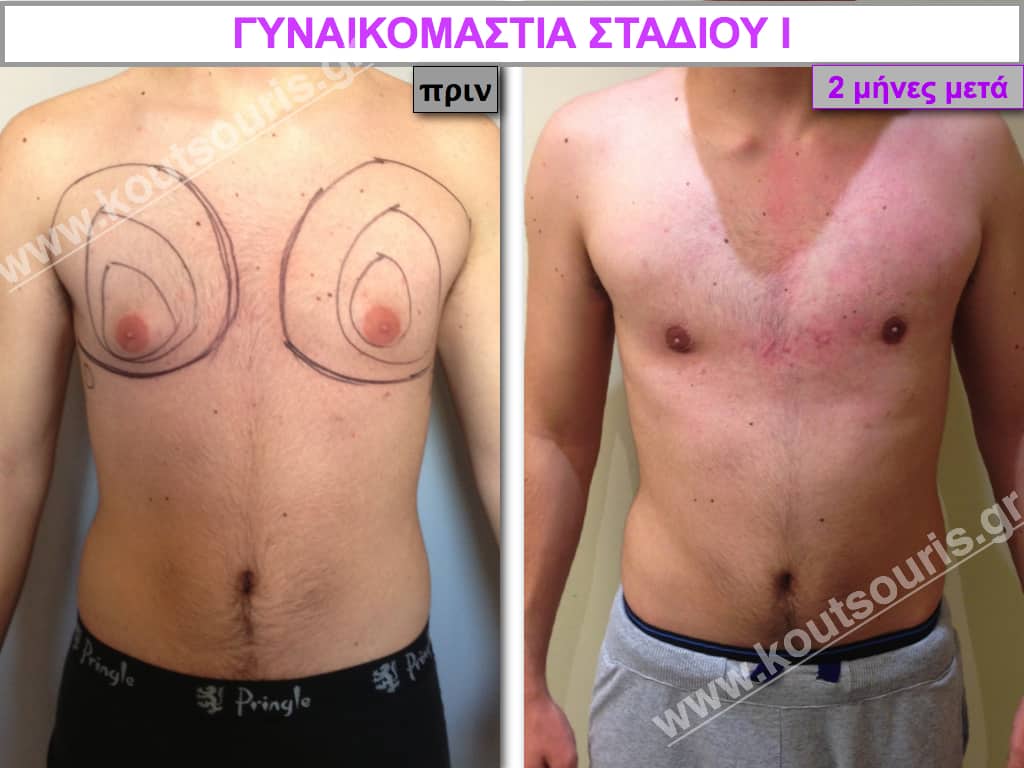
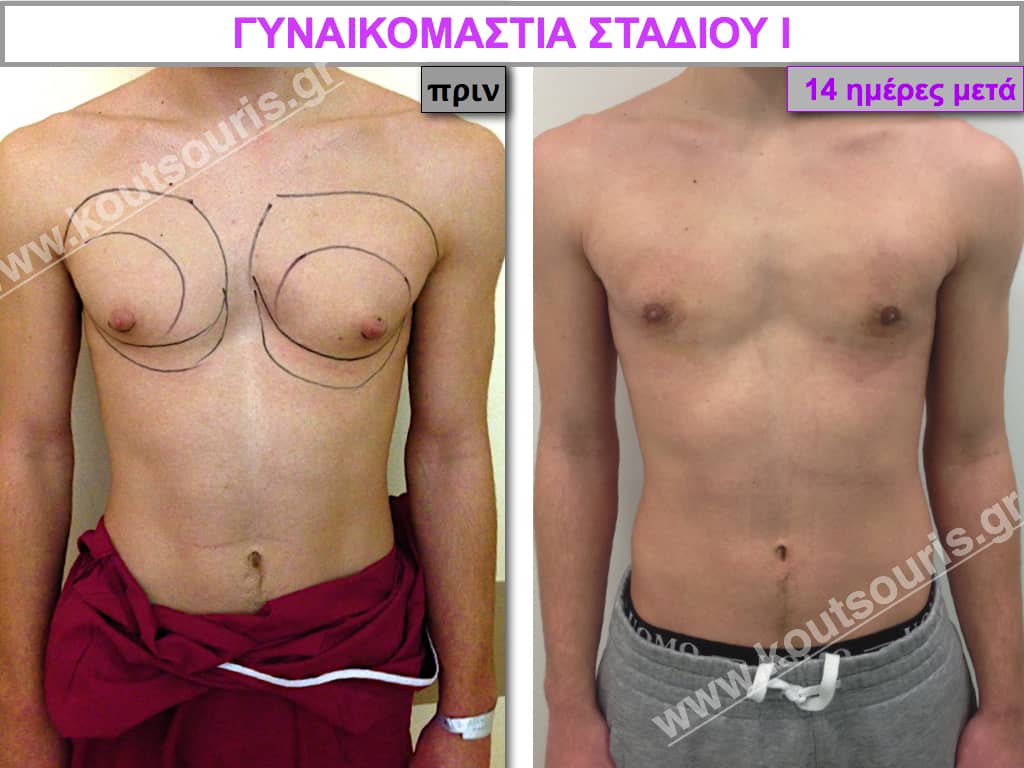
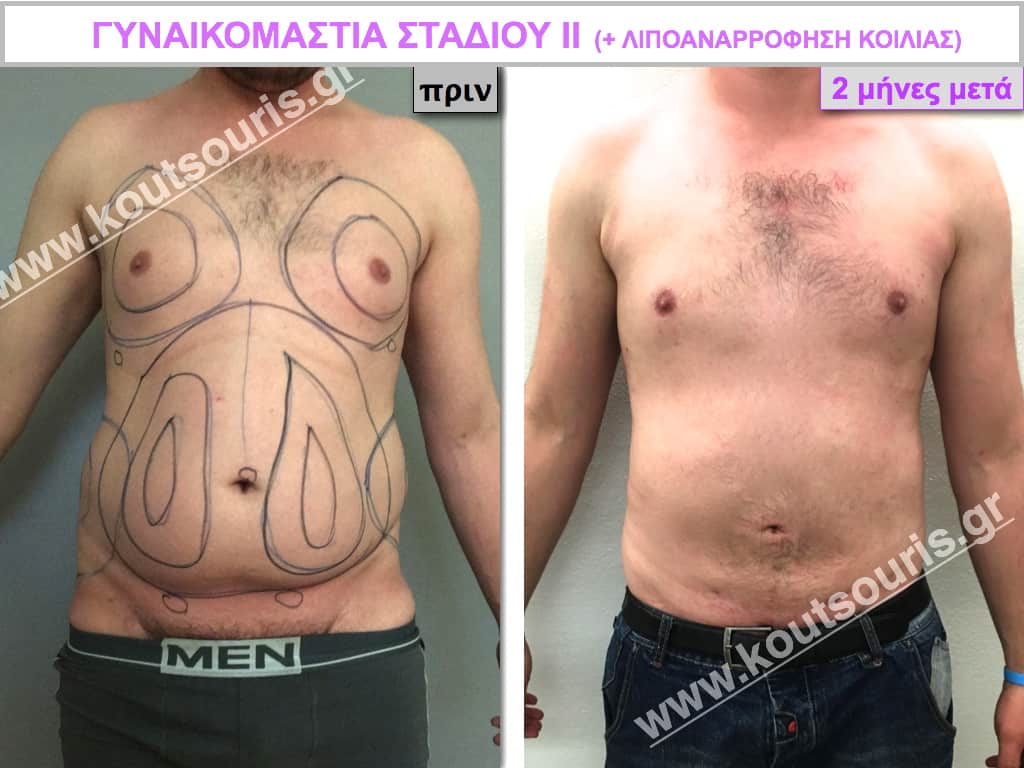
Stage I: low projection of the gland, located just behind the nipple.
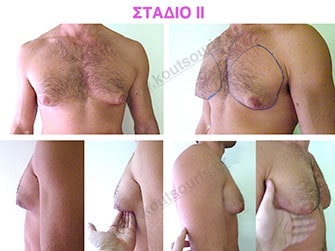
Stage II: medium projection of gland, located more extensively behind and around the nipple.
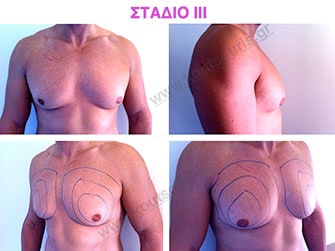
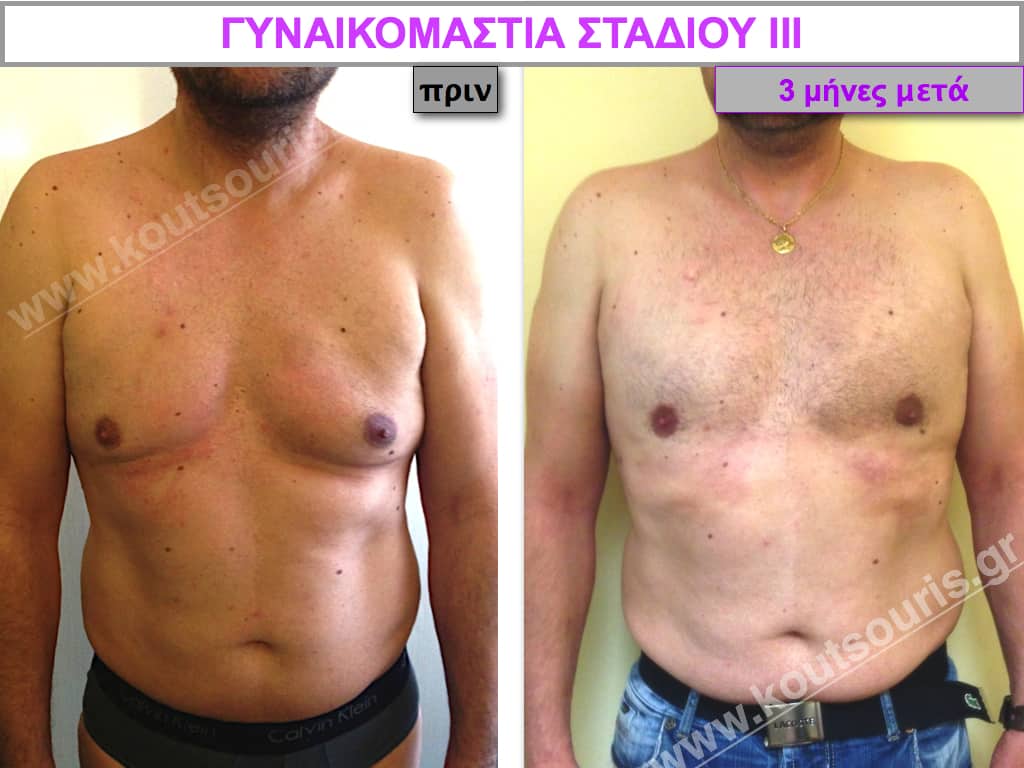
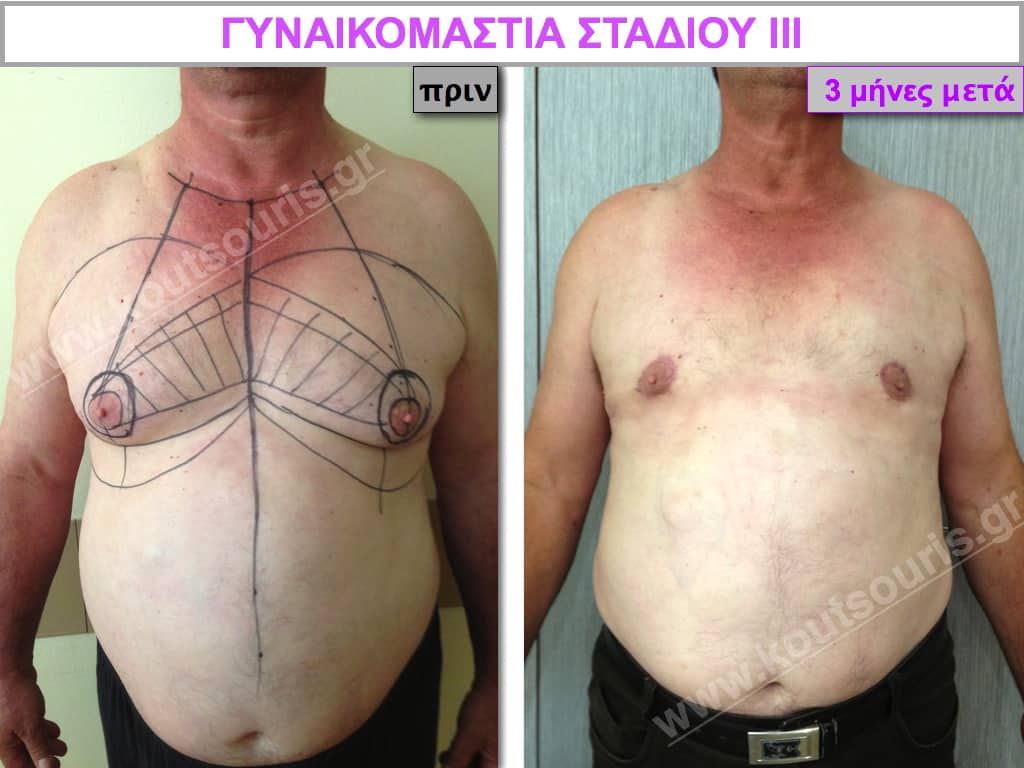
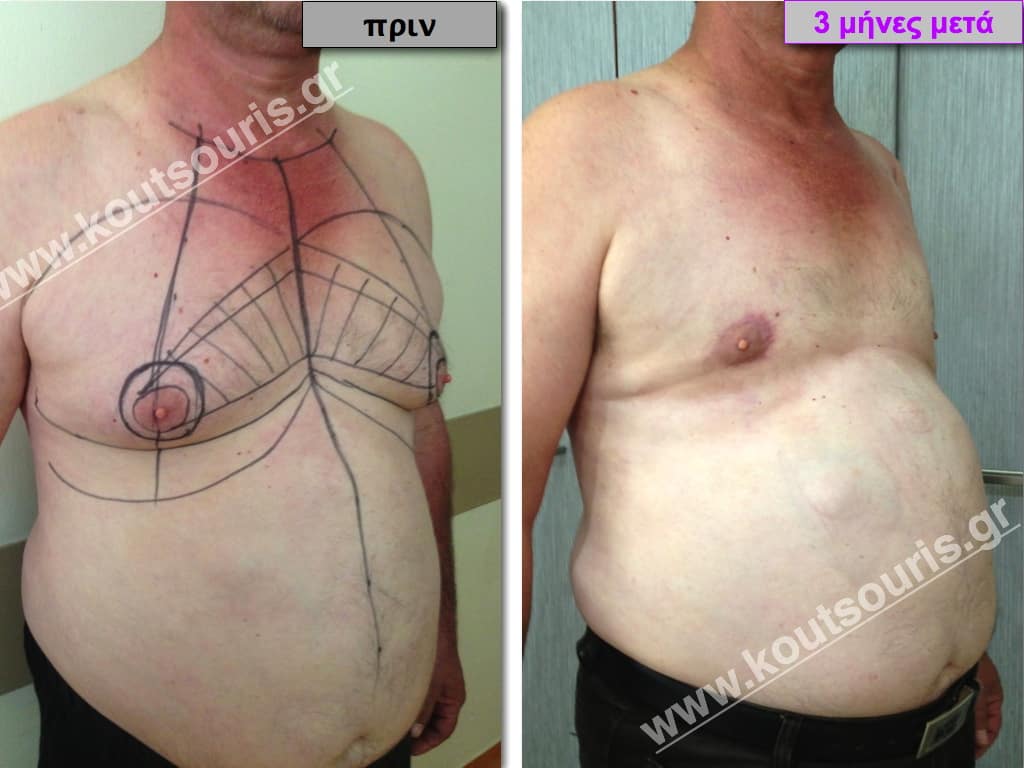
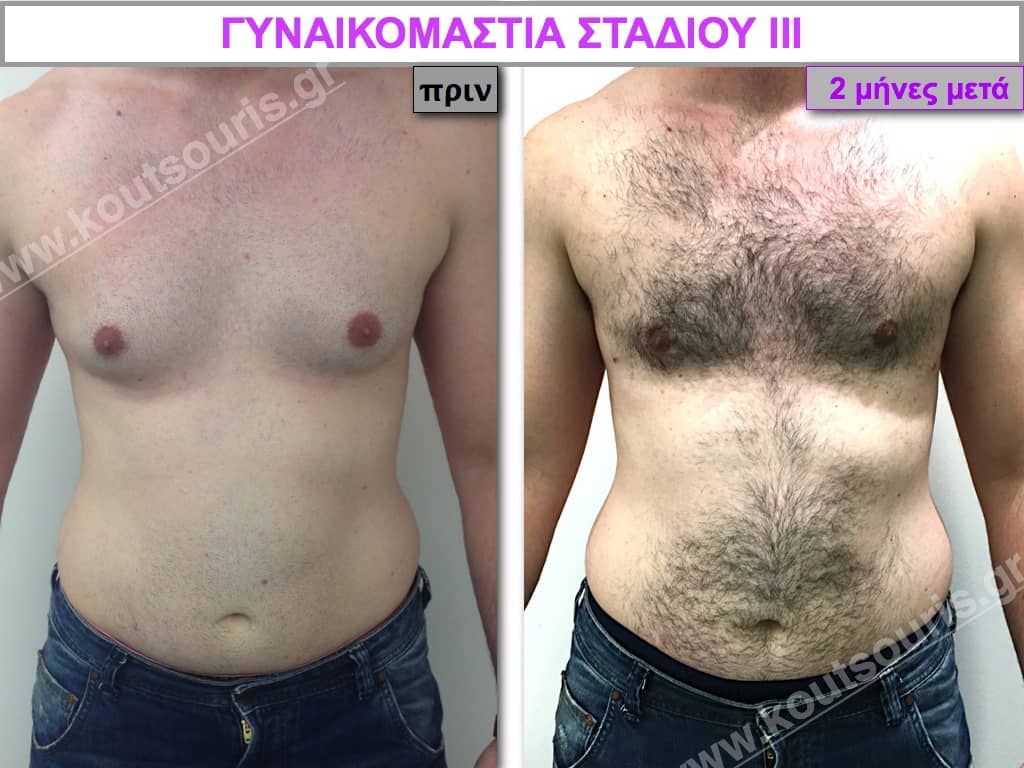
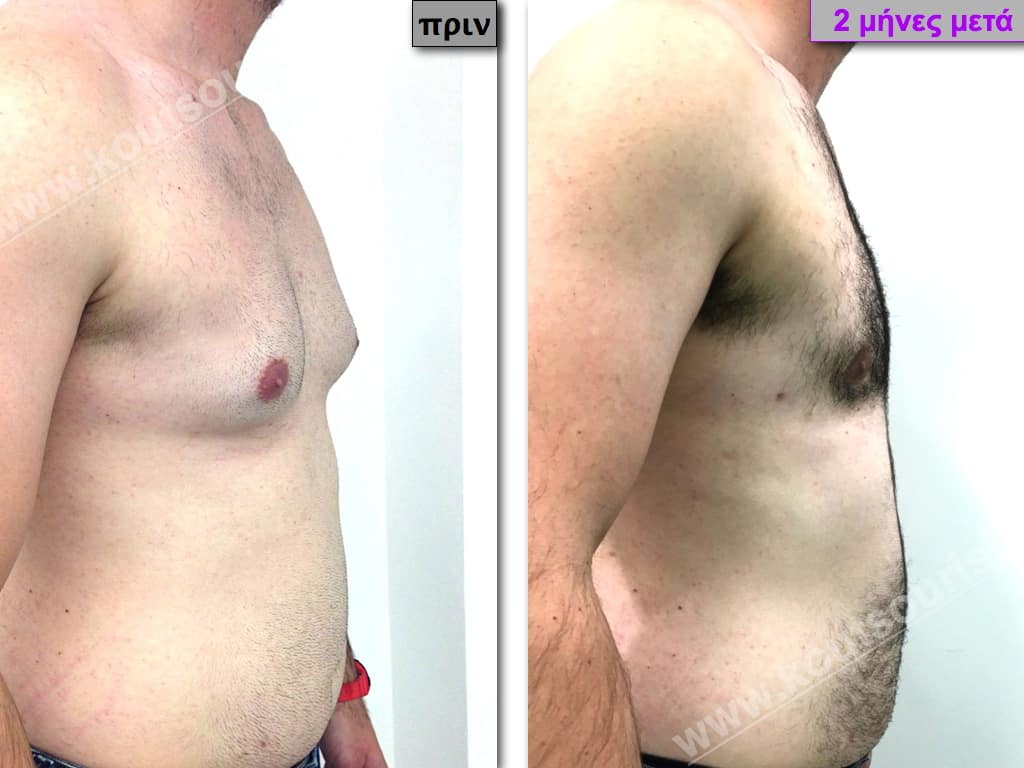
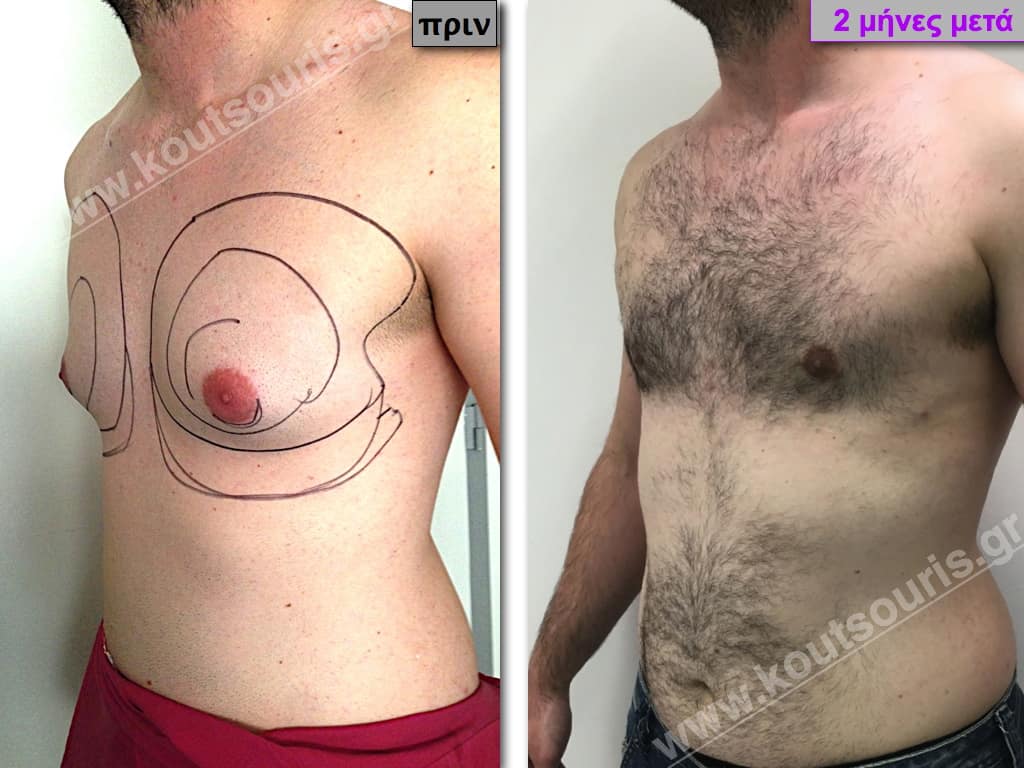
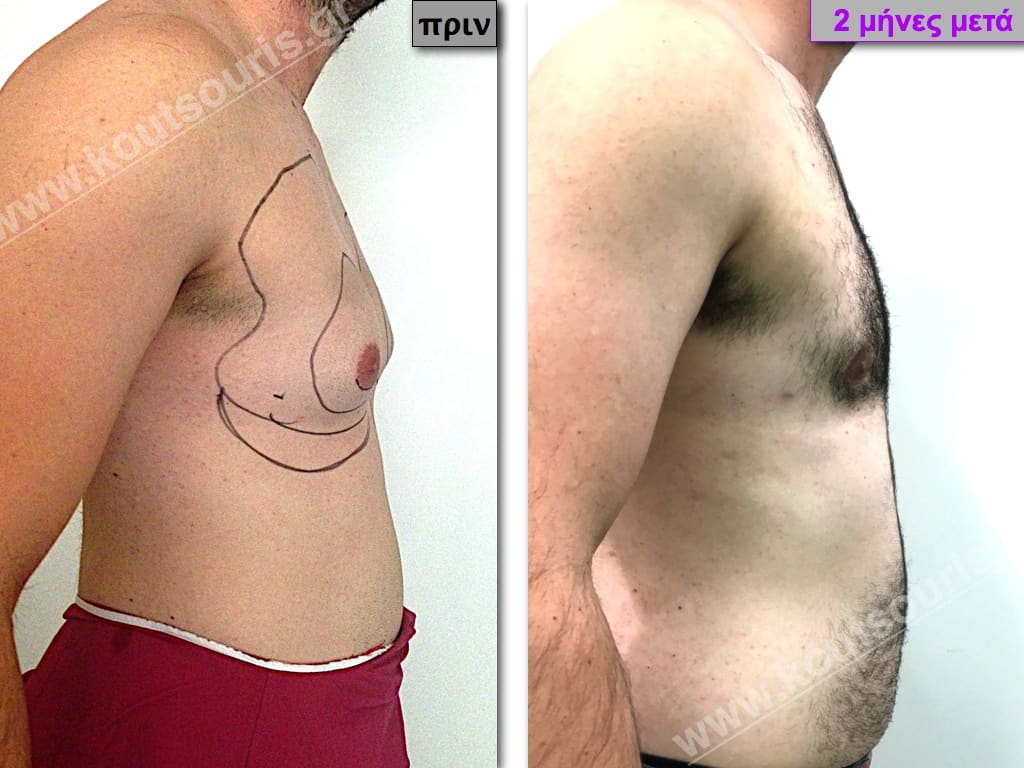
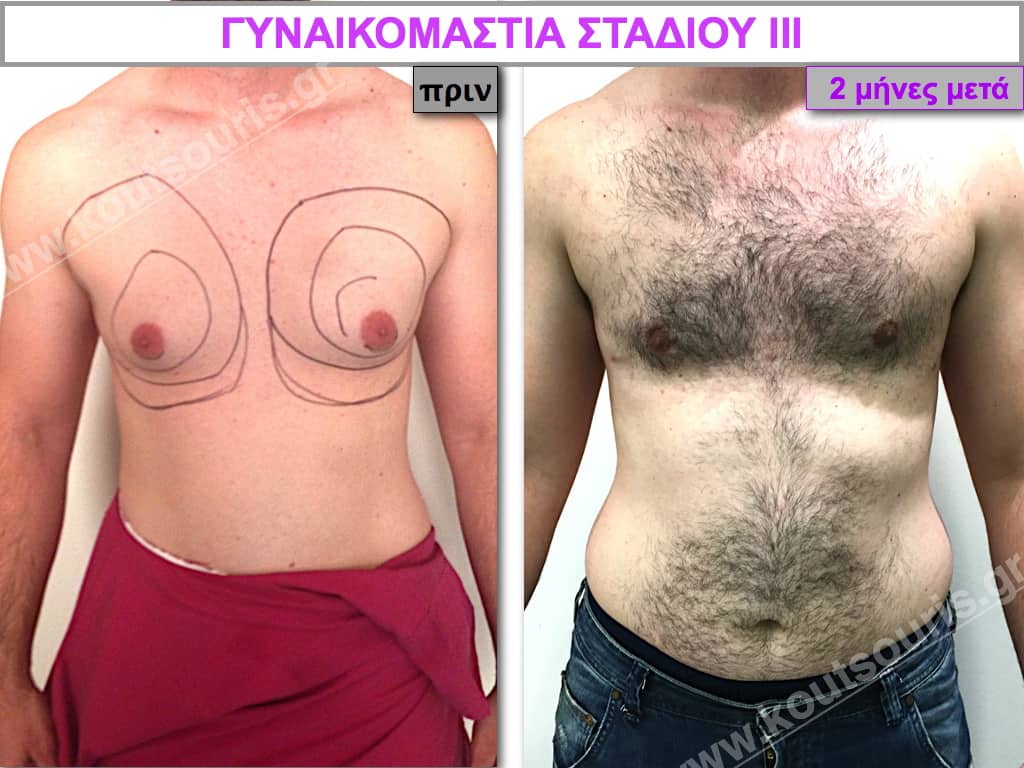
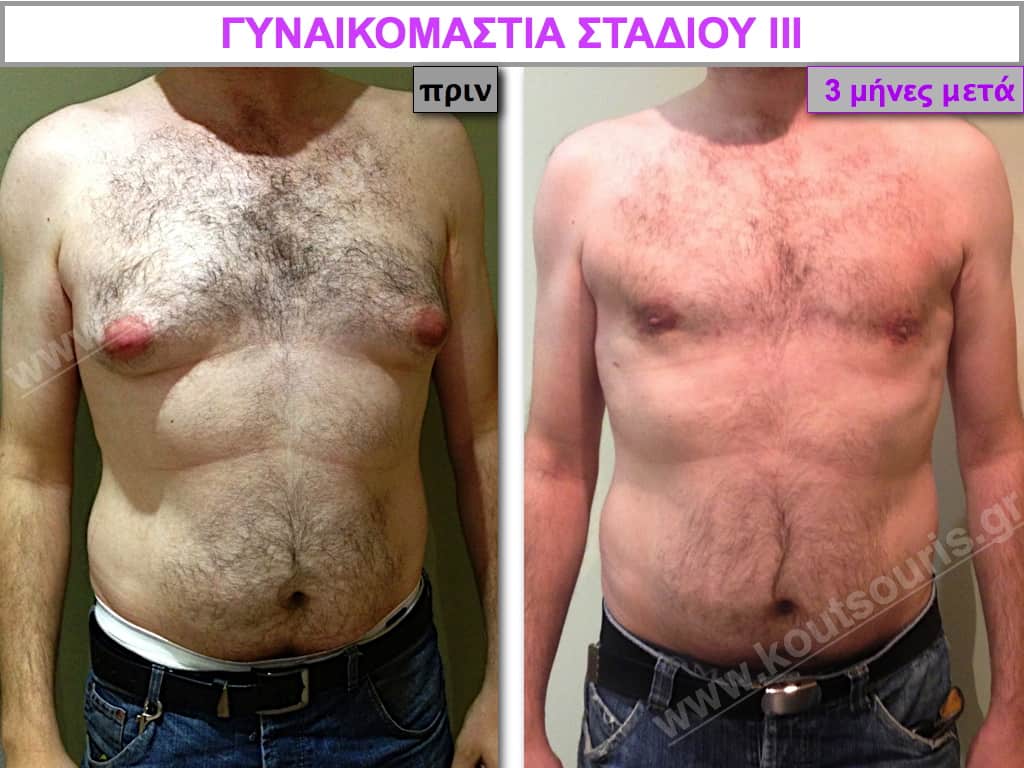
Stage III: medium to high atrophy of gland without any significant falling of breast.
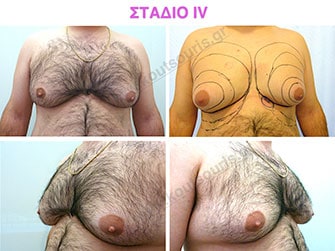
Stage 4: High hypertrophy of gland with a significant falling of breast.
What is the treatment of gynecomastia according to its reasons of appearance?
Taking under consideration the etiology of the gynecomastia phenomenon it is totally comprehensible that we do not need to do anything in newborns, while it is necessary to wait in case of young teenagers, since in most cases the phenomenon of gynecomastia regresses.
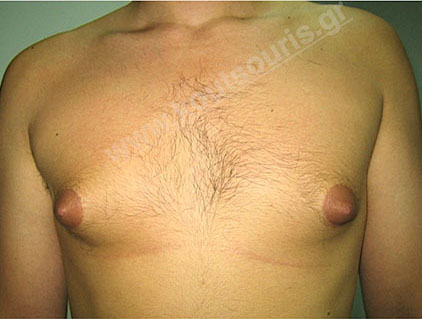
In case that the hypertrophic breast of a young teenager remains stable for two years, then gynecomastia is permanent and should be surgically treated. The surgery should be planned at the end of the age of puberty, i.e. between 17-18 years.
The only solution of the correction of the problem for people appearing gynecomastia during the adult years is surgery, while waiting usually delays the solution of the problem.
We should note that in every case of gynecomastia, we should exclude the fact that gynecomastia is due to pathological reasons, before categorizing this disease as physiological or idiopathic.
Thus, when it comes to pathological gynecomastia, the reason of appearance of this disease should be initially treated and then surgically corrected. For example if the hypertrophy of gland is due to hyperthyroidism, testicular or adrenal glands tumors we should take care of this disease and then treat it. The same thing should be done also in cases with pharmaceutical gynecomastia. We should check the organism exposure to medicines, doping and addictive substances, such as marijuana, alcohol etc. and simultaneously deal with gynecomastia.
Can the treatment of gynecomastia be surgically treated or it can be treated with the administration of medicines?
When gynecomastia exists for more than two years, then it is considered to be permanent and it does not improve the image at all.
We should clarify that the surgery is the only treatment for gynecomastia, since it is a definitive and permanent solution. Lately this surgery has become simpler and more effective even in most difficult cases thanks to the technological revolution and the invention of new surgical techniques.
Despite the existence of several medicines reducing the mammary gland such as testosterone, antiestrogens etc. the medical treatment may have significant side effects, unsatisfactory results and it cannot lead to a complete regression of the disease, something that can be achieved only surgically.
What is our goal during the gynecomastia surgery?
The aim of the gynecomastia surgery is the reconstruction of the male breast reducing the size and projection of the mammary gland in order to restore the male thorax without leaving any unpleasant spots and apparent scars on the skin.
In cases of severe gynecomastia, due to detected lipomasty, one of the basic problems during the surgery is the excess of skin when the breast is large.
The former performance of the treatment according to classic surgery techniques was the removal of mammary gland along with the skin excessiveness. As a result, the appearance of unpleasant scars in the thoracic area was a commonplace. Simply put, the patient was primarily ashamed of showing his or her breast due to its excessive size and projection. Nonetheless, this feeling of shame remained after the surgery as well, due to the appearance of anti-aesthetic scars.
Is there a contemporary treatment of plastic surgery for gynecomastia?
The solution for the reduction of breast volume without removing any excessive skin is provided by a new surgical technique of plastic surgery combining
- Endoscopic surgery with
- the technique of Liposuction.
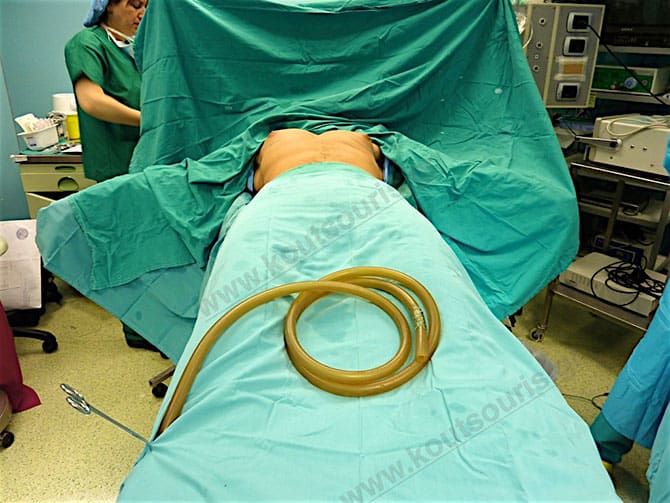
The treatment starts with the administration of anesthesia and the patient is placed in a supine position.
What is liposuction?
The liposuction surgery is a very “intelligent” treatment performed through very small holes without removing any skin. By doing so, we can remove the excessive subcutaneous fat from spots with local lipodystrophy.
This treatment is performed with surgical tools, known as cocks and with the help of a special liposuction device.
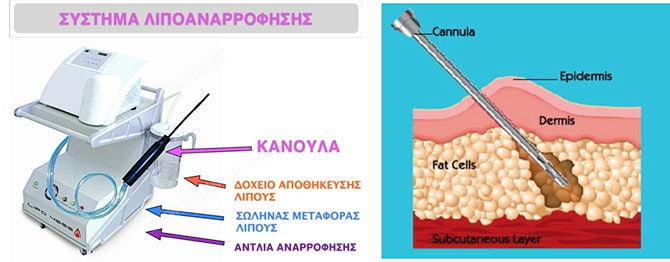
What kind of anesthesia is administrated for the gynecomastia surgery?
The gynecomastia surgery is performed with general anesthesia. In case of less severe gynecomastia we can combine both local anaesthesia and neuroleptanalgesia.
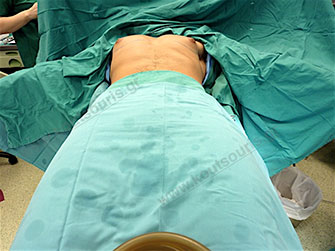
We should point out that in contrast to what it is believed by many people, the general narcosis in patients without pathological problems is the safest narcosis since the vital systems of patient are totally controlled by the anesthesiologist, a fact that does not happen in other types of anesthesia.
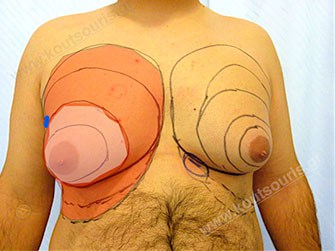
Which are the surgical techniques of the gynecomastia treatment?
The gynecomastia treatment starts with the liposuction of the anterior chest wall.
The patient is placed in supine position and is subjected to anesthesia. In the beginning we inject a solution of topical anesthetic and vasopressor medicine, in order to avoid any possible post-surgical pain and bleeding during surgery.
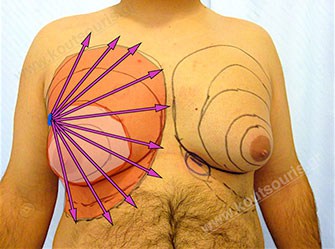
After a few minutes we perform liposuction in the hypertrophic gland area with the help of a super fine cock of 2, 5-3 millimeters diameter into a fine incision of 3-4 millimeters length close to the ipsilateral axilla.
Our primary aim with the revolutionary application of Liposuction is not only the removal of excessive fat in the breast area and the reduction of its projection, but also the expansion of the skin’s detaching from the subcutaneous tissue in the anterior chest and in the upper abdominal wall through a very small and invisible incision.
What happens with the excessive skin?
When the subcutaneous skin is released from the underlying fat tissue with the liposuction technique, then the skin is getting shrunk. As a result, in most cases, there is no excessive skin left after liposuction, so there is no need of any skin removal and there are no scars in the thorax, as happens with the former plastic surgery techniques.
What should we do after liposuction in order to restore gynecomastia?
The gynecomastia surgery, in case of pure lipomasty coexisting with a very small mammary gland, may be prevented in this stage and the result of surgery will be absolutely sufficient.
However, in most cases of gynecomastia, the problem is due to a hypertrophic mammary gland coexisting with the adipose tissue.
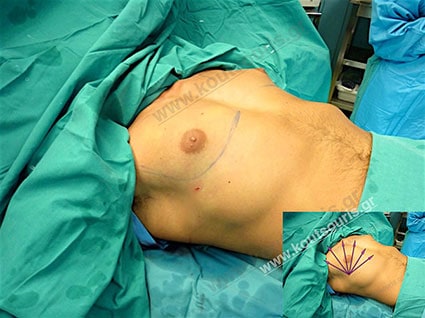
So, in most cases the surgery is continued with a very small Incision of 3-4 cm length designed like a crescent in the lower limit of the nipple so that is postoperatively hidden in this anatomic site
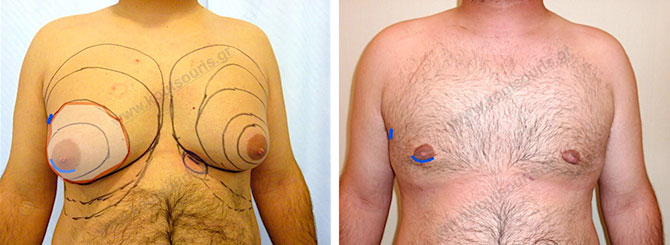
The surgery ends with repetitive liposuction in the area of the anterior chest wall and we smoothen out any asymmetries created by the removal of the gland.
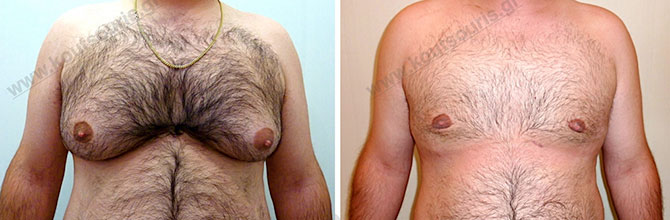
Is there any possibility of making large incisions on the skin with the new surgical techniques for gynecomastia?
By alternating Liposuction – Endoscopic Surgery – Liposuction it is not necessary to remove any excess skin since it is getting shrink after its release from the underlying tissues, something which can be achieved in most restorative gynecomastia treatments.
This way, we avoid making any large anti-aesthetic incisions on the skin, since the surgical incisions are very small, designed in relatively non- visible positions.
On the other side, alternating the techniques of Liposuction – Endoscopic Surgery we manage to remove the hypertrophic mammary gland, without causing any dents and asymmetries in the anterior chest wall, through the normalization of tissue with the liposuction cannula.
In very rare cases of exaggerated gynecomastia or after a significant weight loss, it may be necessary the reduction of excess skin, something that does not happen during the surgery, but 6-8 months after the first gynecomastia surgery.
As long as the time goes by the skin image is getting improved, so that we have to wait the same time because the skin area needed to be remove will surely be less, so the skin incision will be significantly smaller.
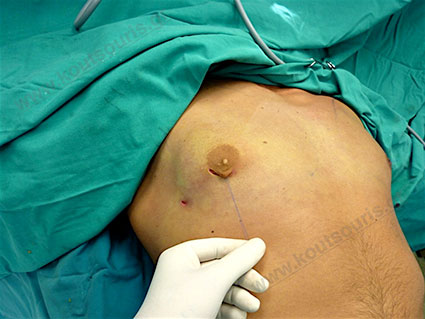
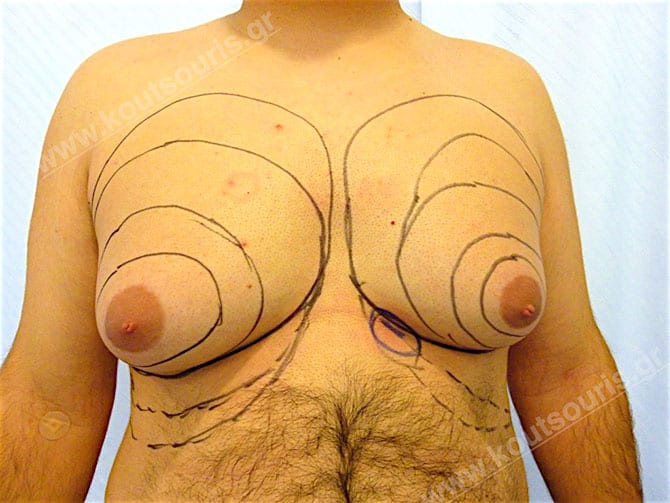
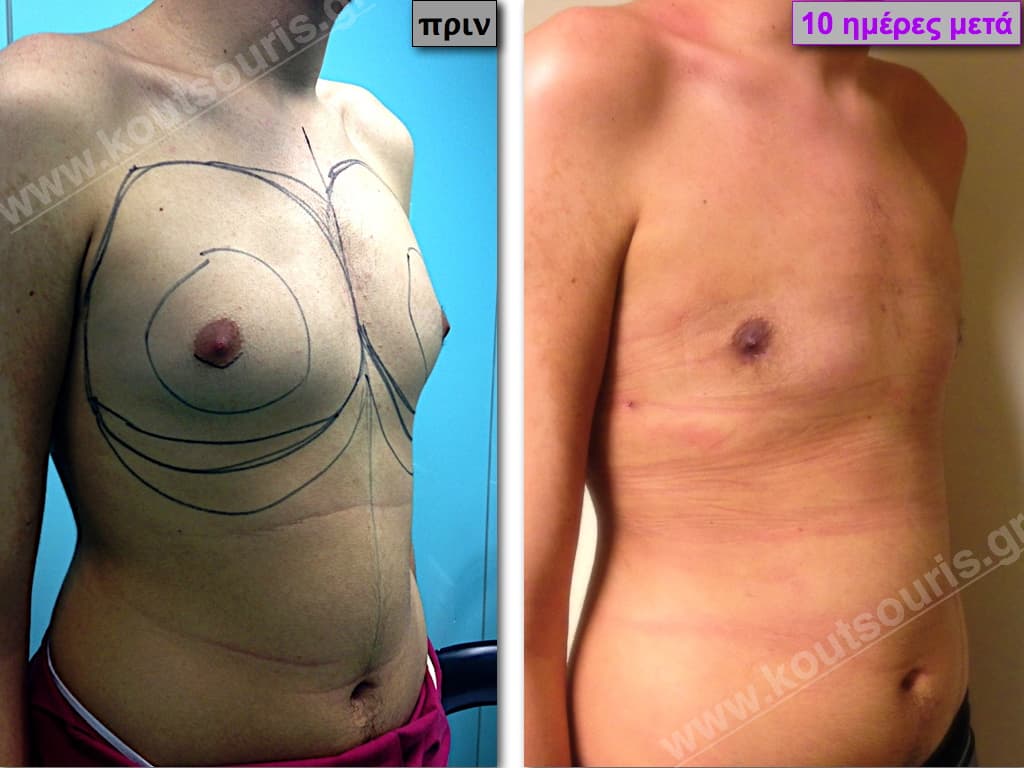
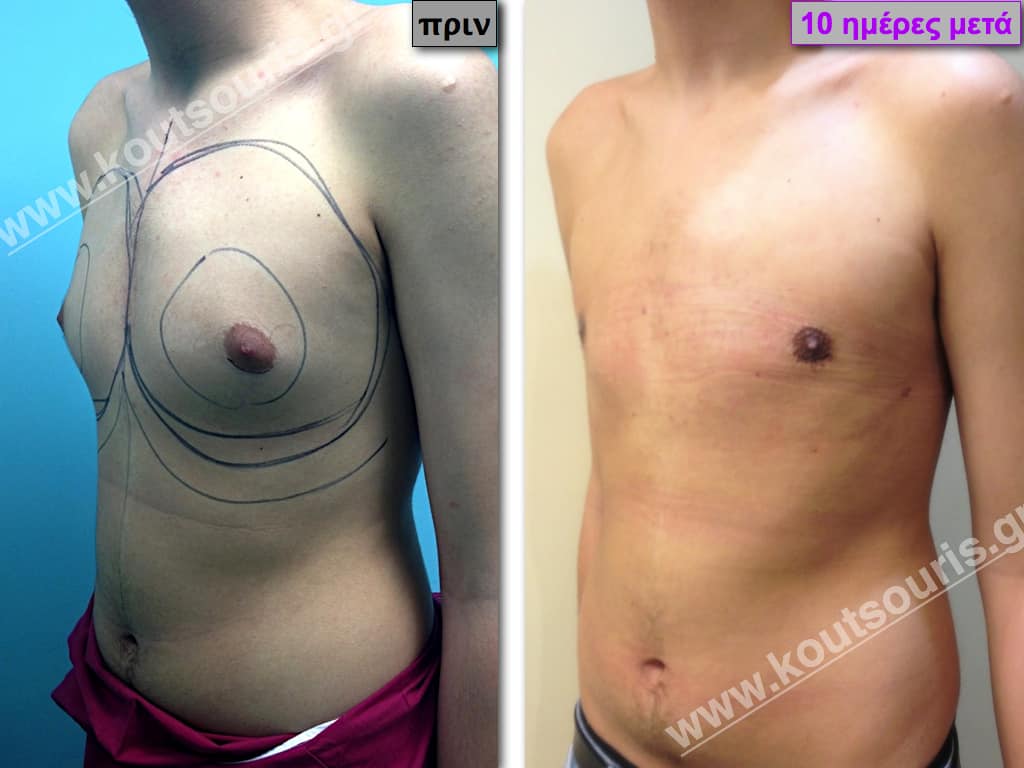
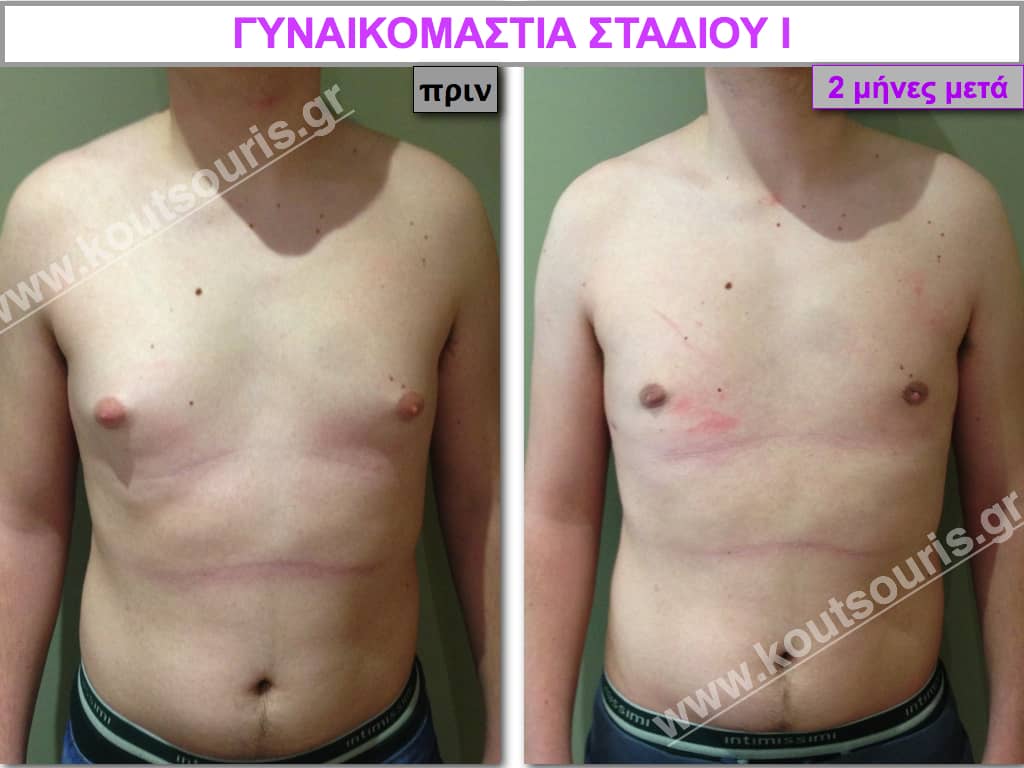
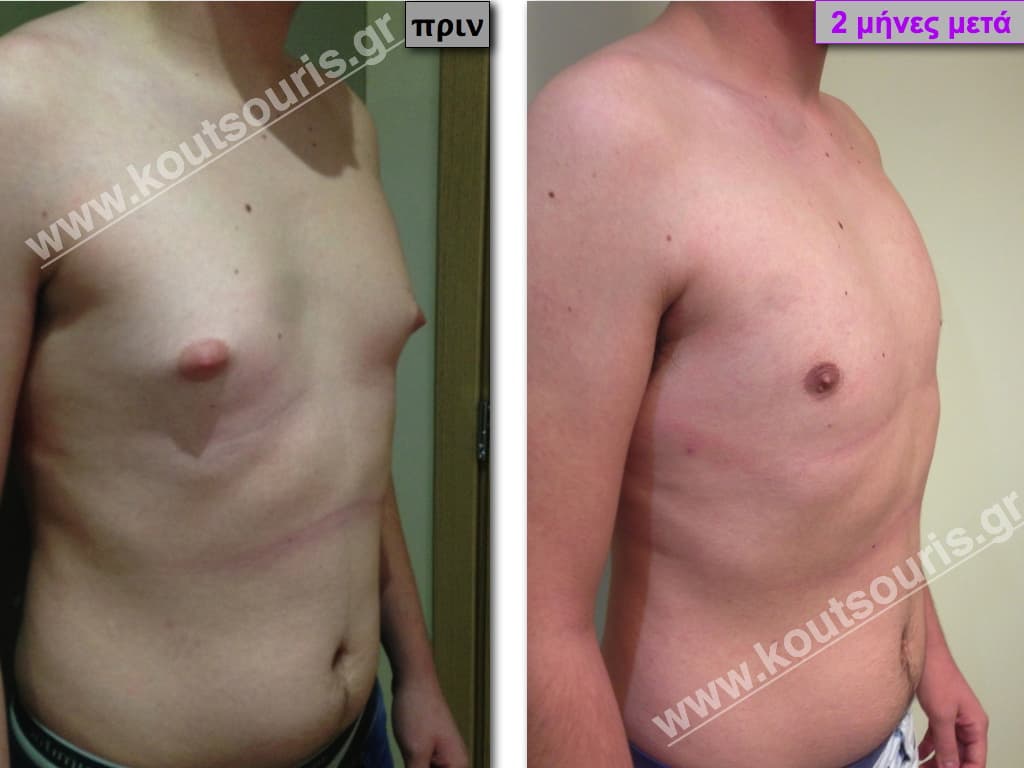
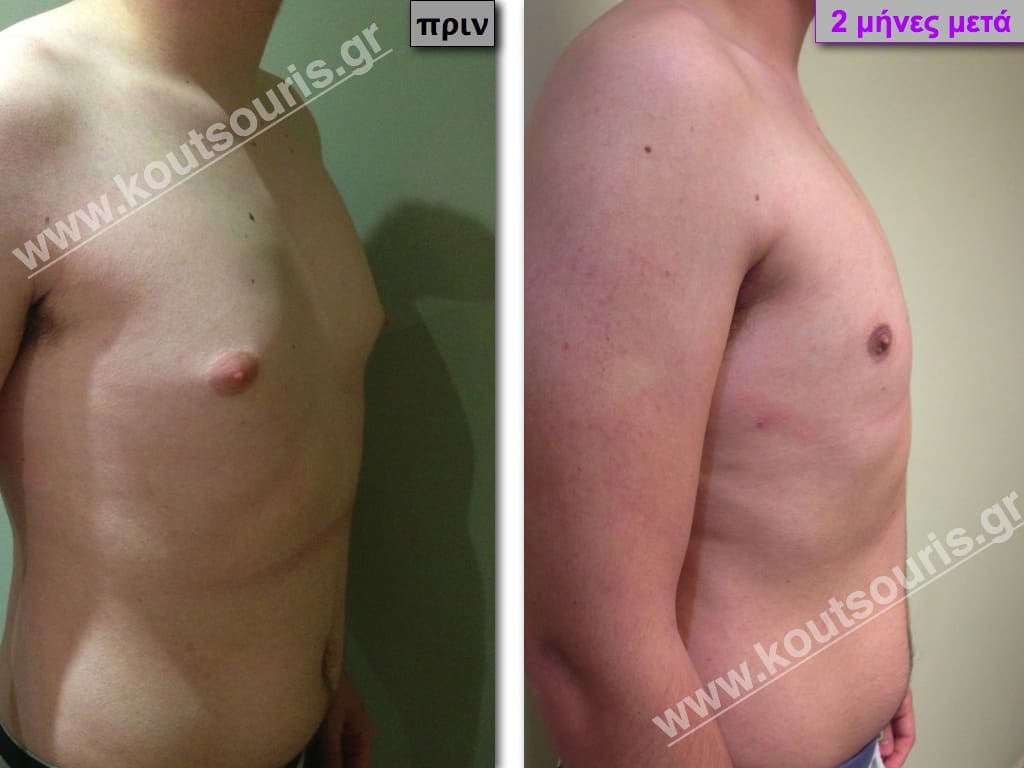
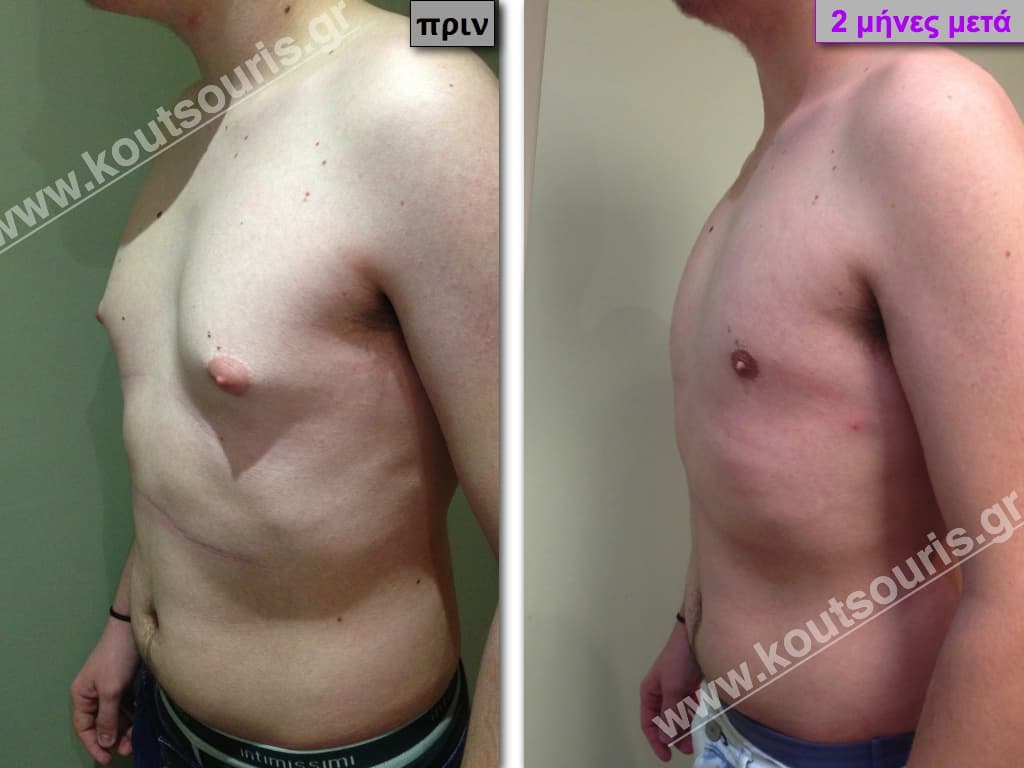
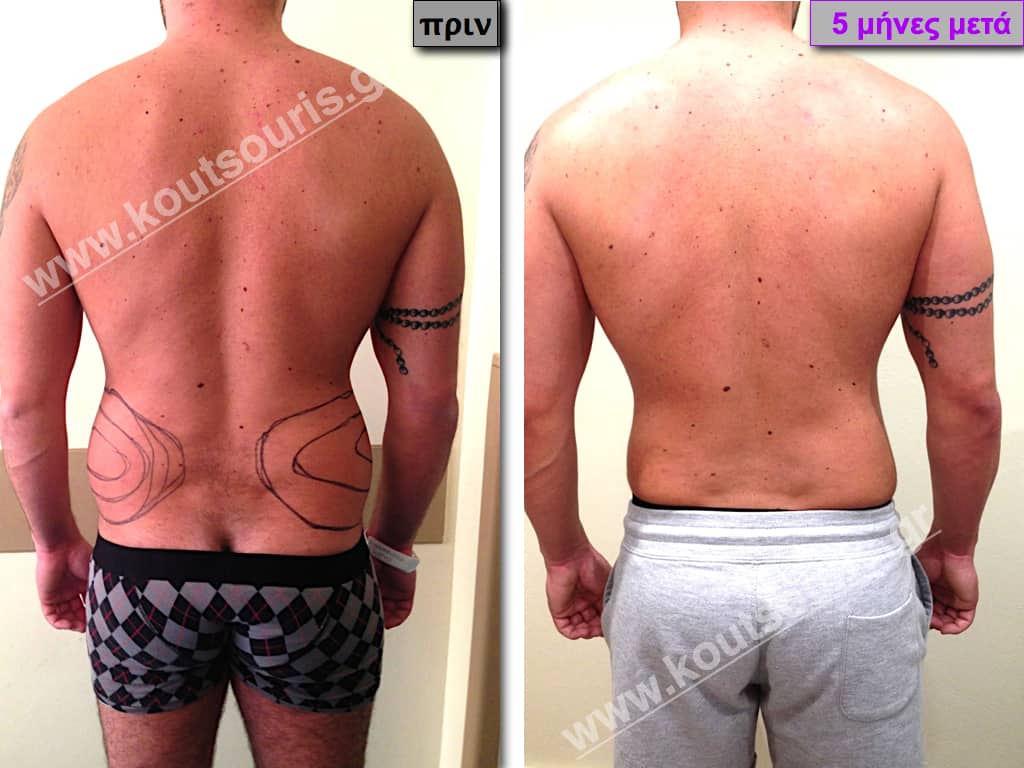
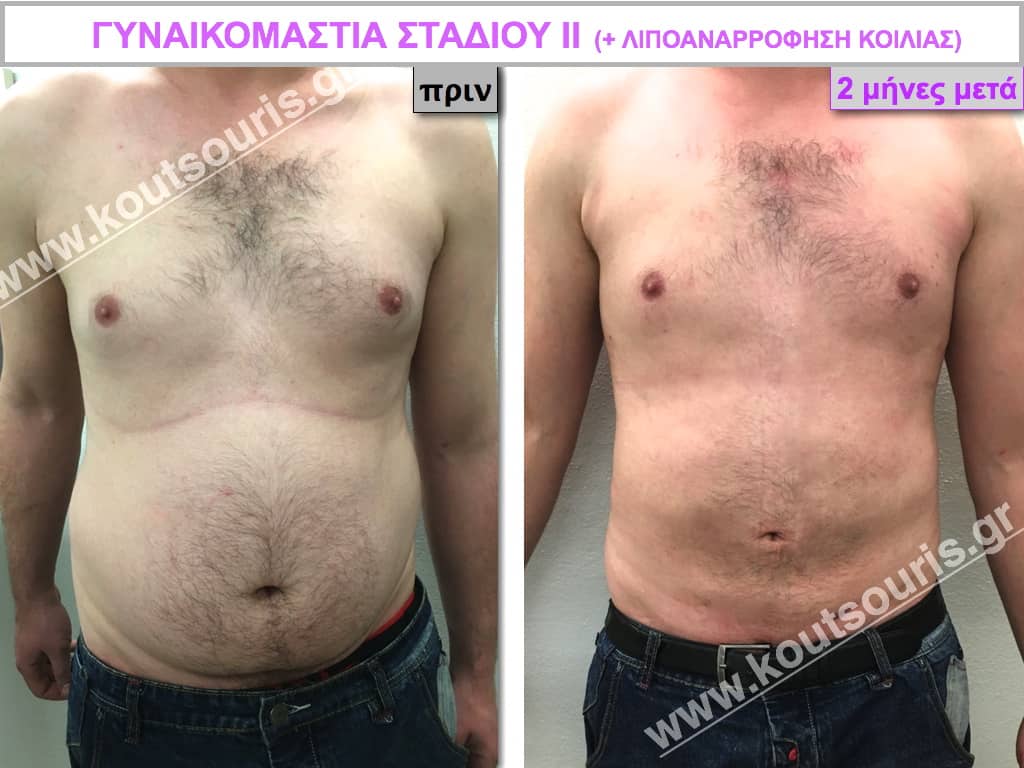
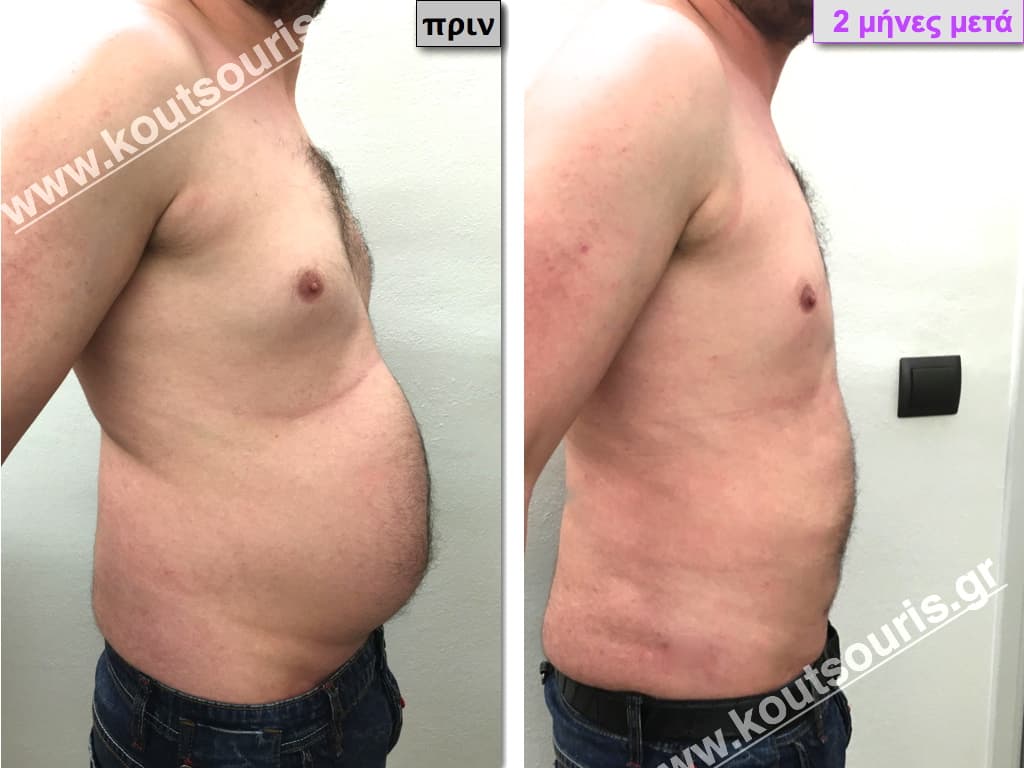
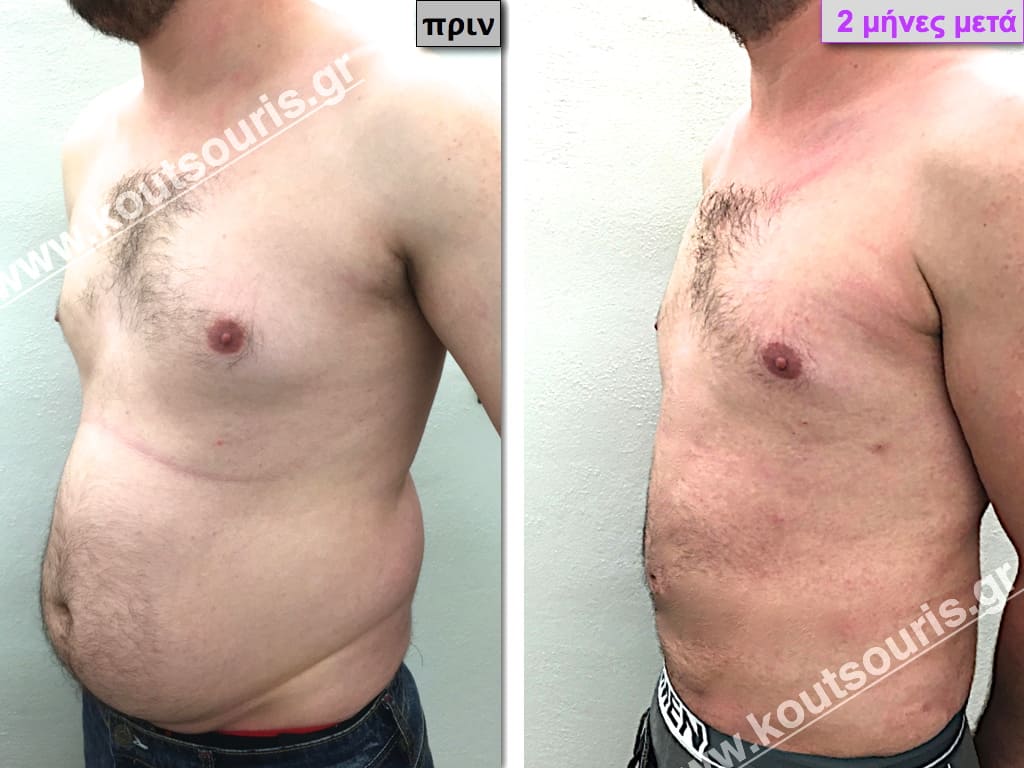
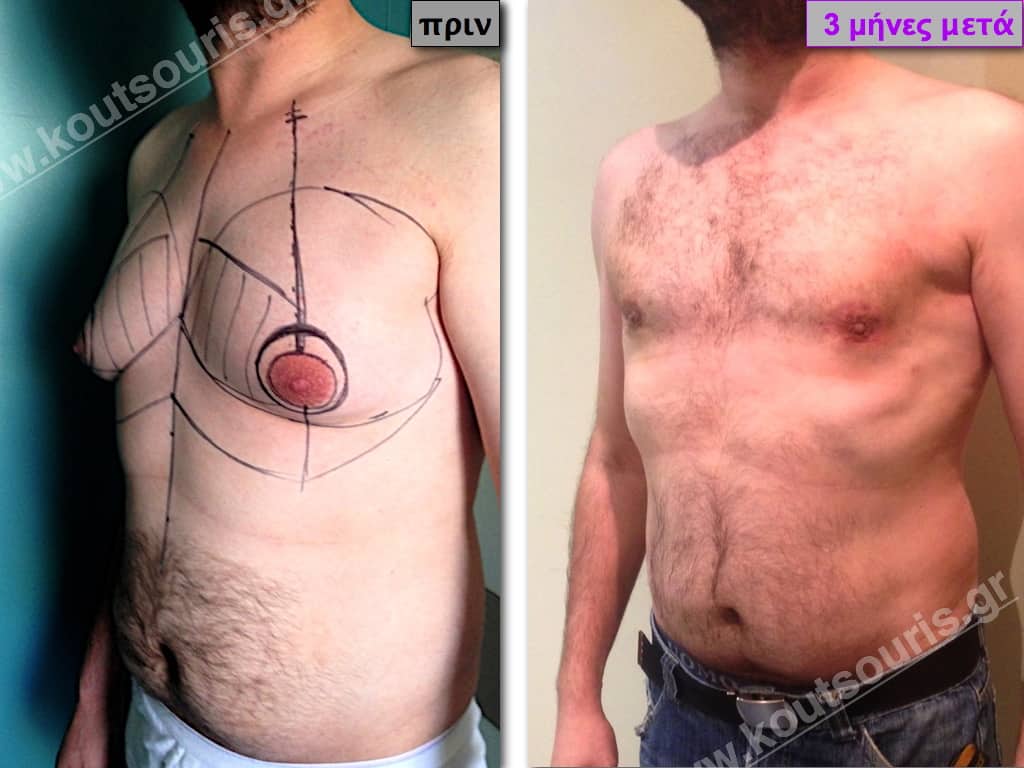
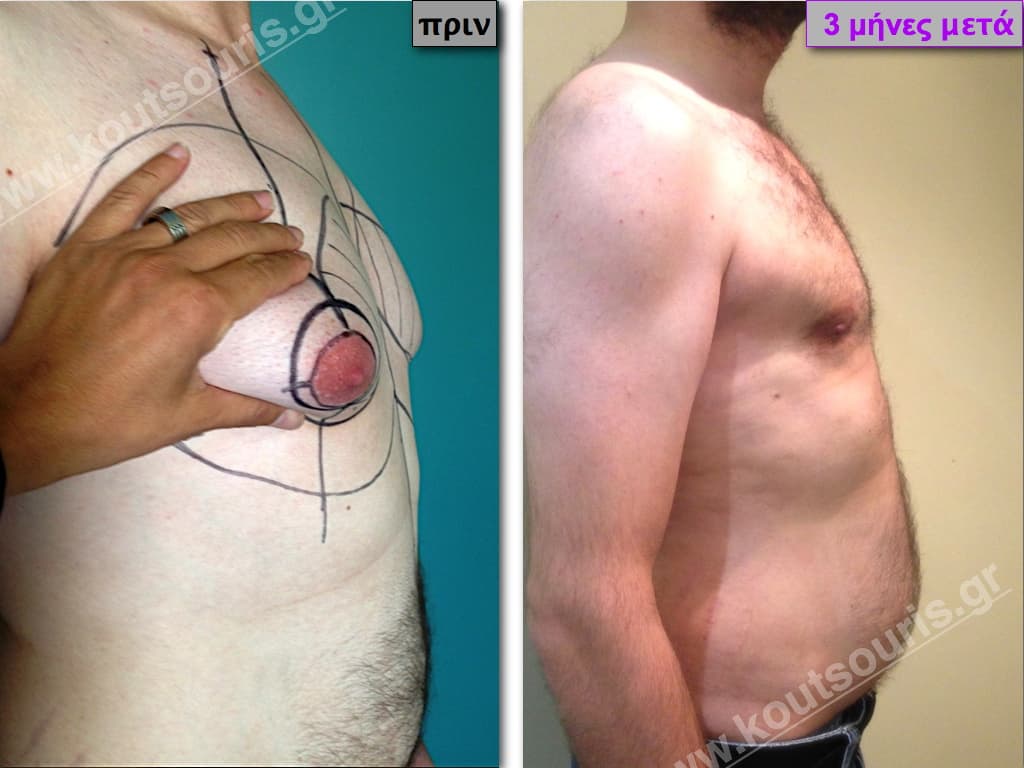
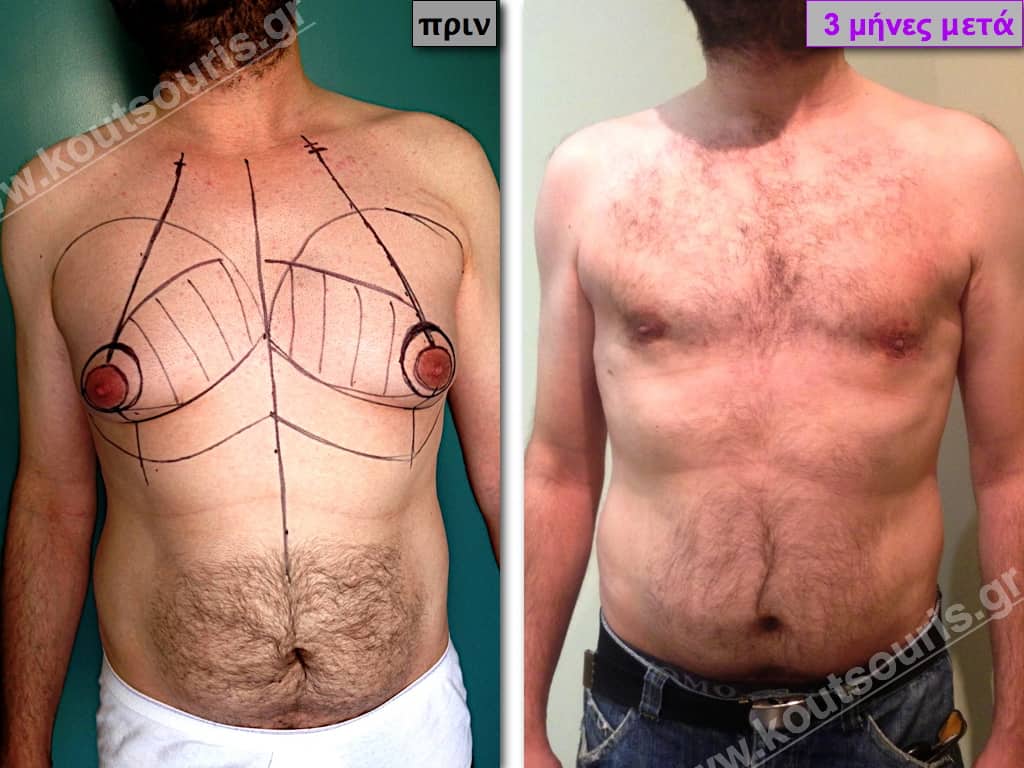
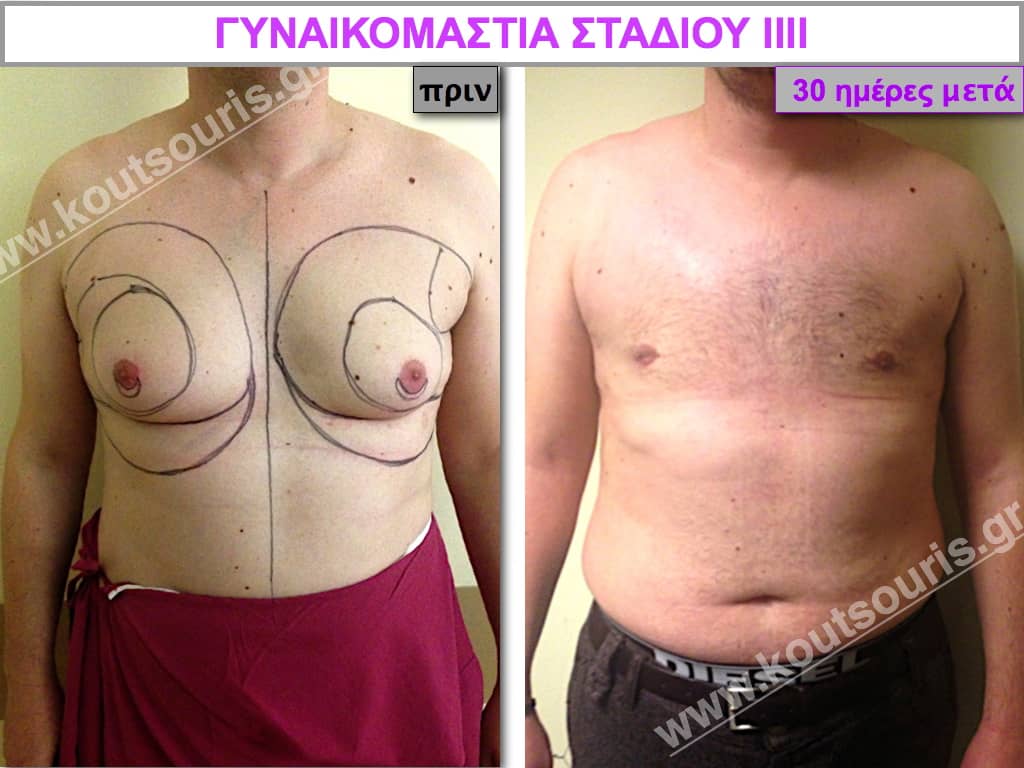
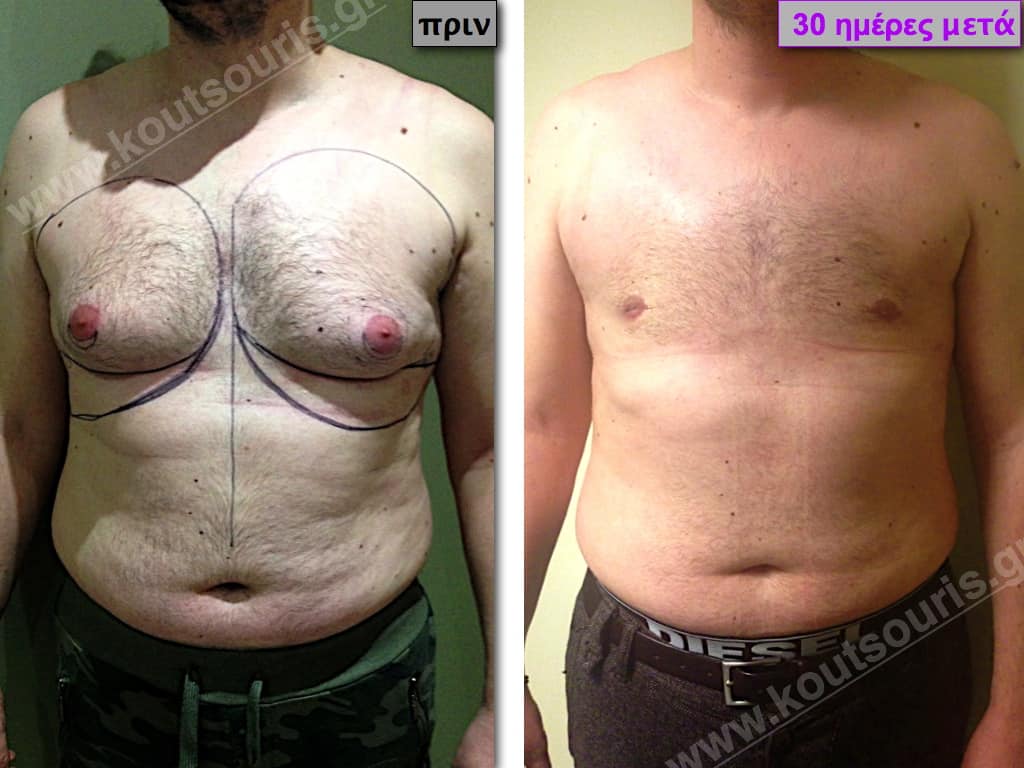
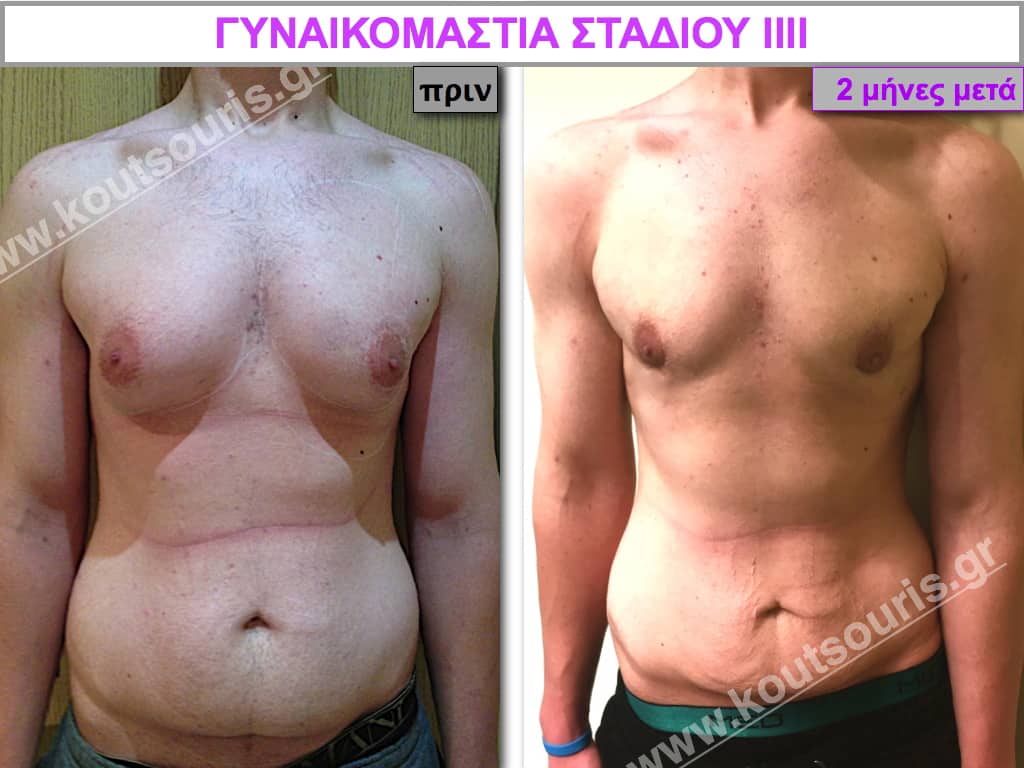
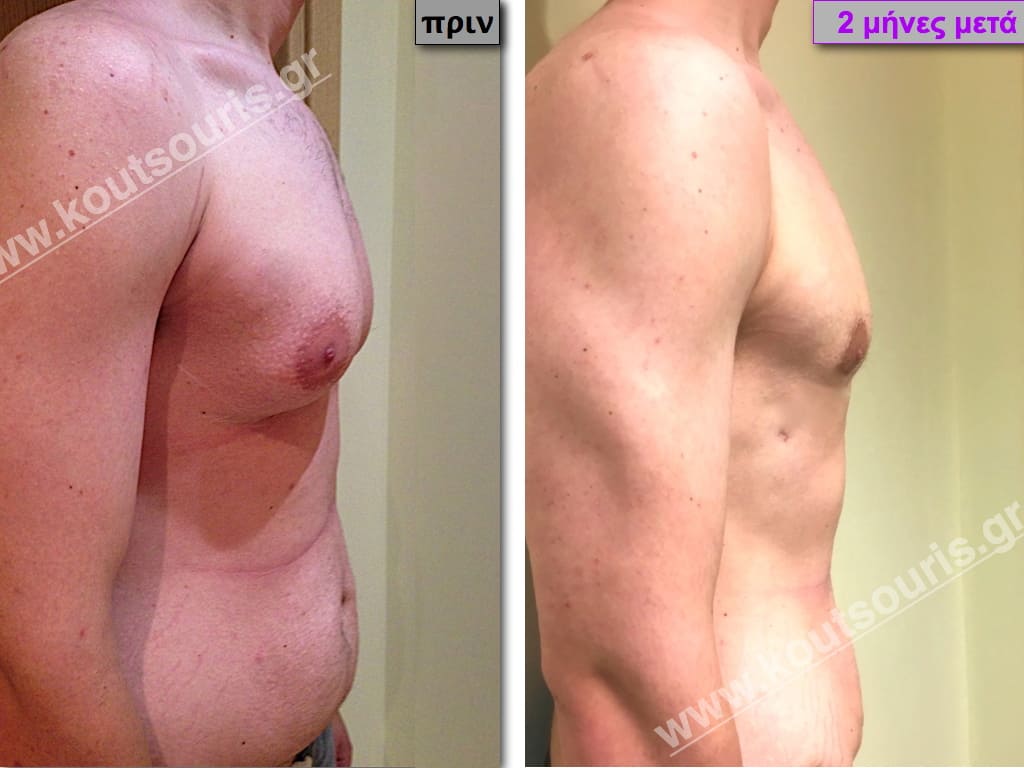
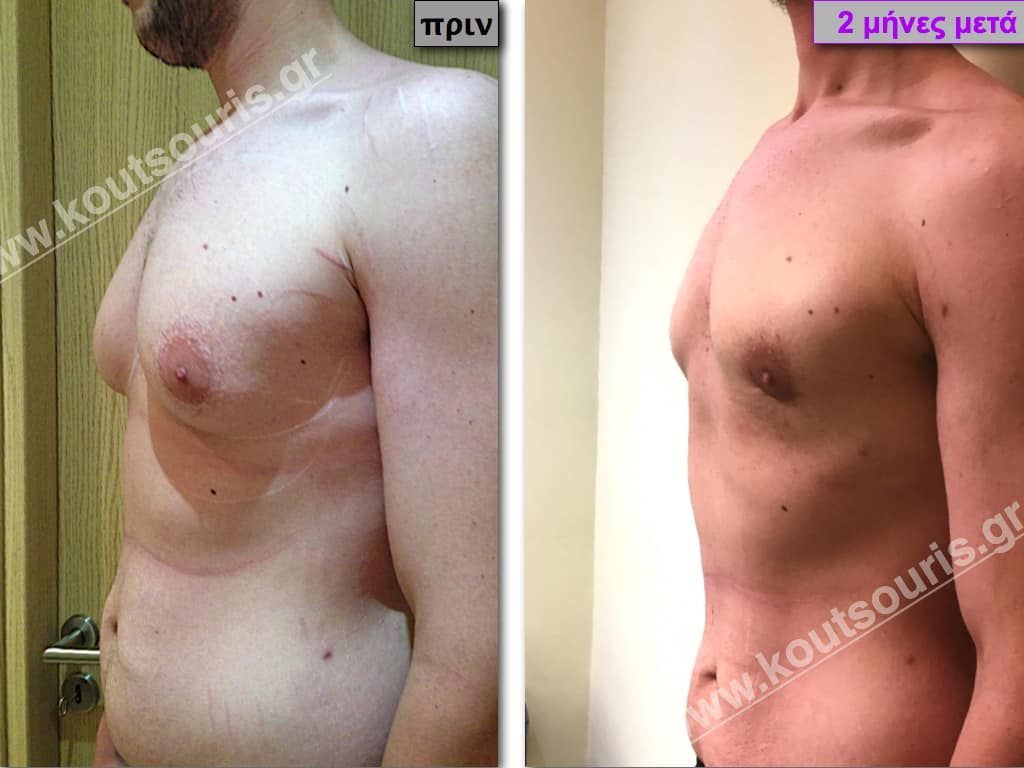
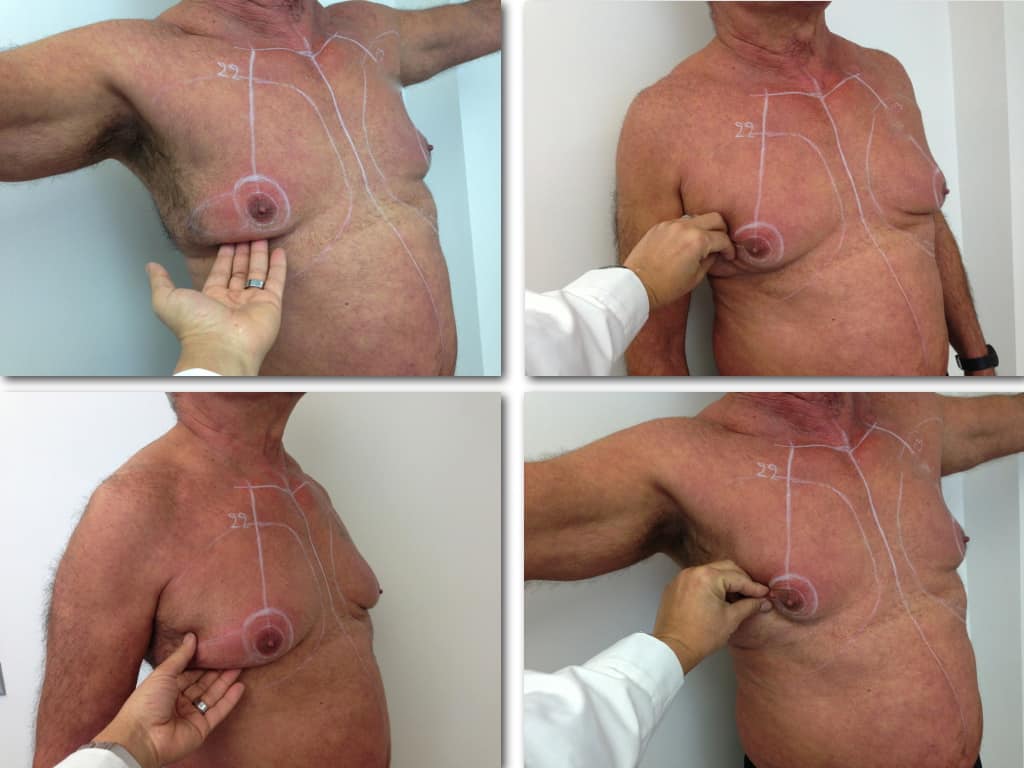
Description of Gynecomastia restorative surgery.
In the following pictures we can observe the Gynecomastia restorative surgery inside the operating room following the contemporary technique of plastic surgery alternating with liposuction-endoscopic surgery-liposuction.
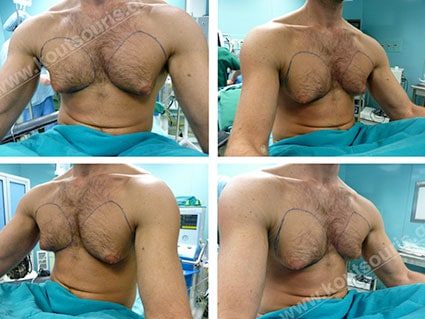
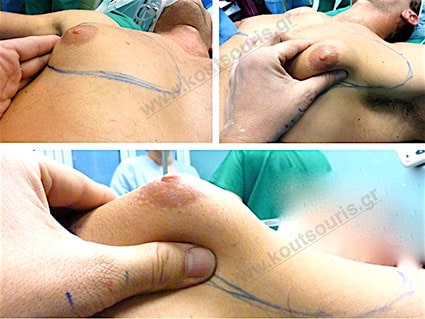
Gland check and estimation of the extent of the problem.
With our hand we palpate the breast tissue and recognize its relationship to the subcutaneous fat in the chest area.
This way, the gland is released from the adjacent tissues.
See how it looks the right breast after liposuction. Endoscopic removal of the right mammary gland and refining of the results with new Liposuction technique.
The left breast has not been restored yet.
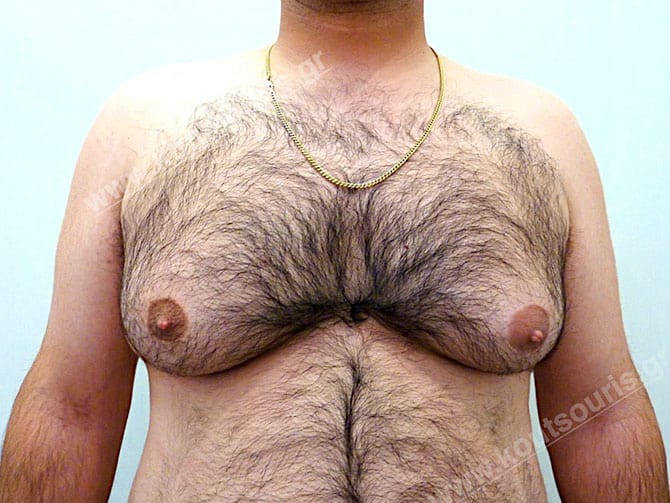
The mammary gland projected in gynecomastia is the main reason of its appearance. It is a whitish, solid, hard gland with fiber elements, which looks like a “rubber” and it can be only surgically removed.
The above photo depicts the right and left mammary gland after surgical resection using surgical endoscopes.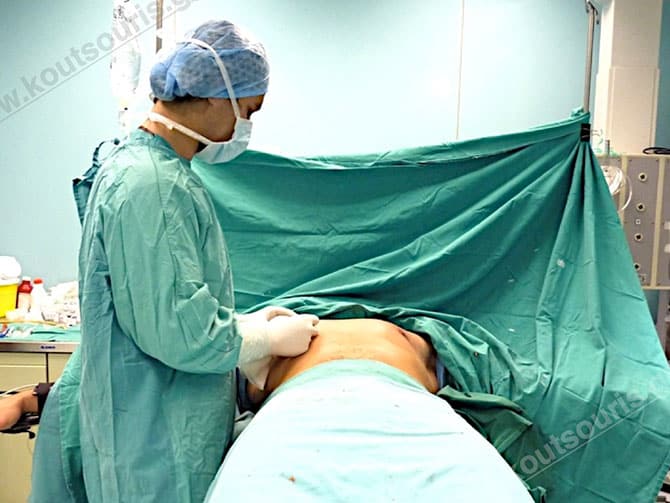
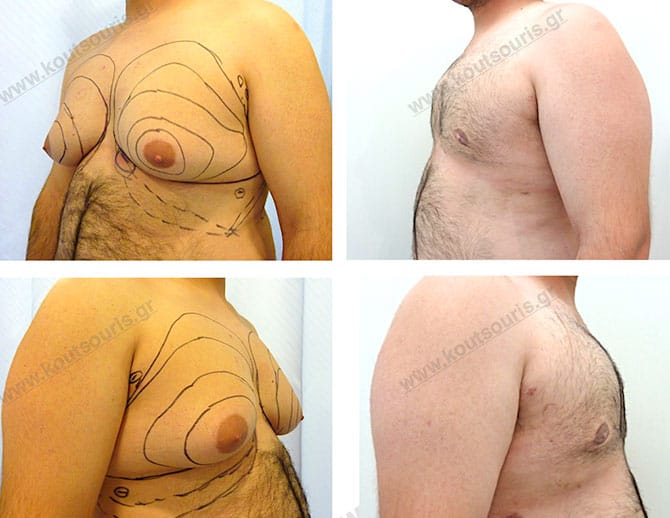
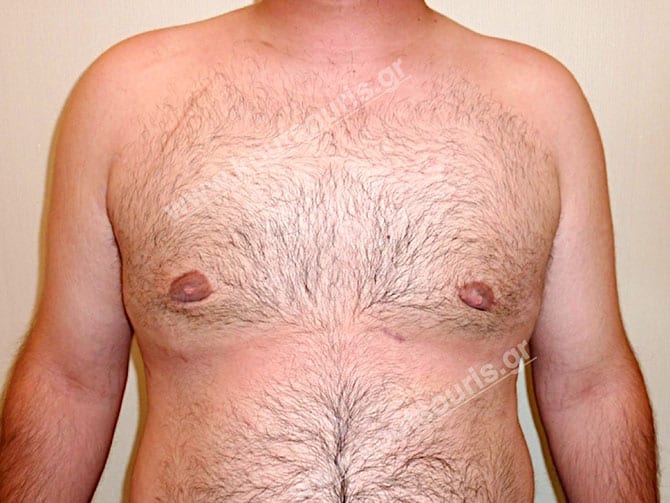
How is the breast looking after surgery?
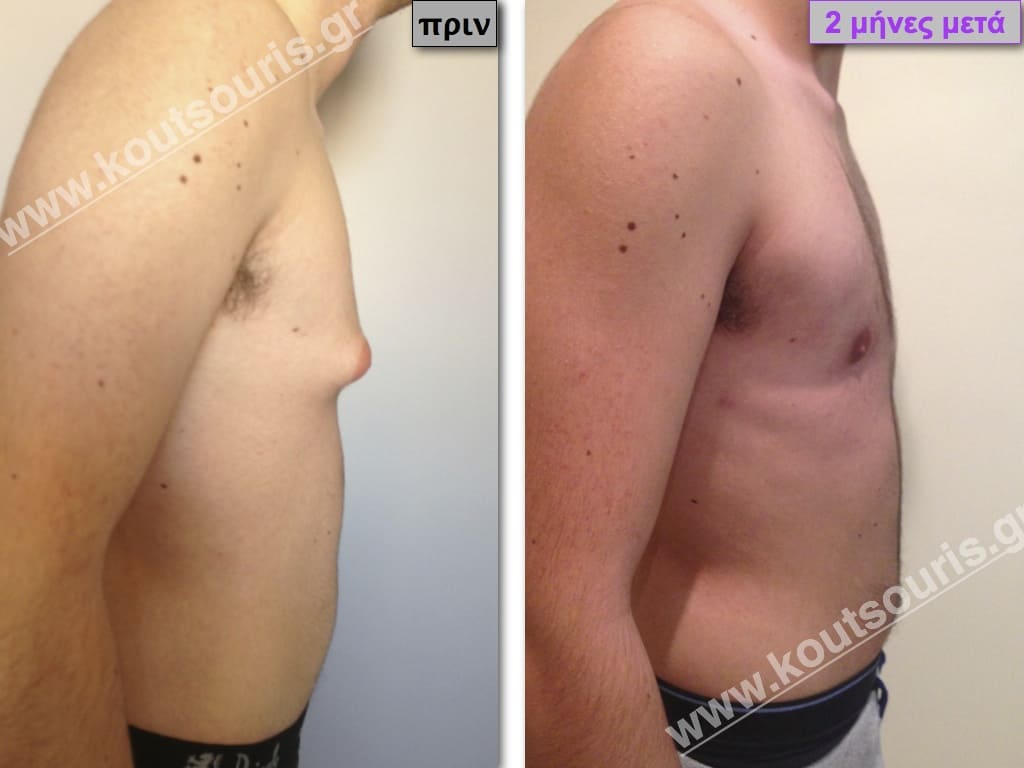
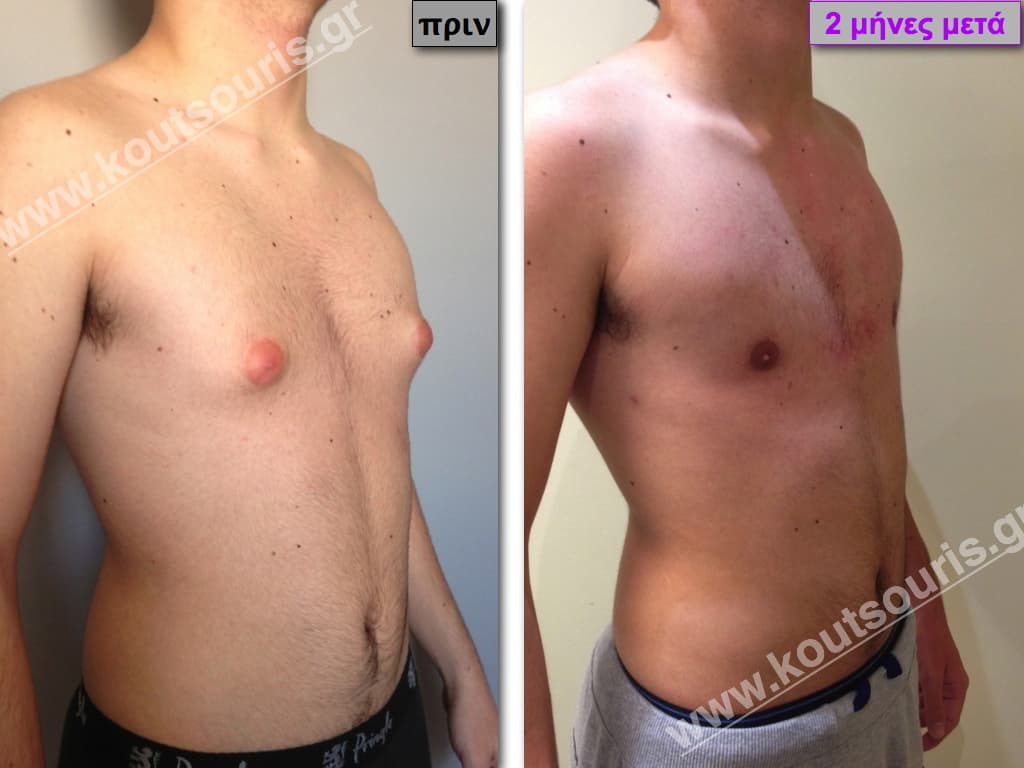
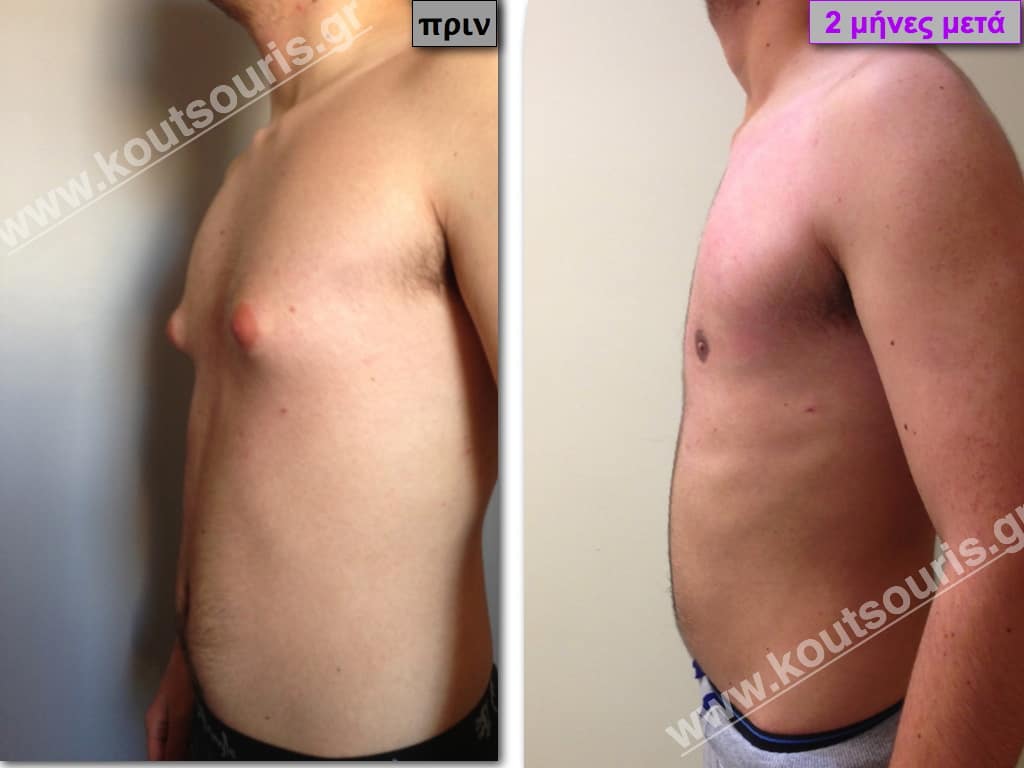
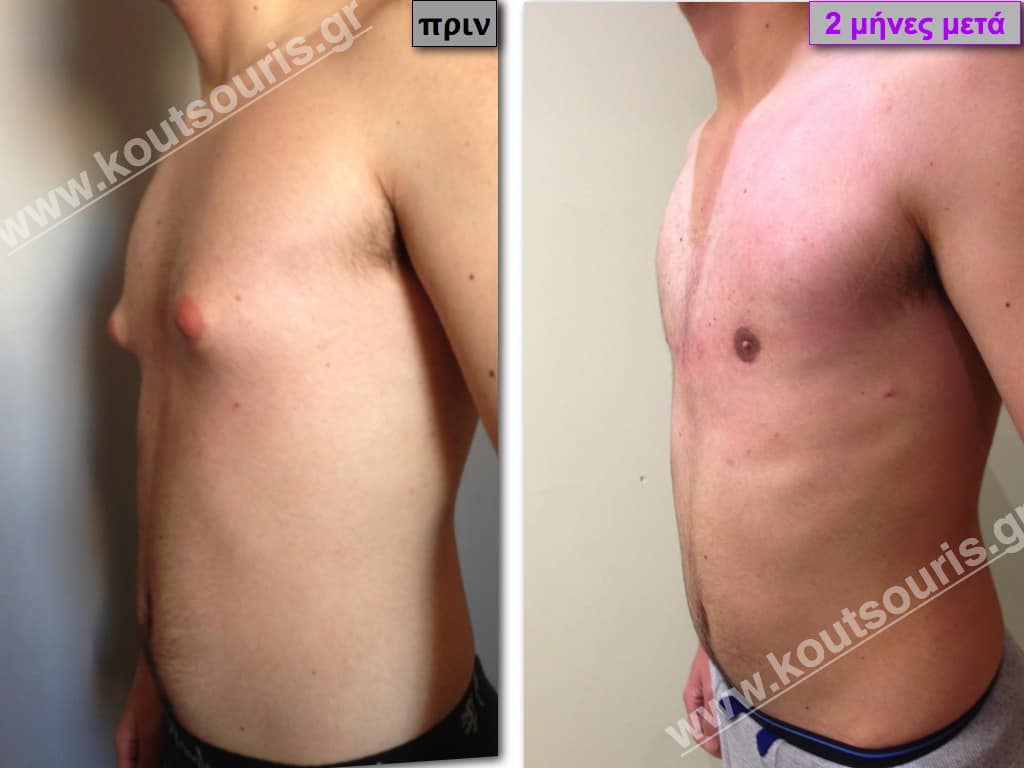
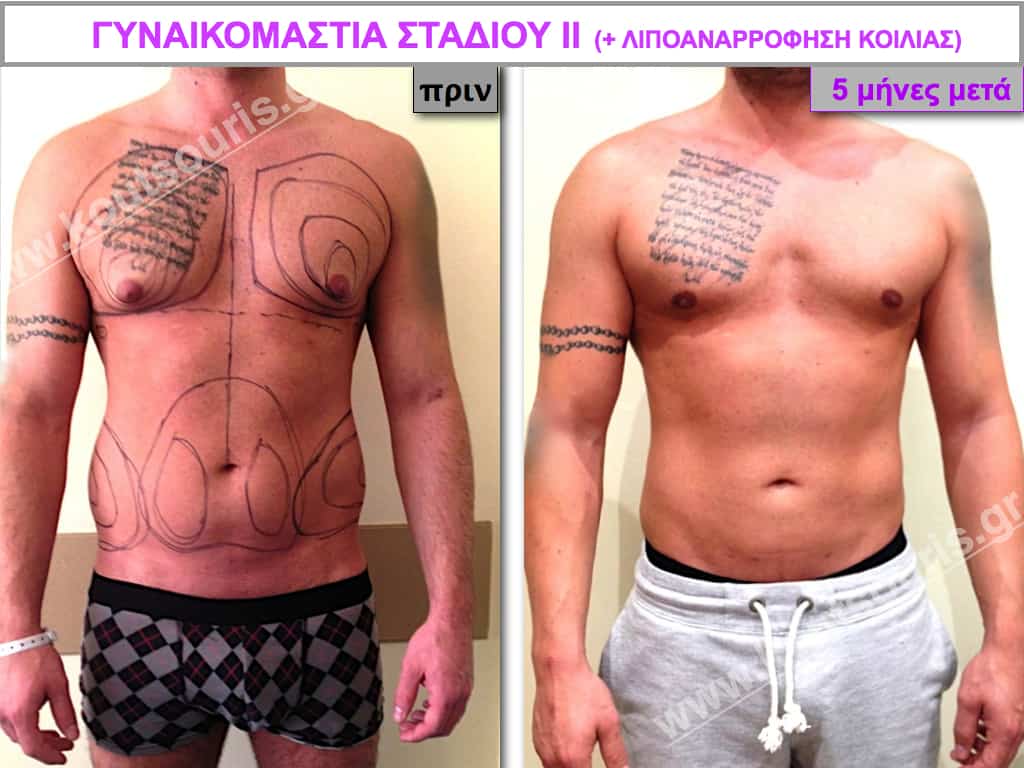
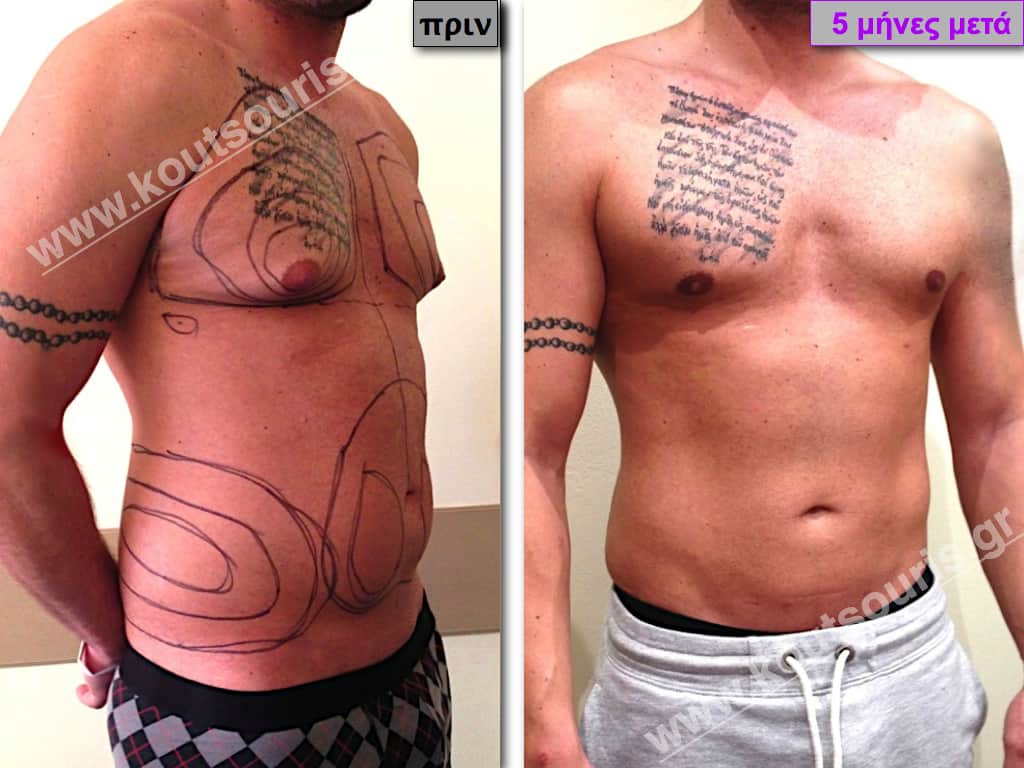
In most cases of gynecomastia recovery, there are two incisions remaining on the skin after surgery:
- a very small almost invisible incision of 3-4 millimeters length in the side of chest close to the ipsilateral axilla due to liposuction and
- an incision of 3-4 cm length in the lower limit of each nipple , which is not easily recognized and it is totally camouflaged due to its anatomical position.
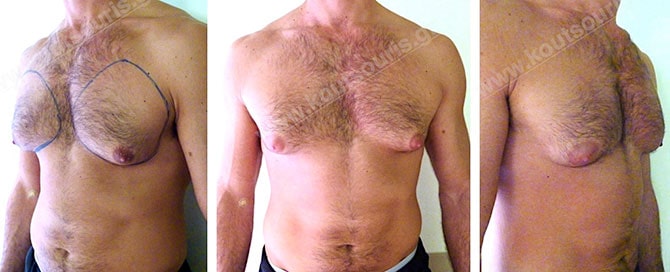
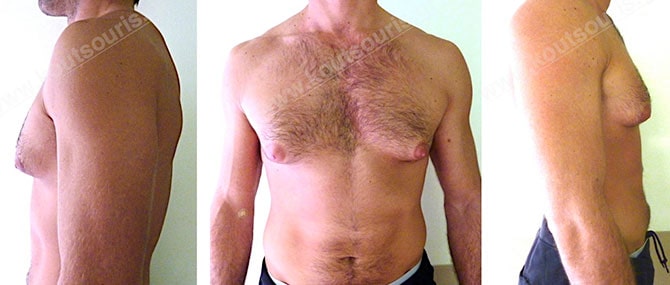
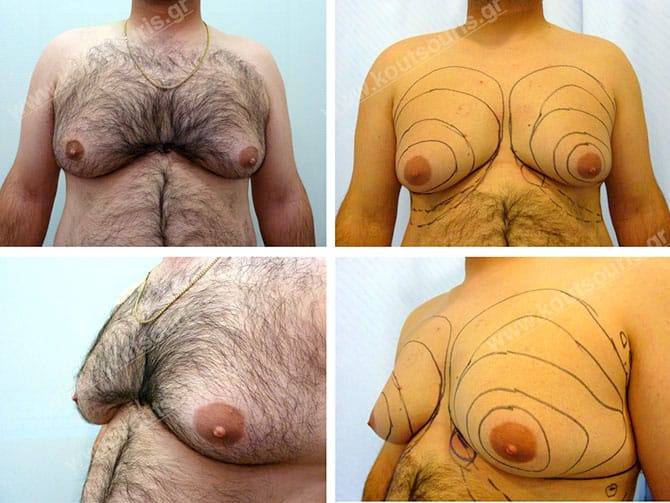
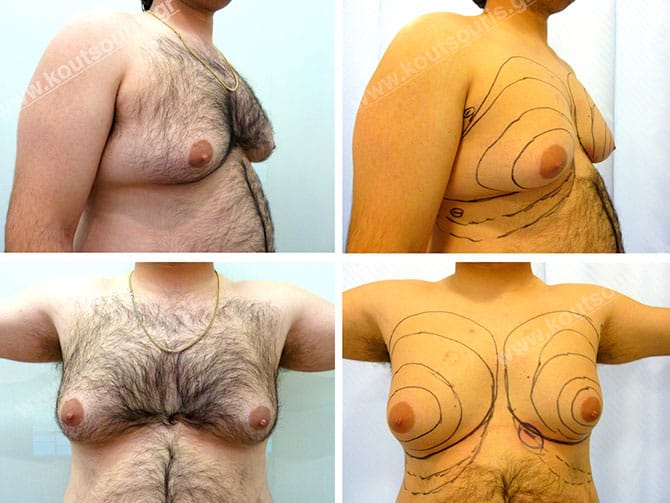
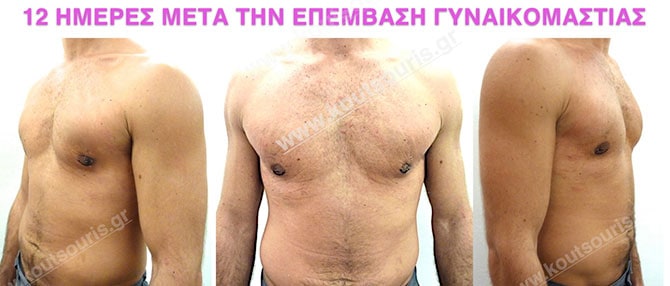
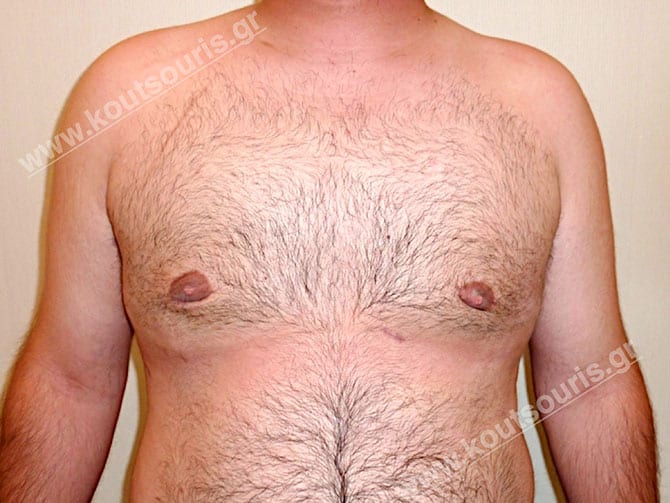
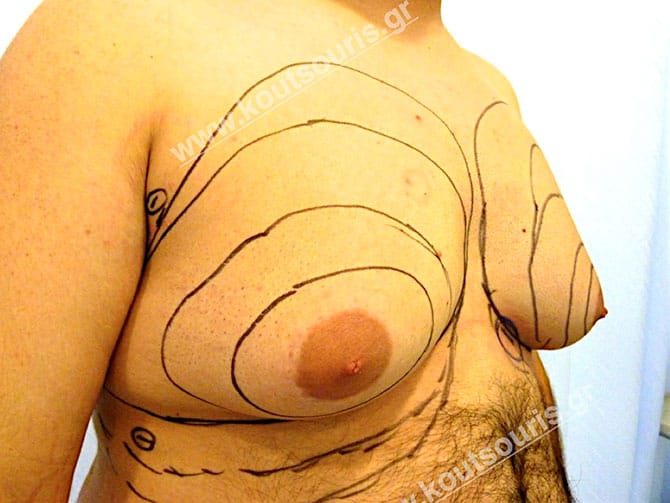
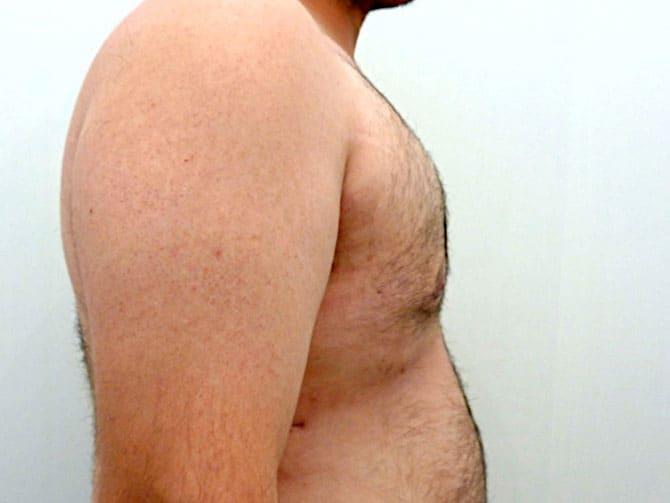
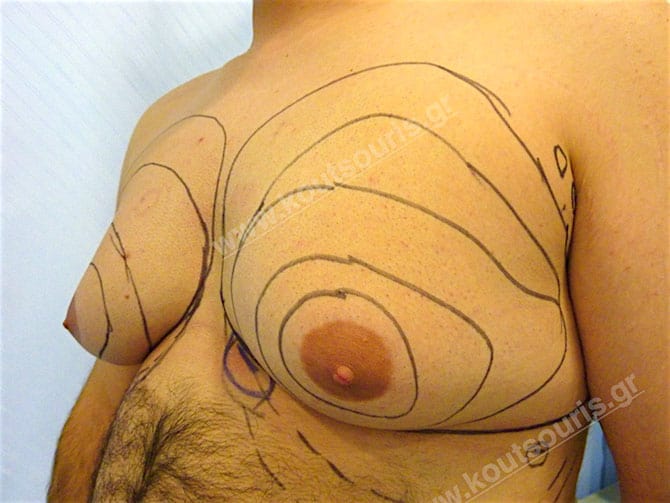
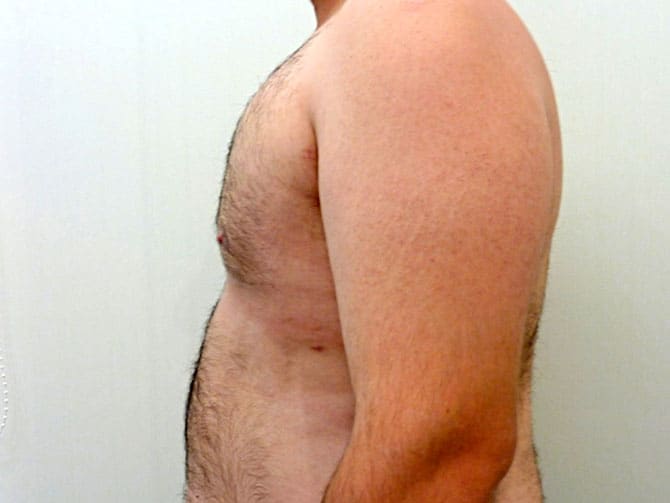
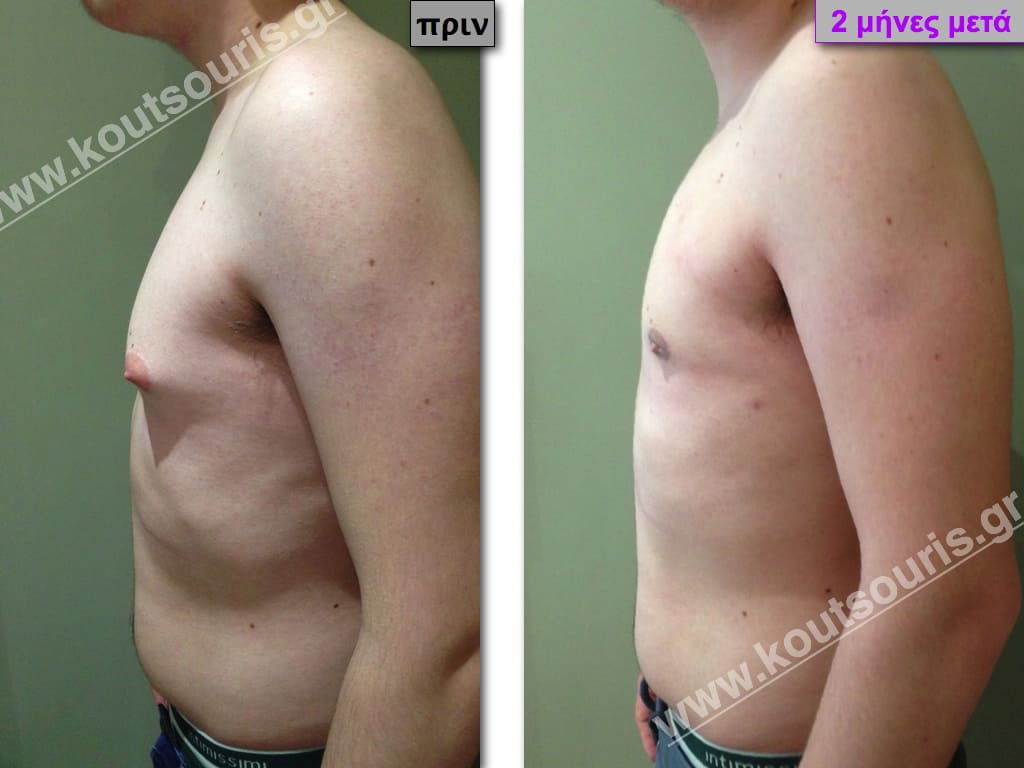
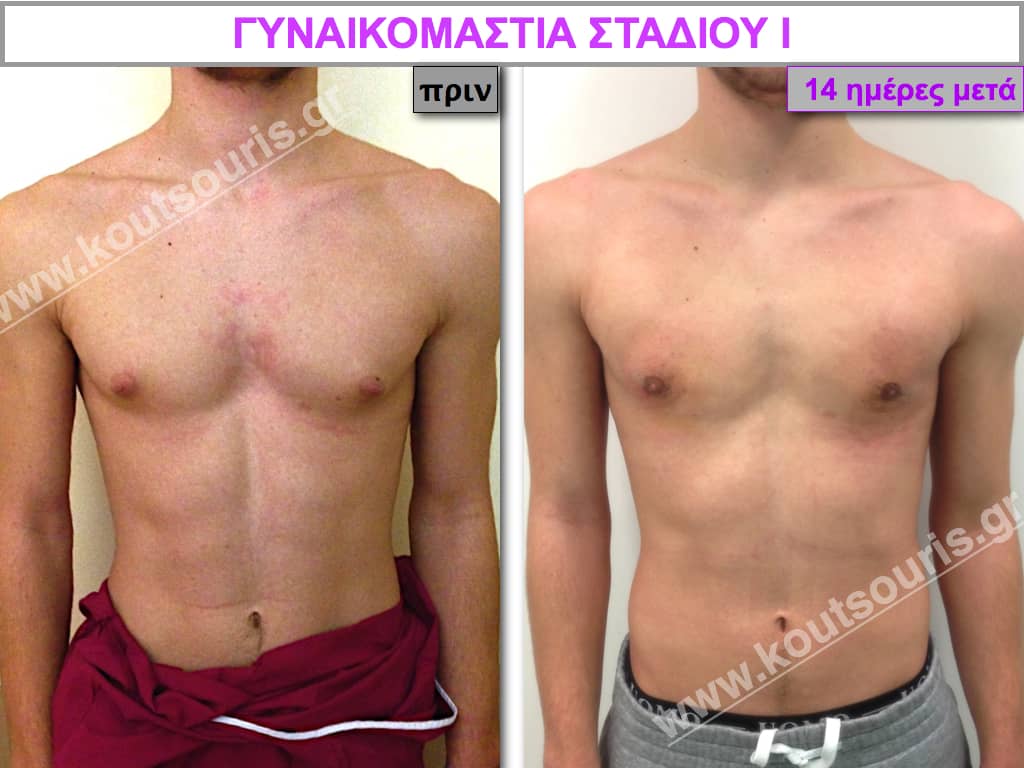
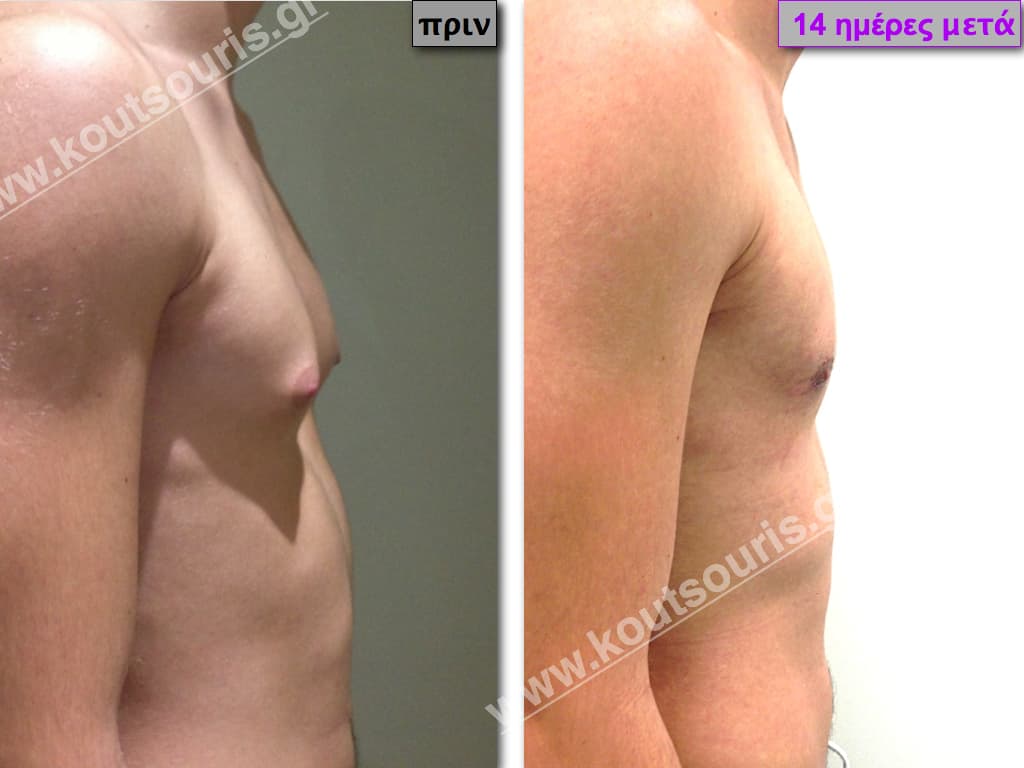
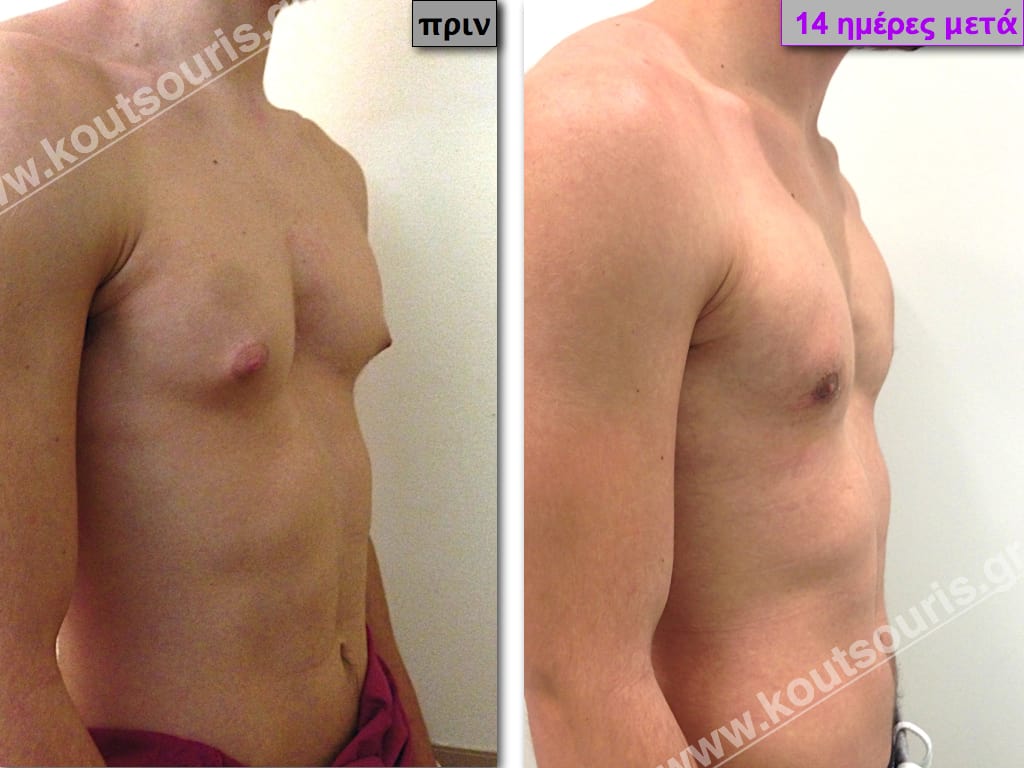
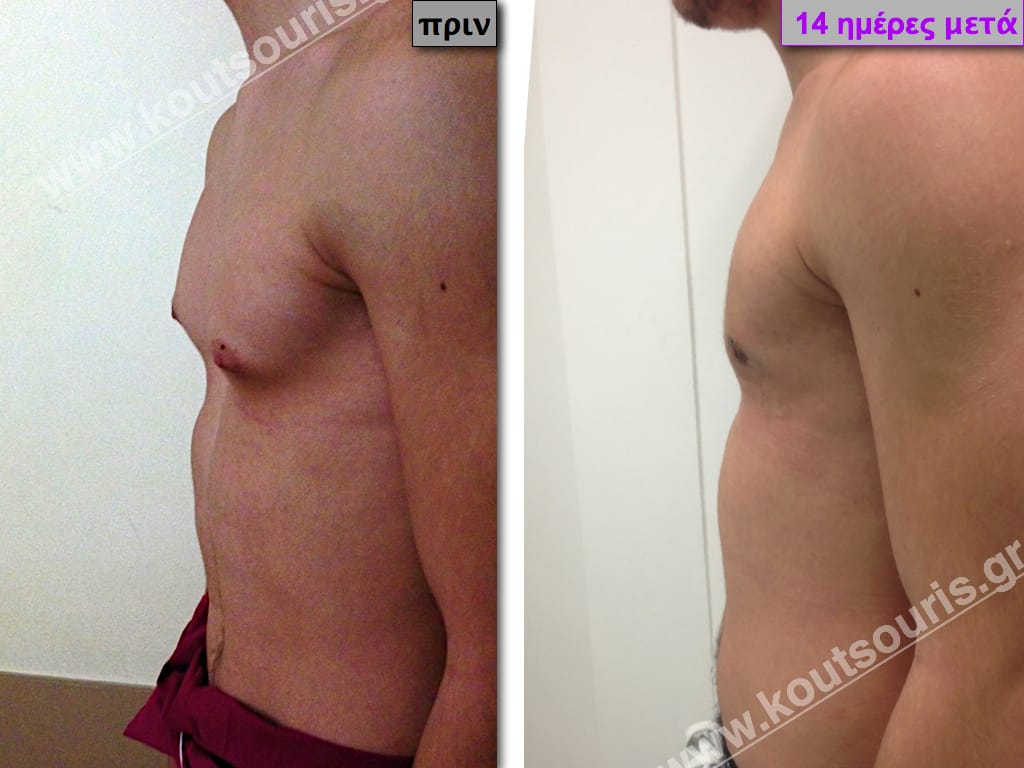
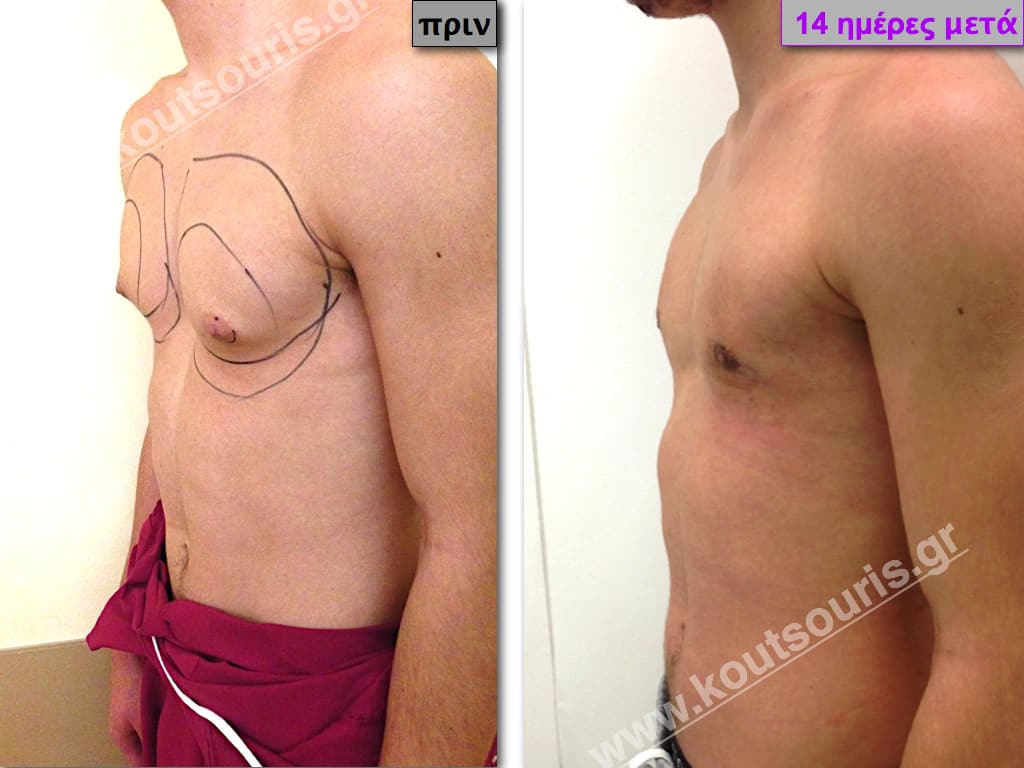
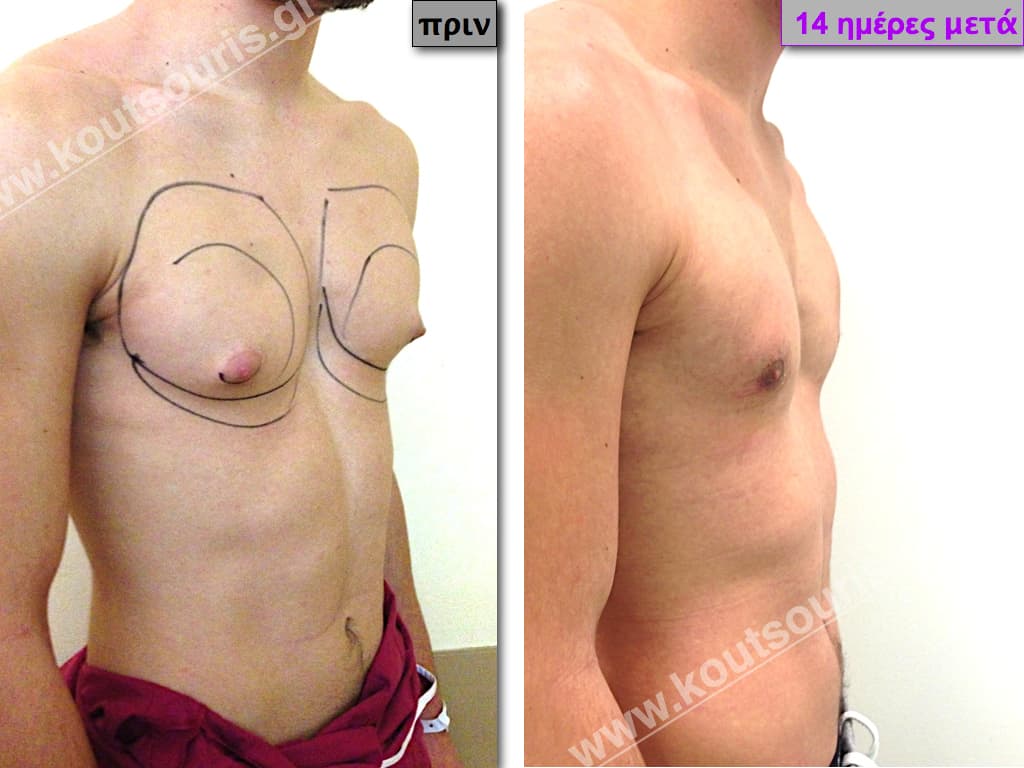
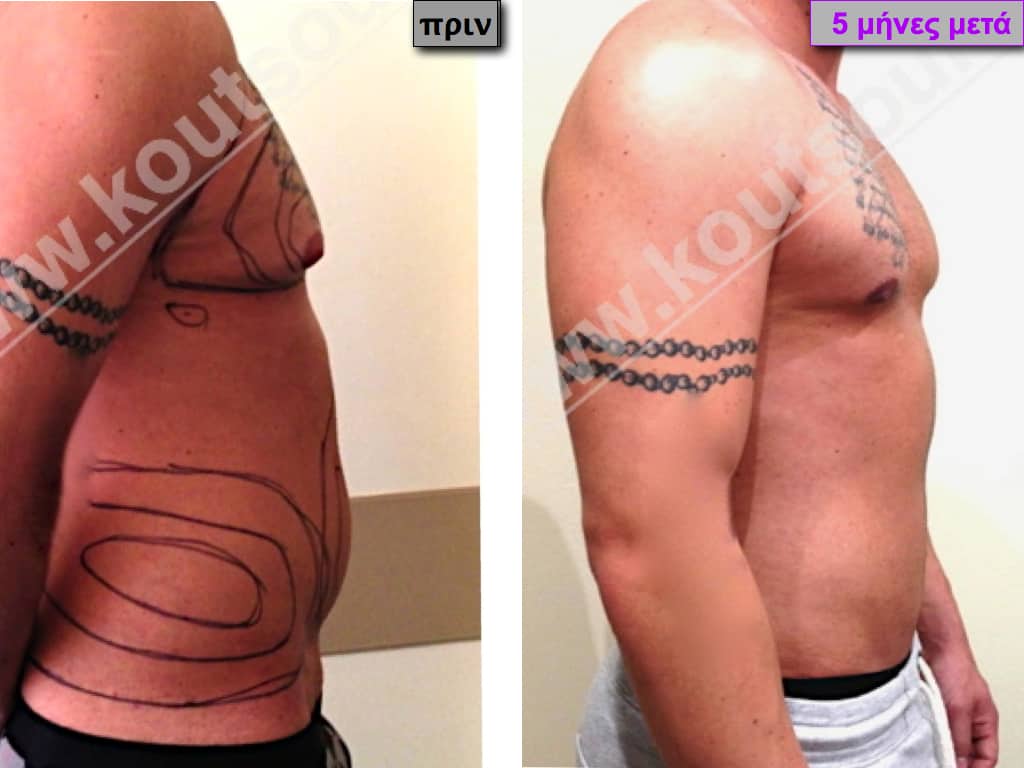
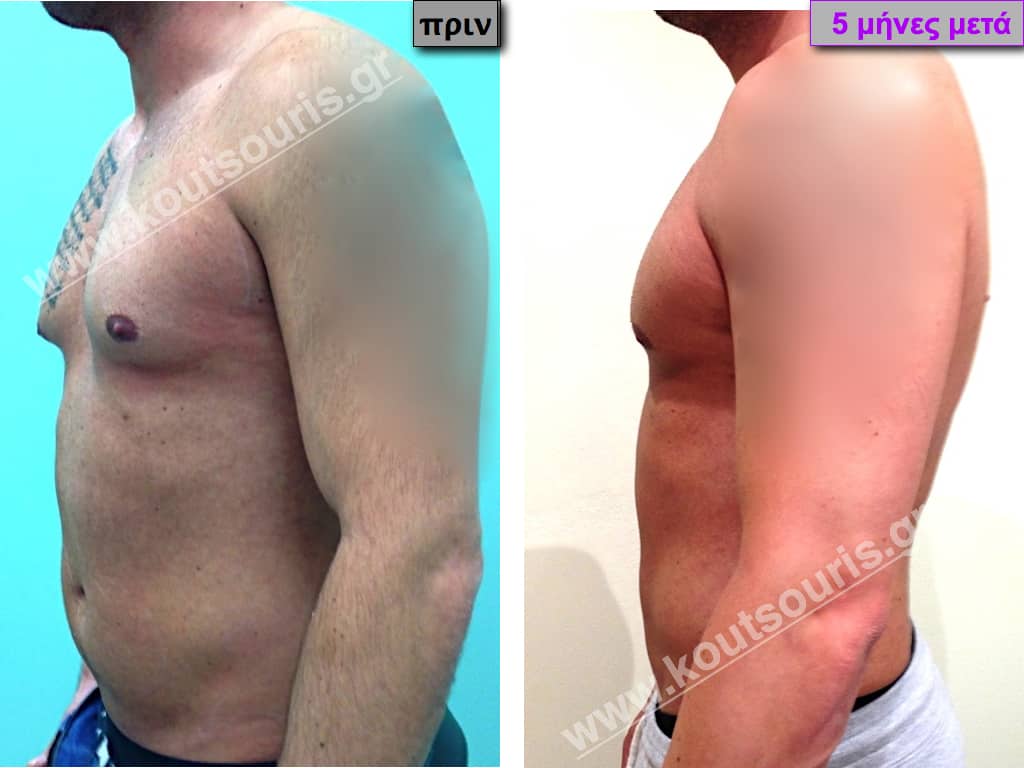
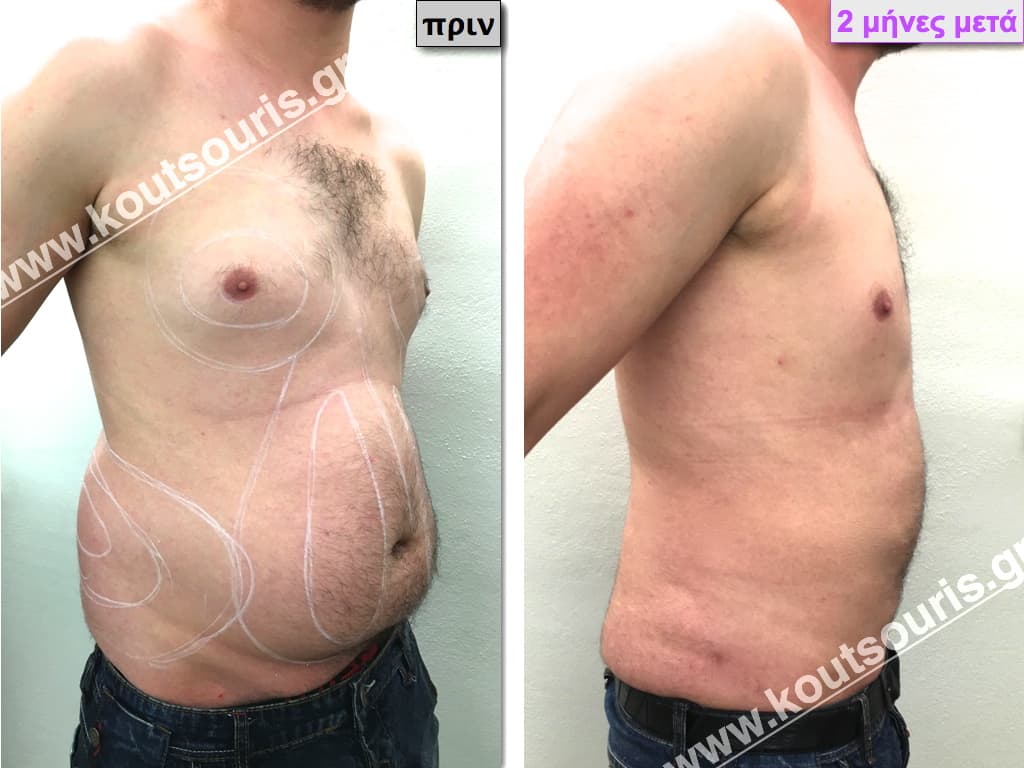
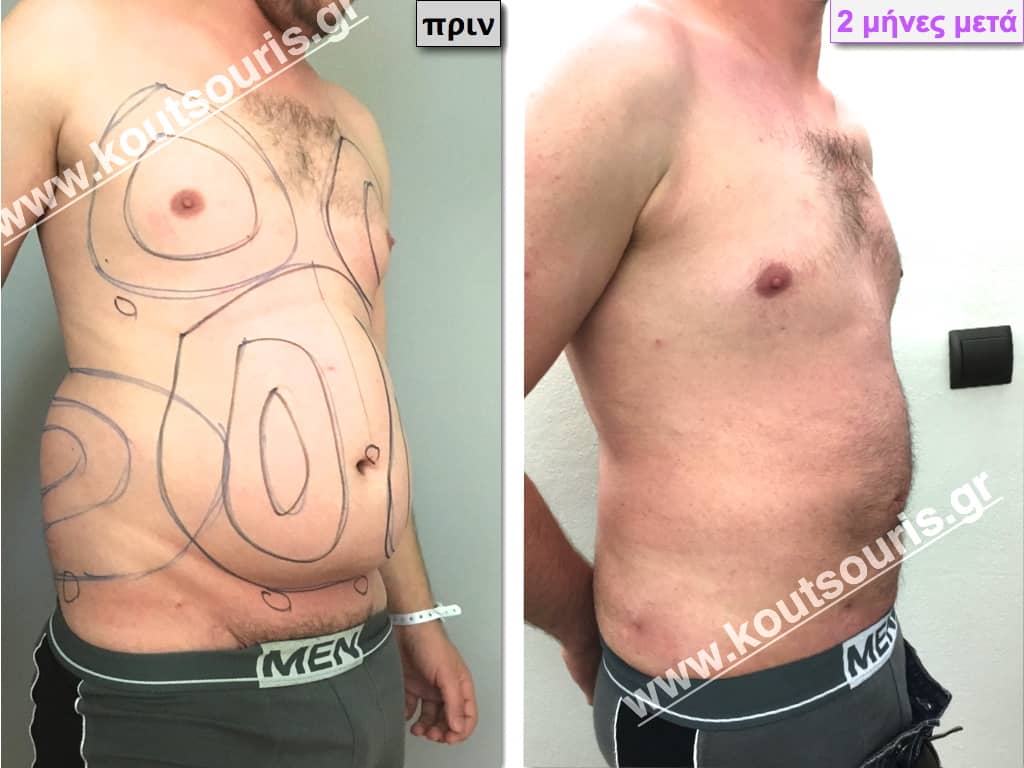
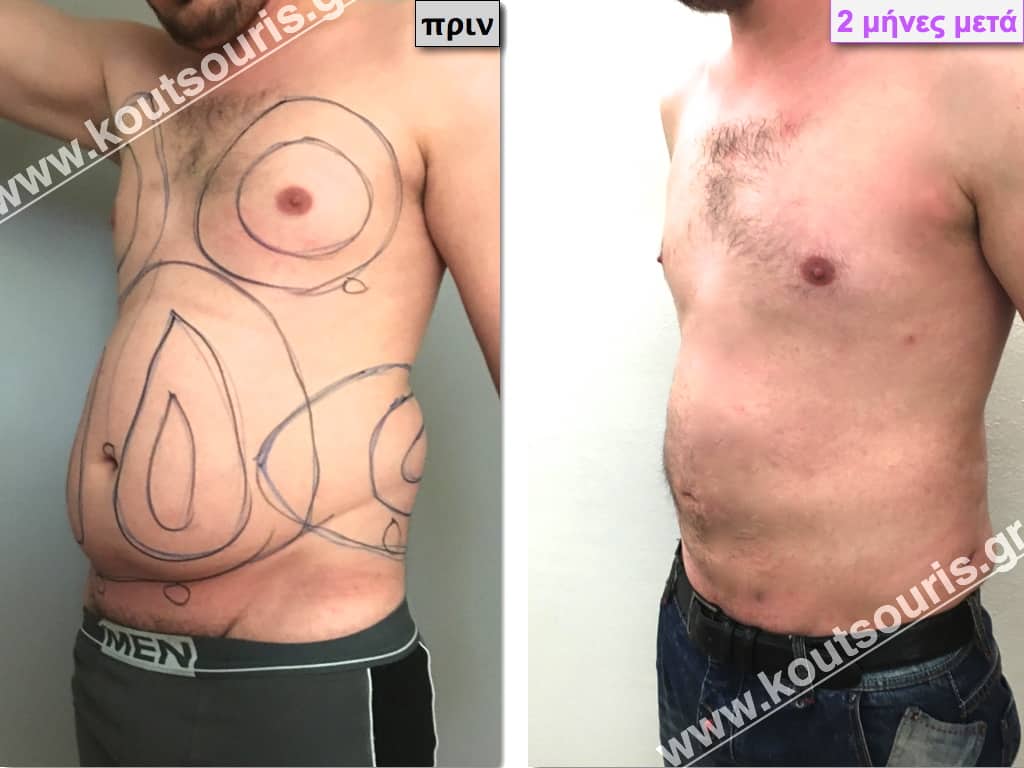
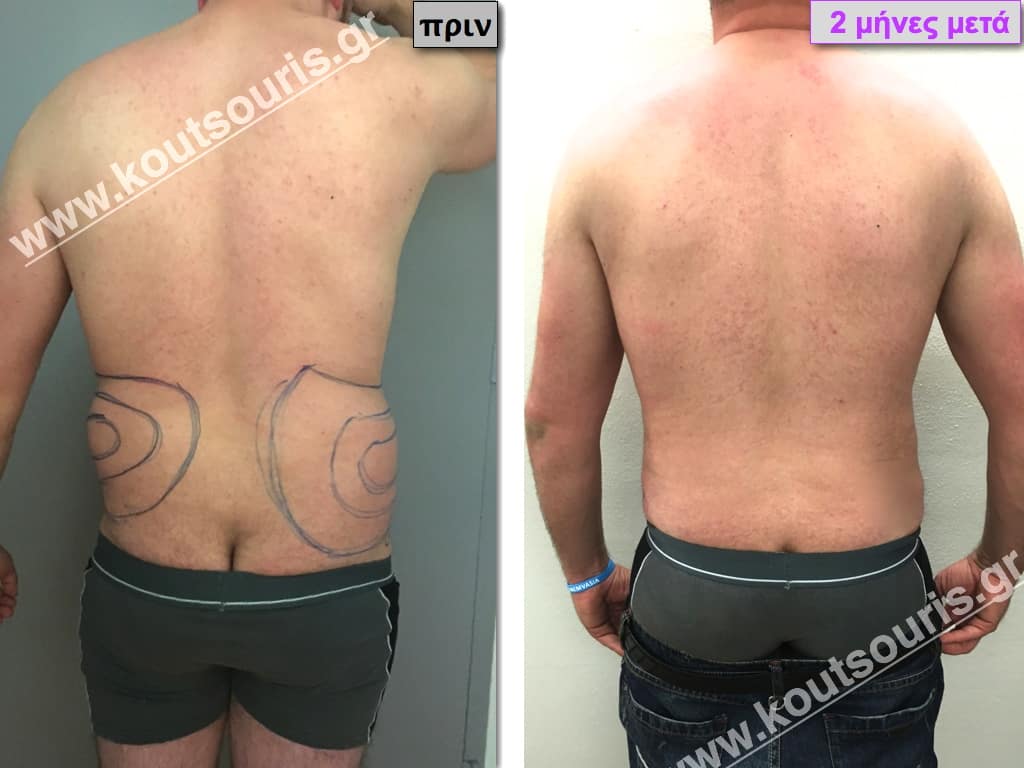
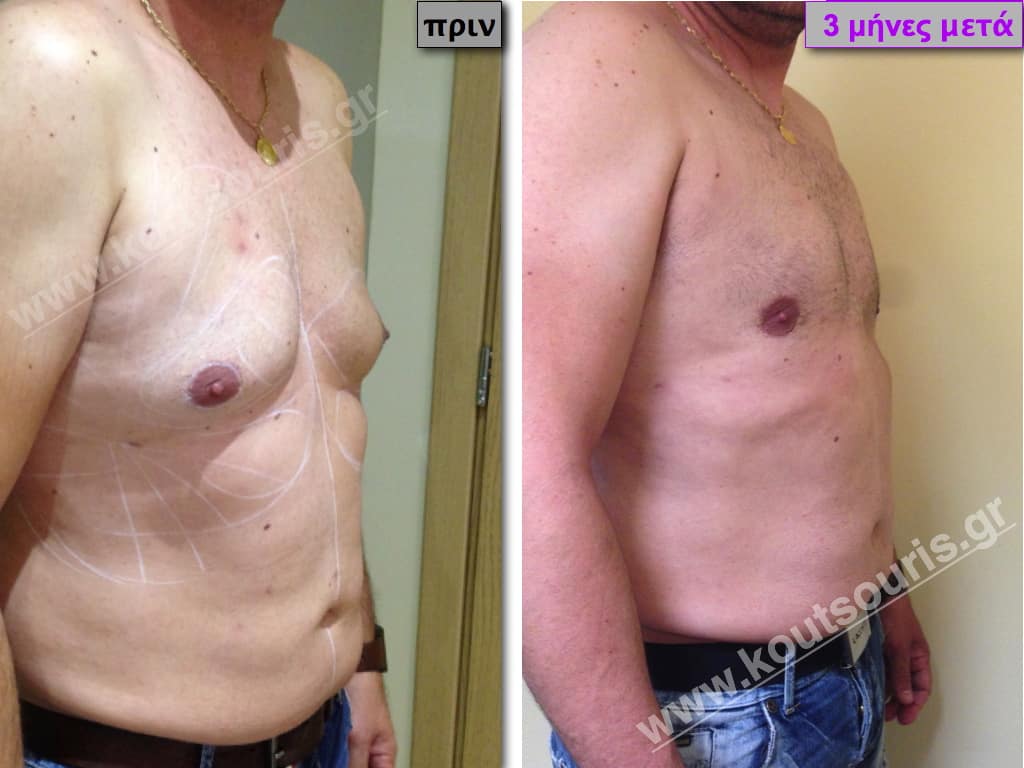
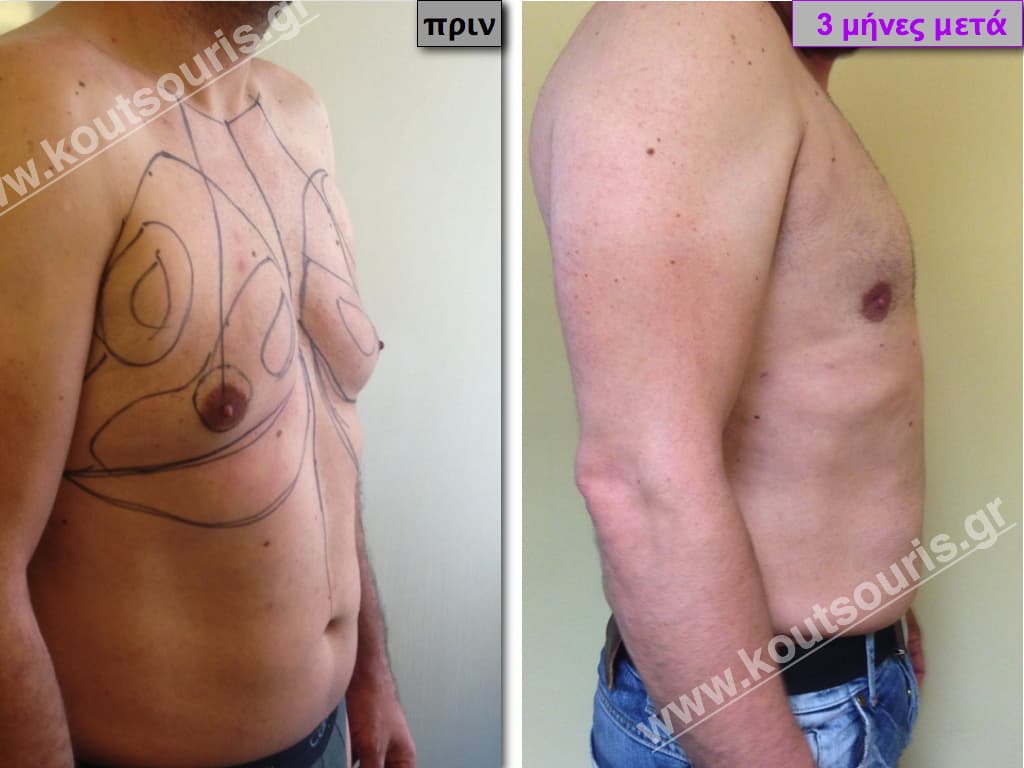
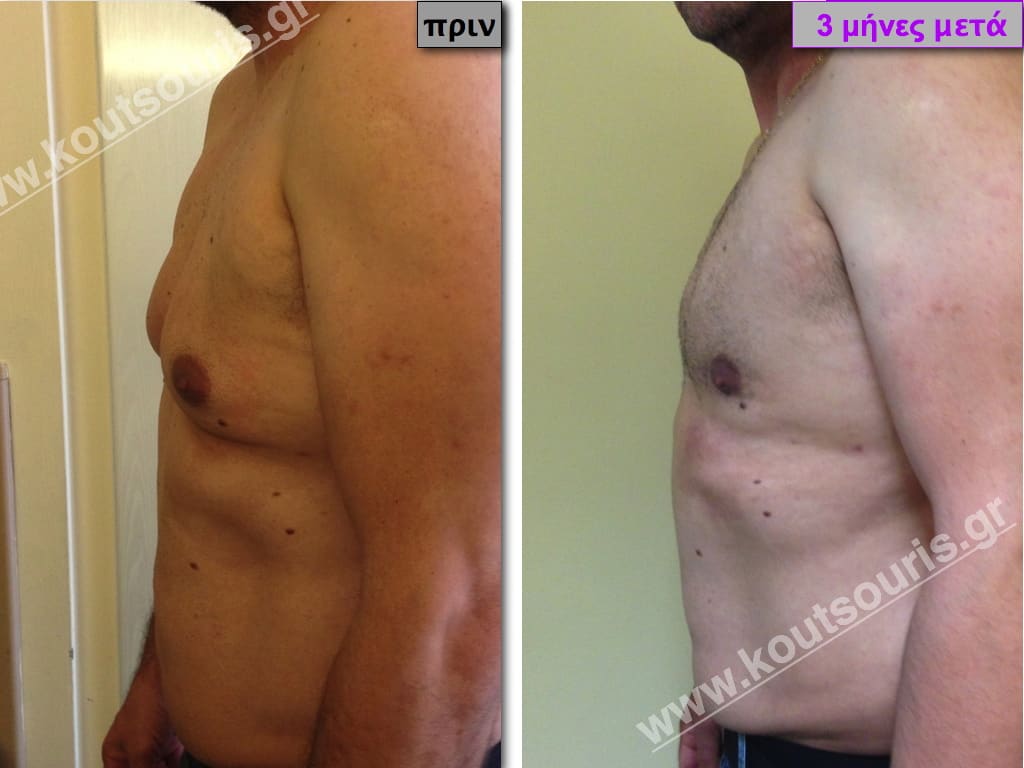
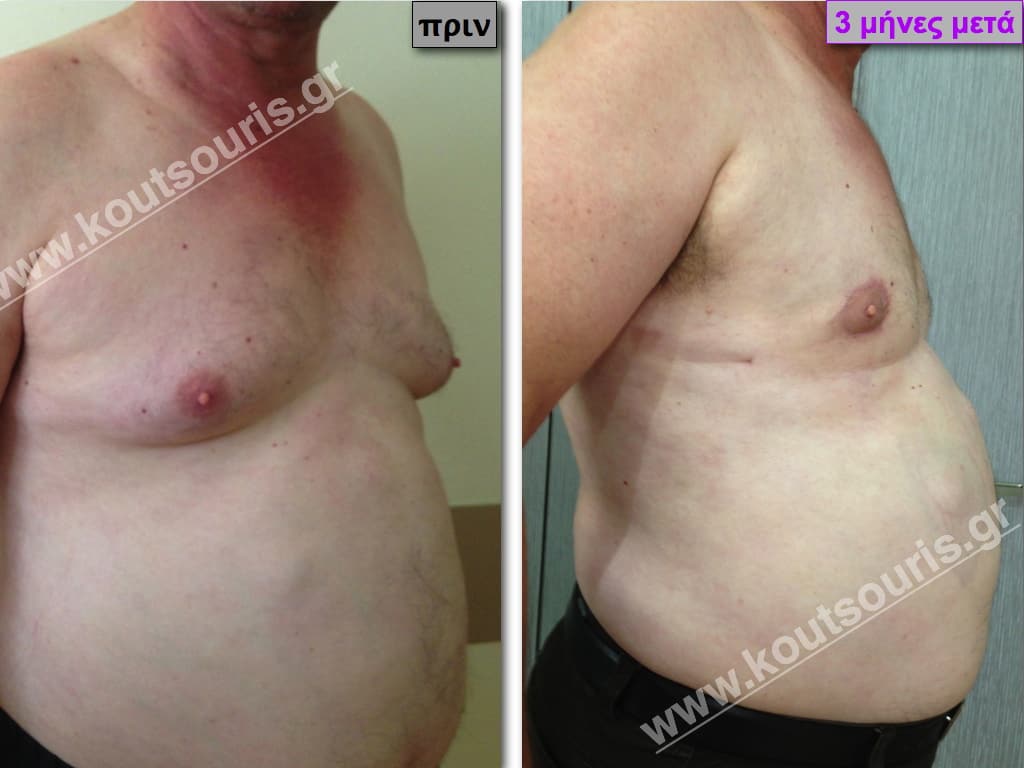
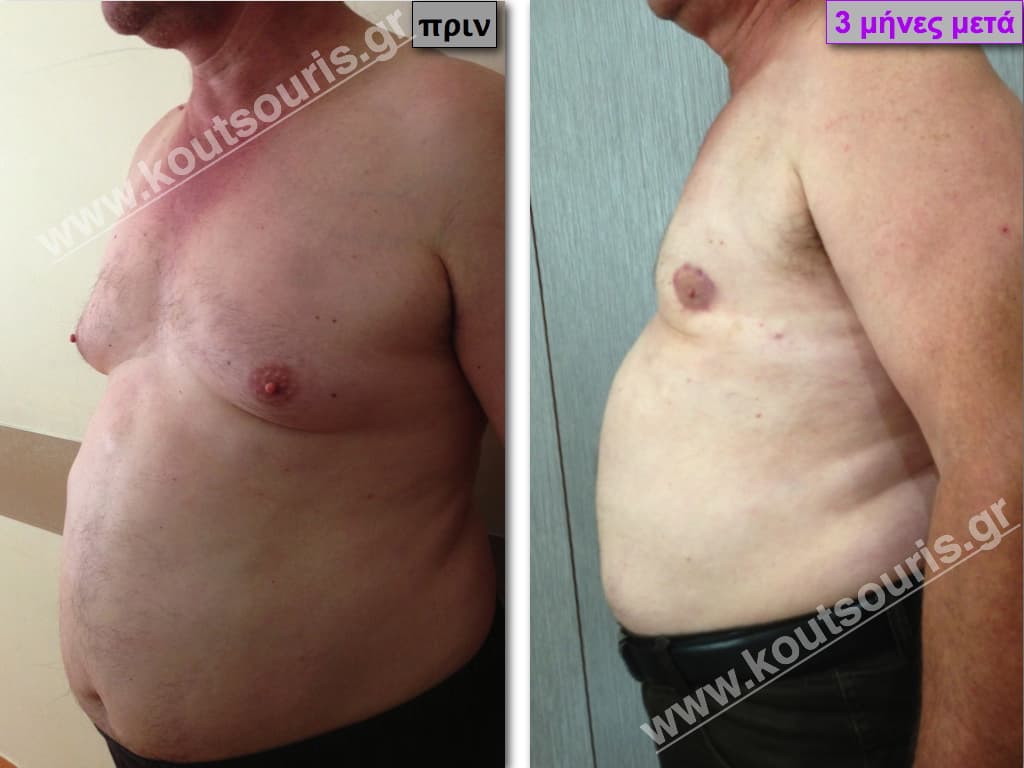
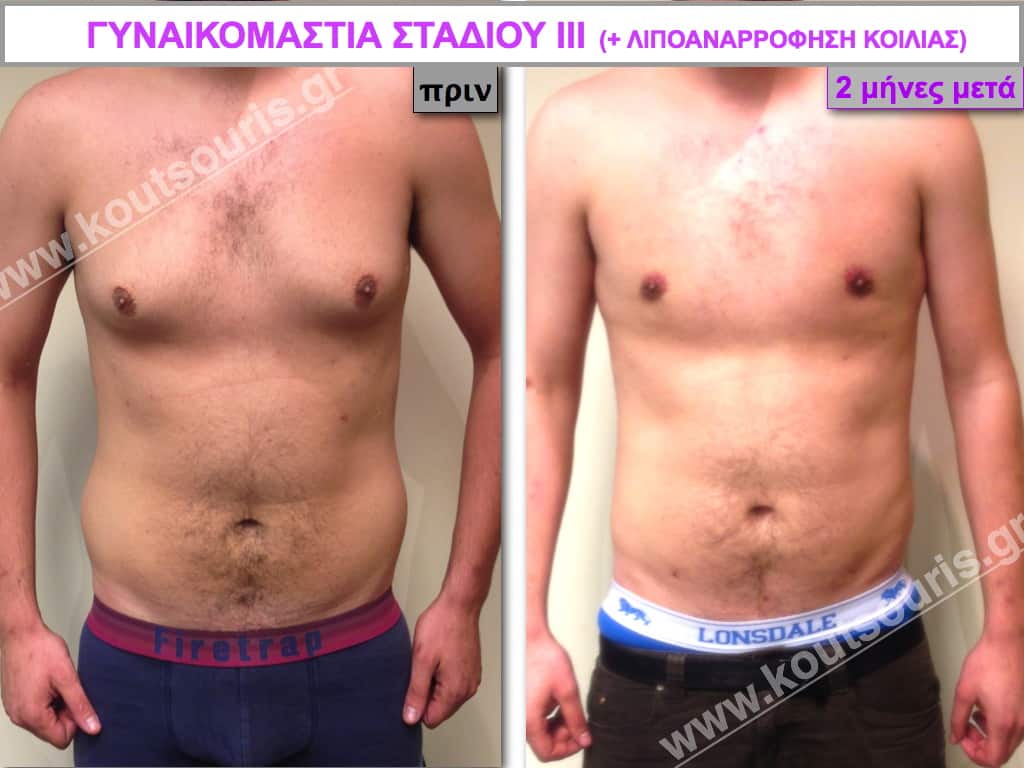
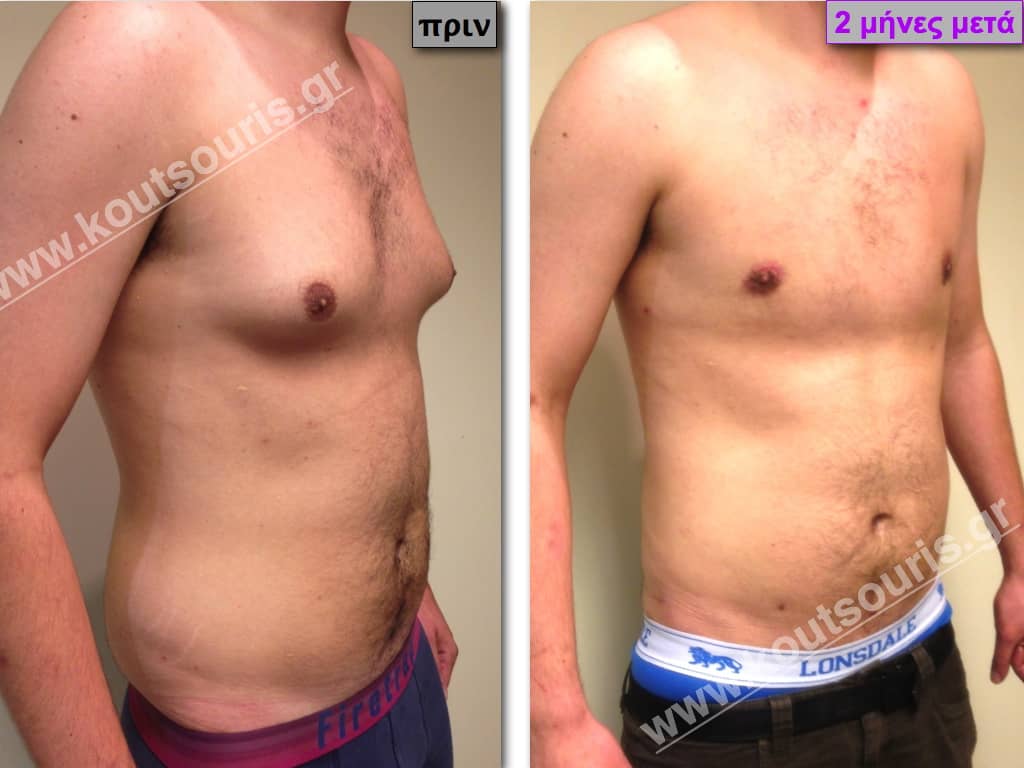
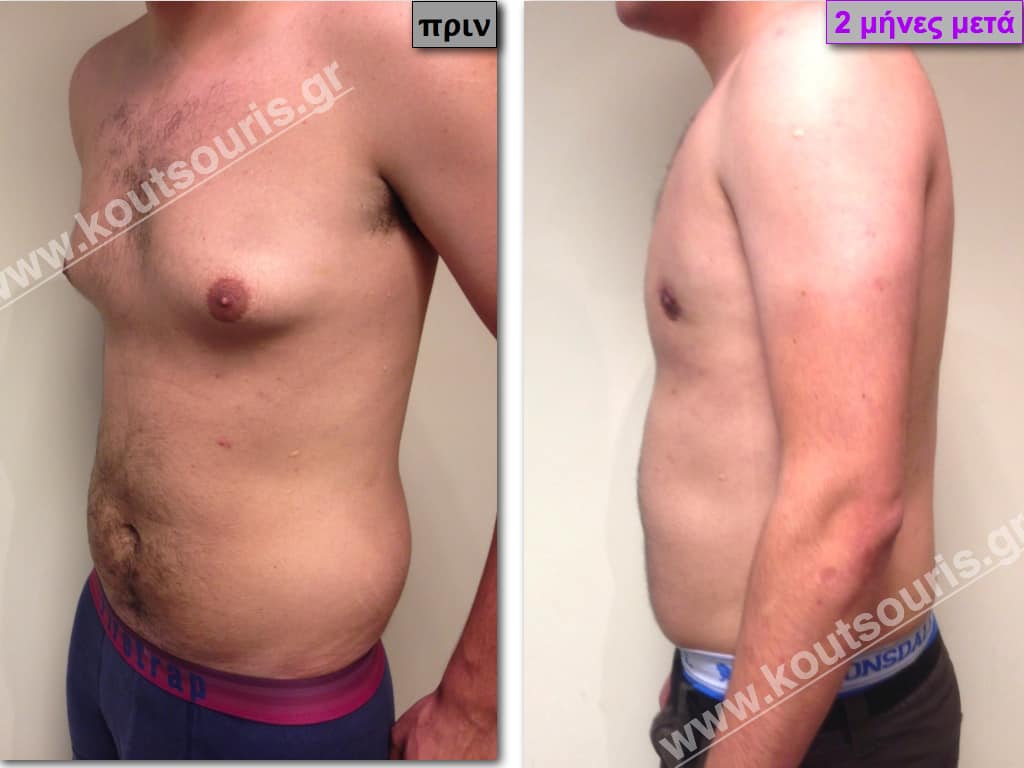
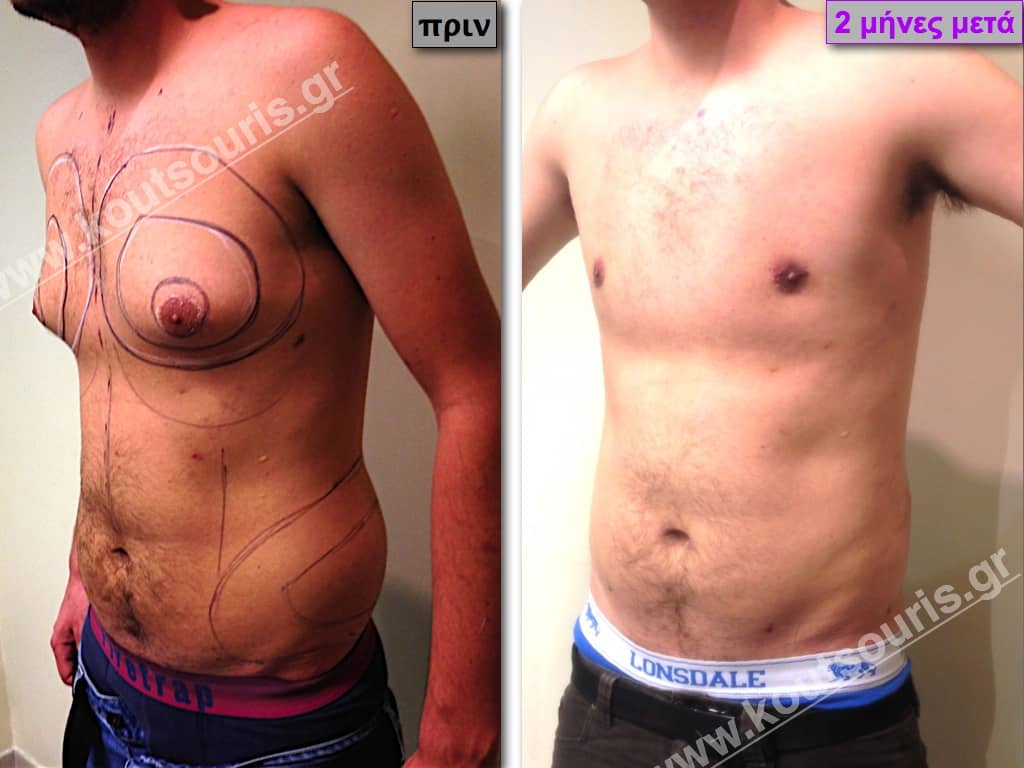
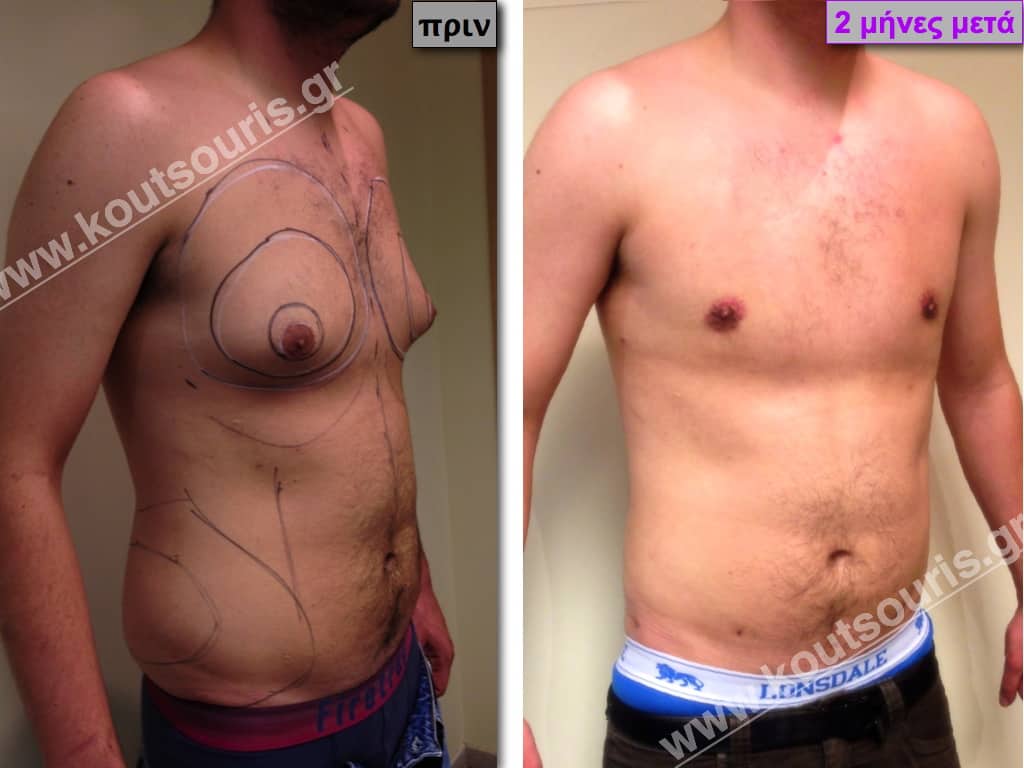
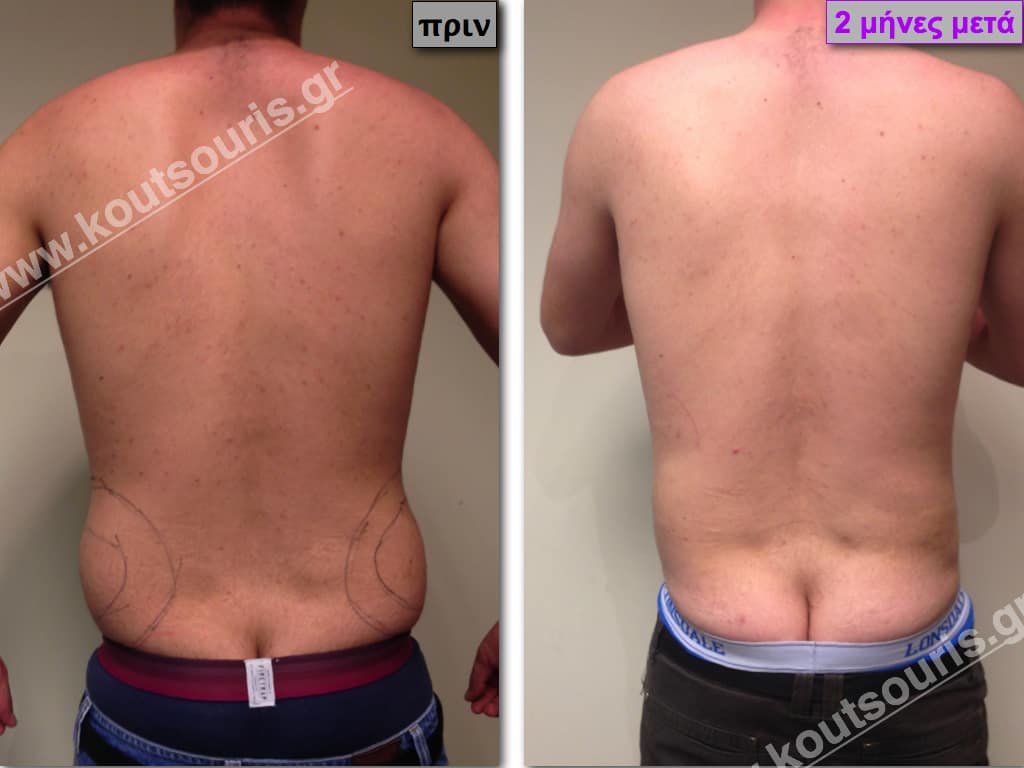
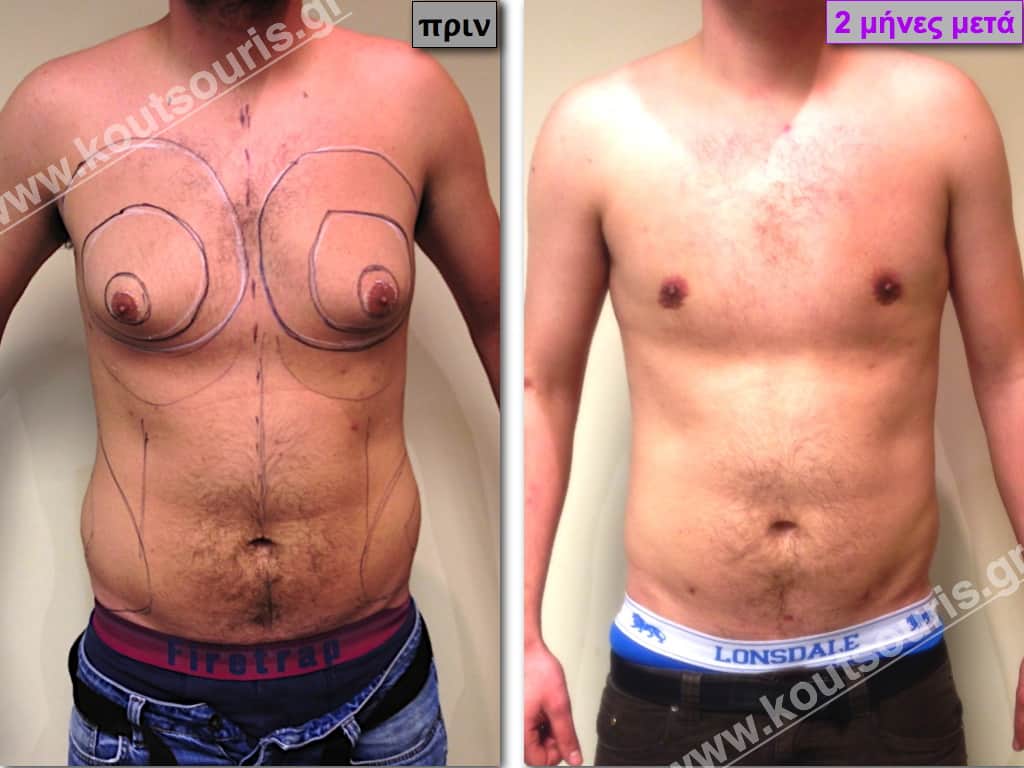
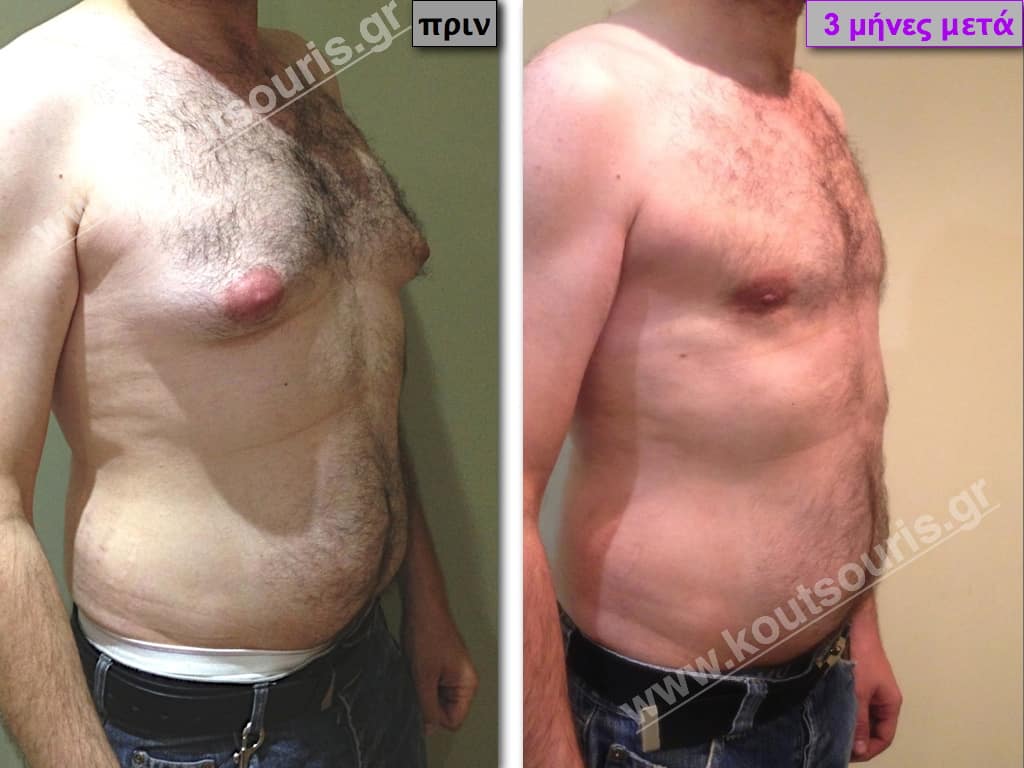
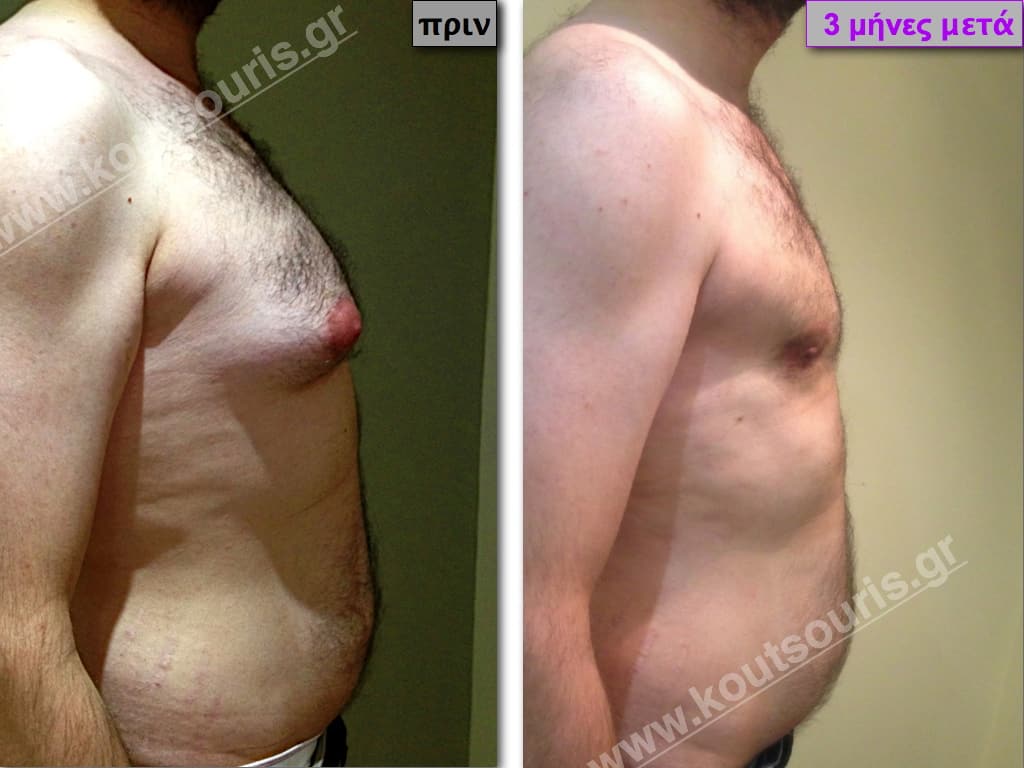
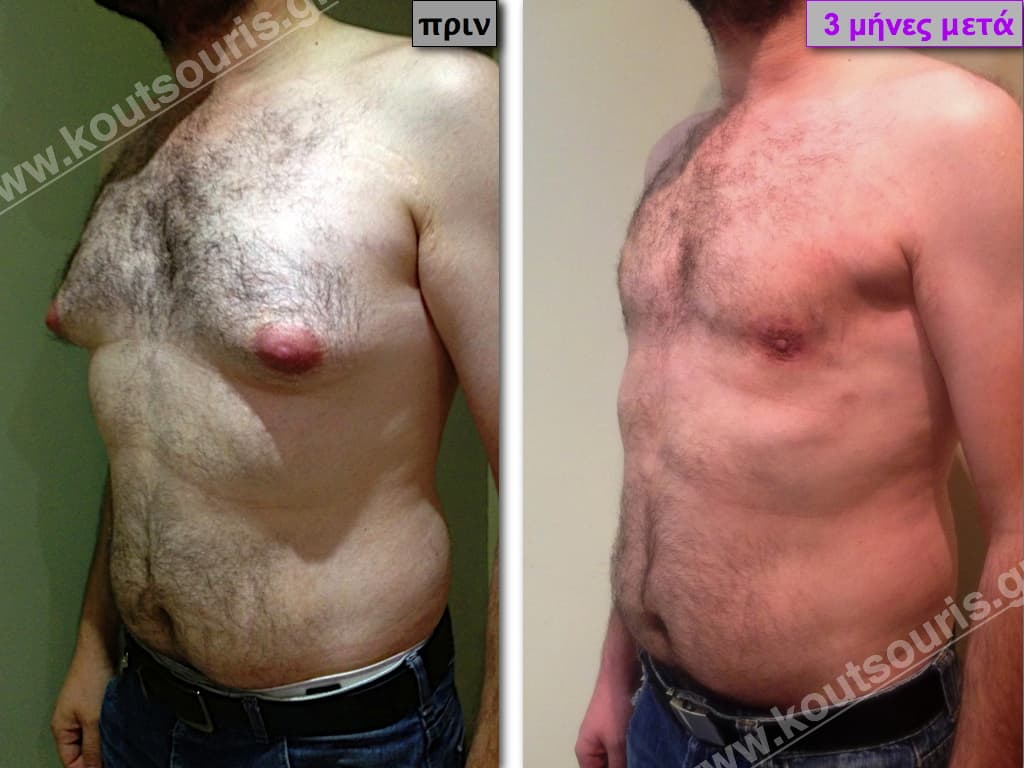
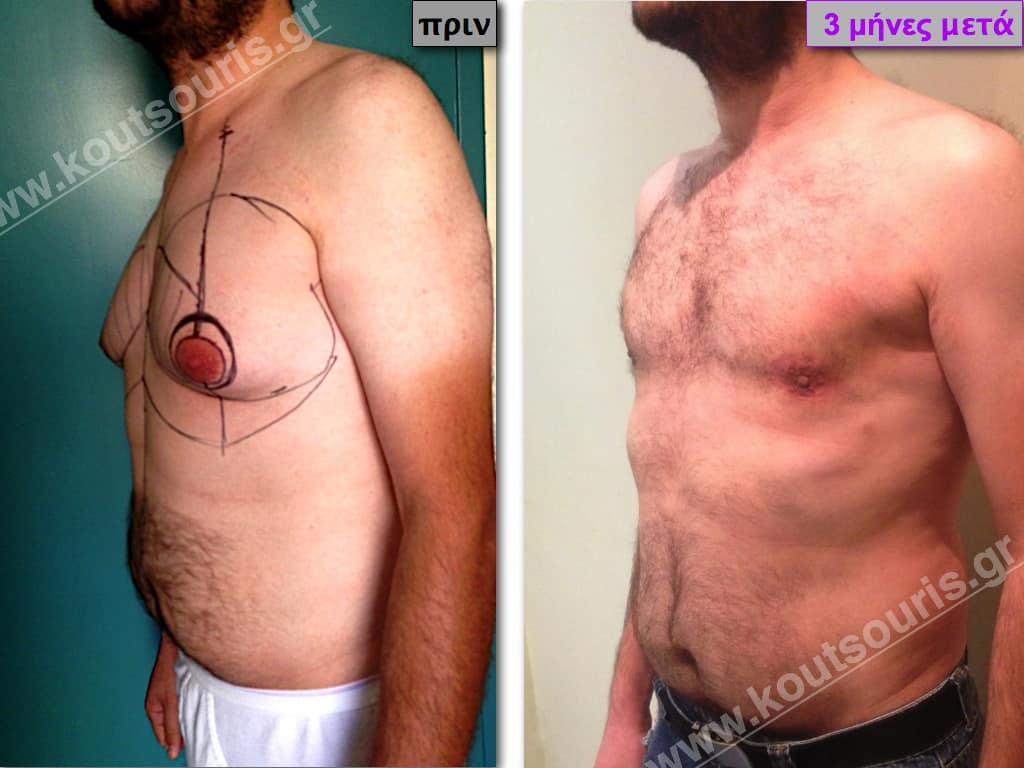
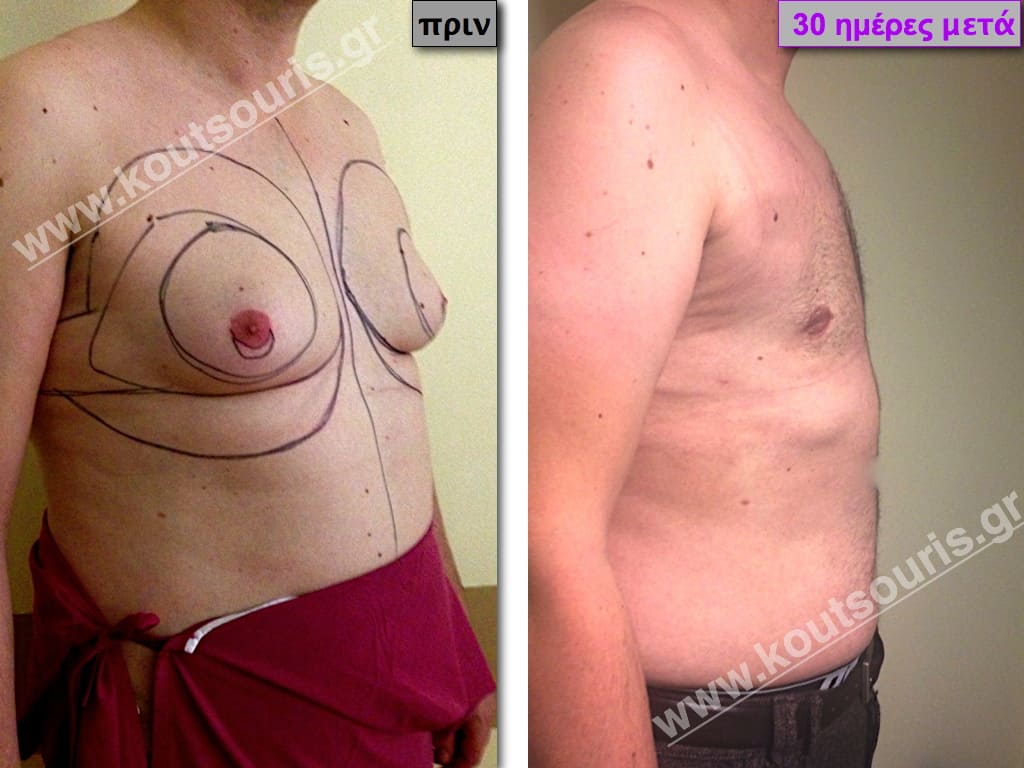
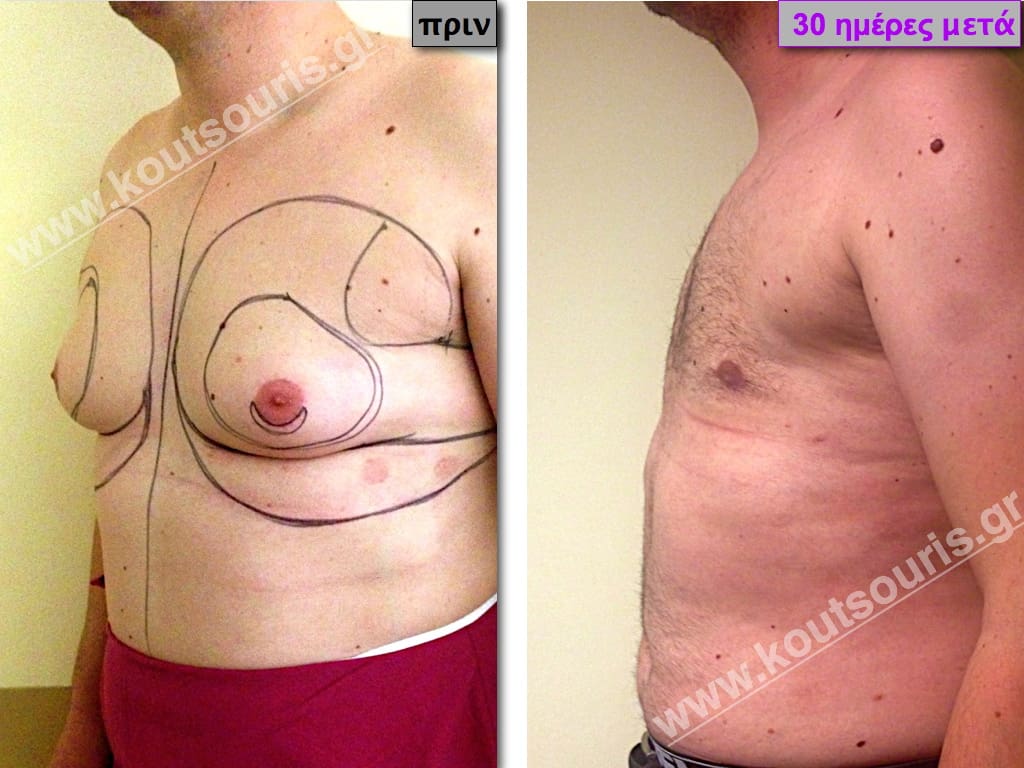
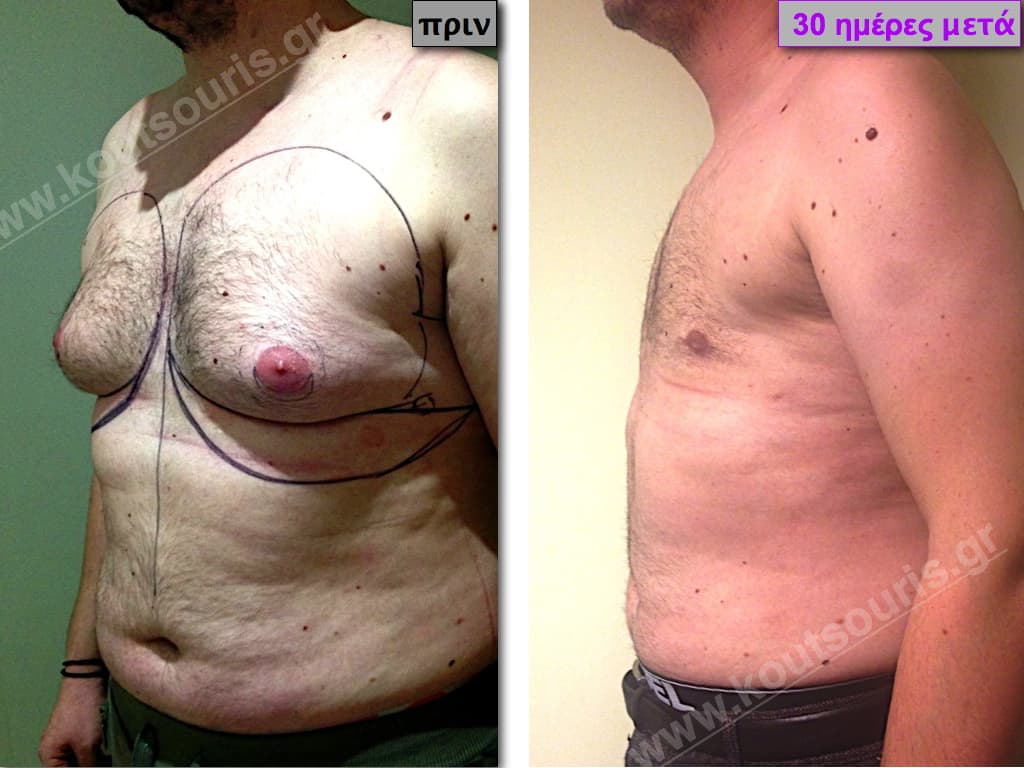
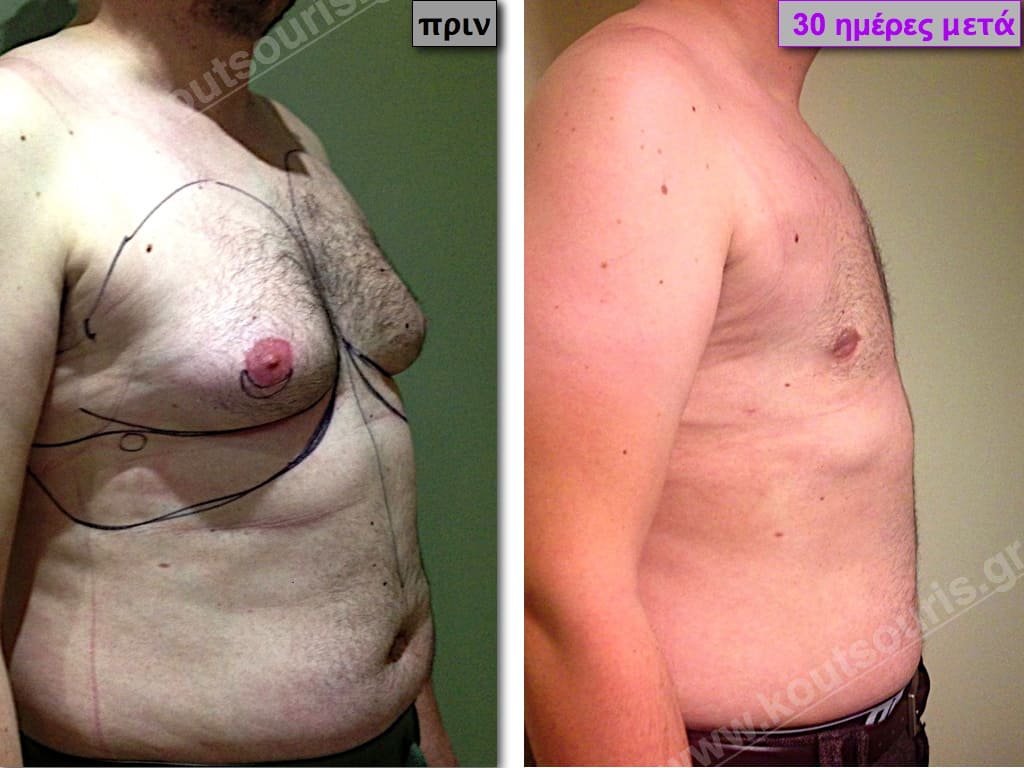
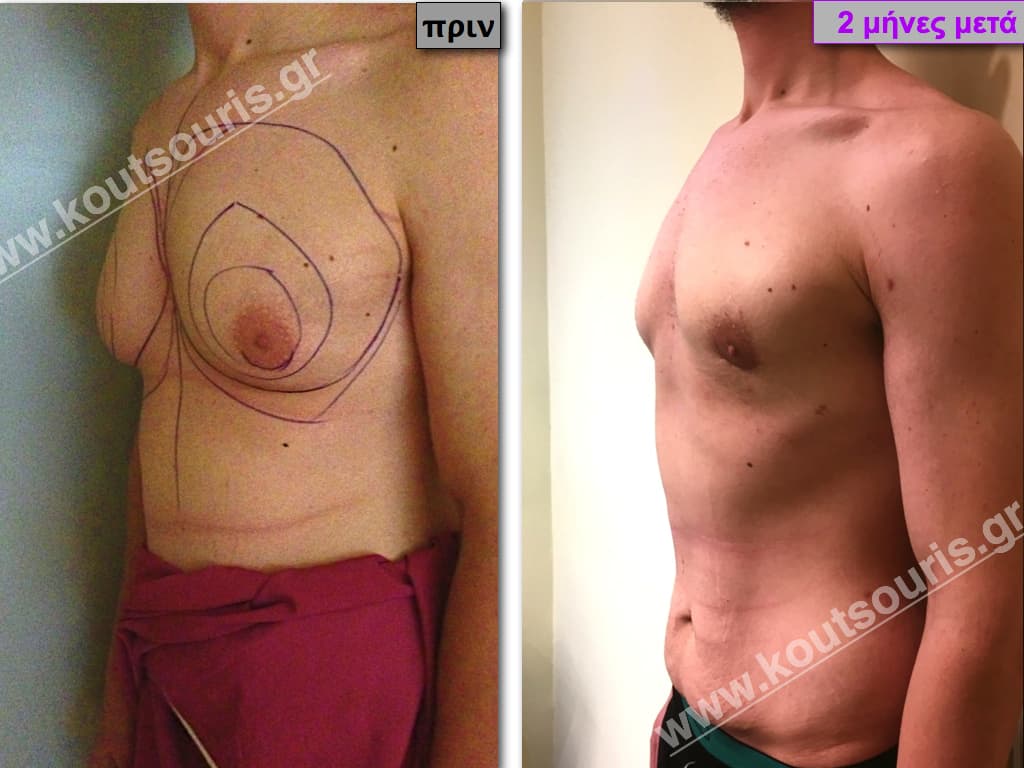
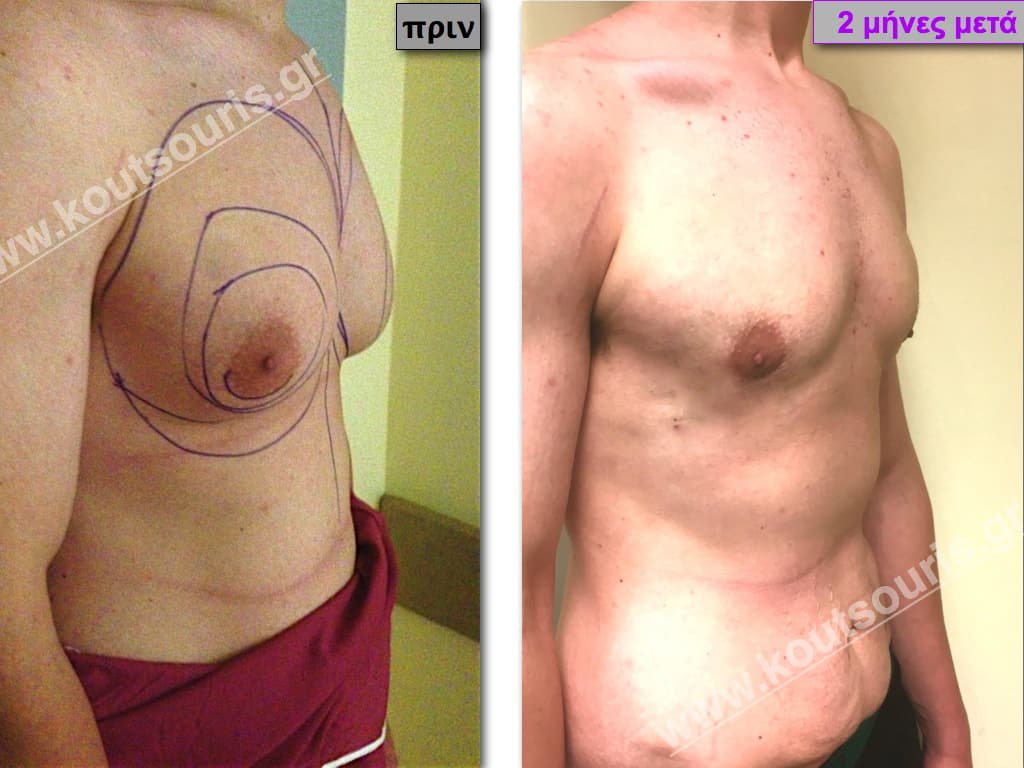
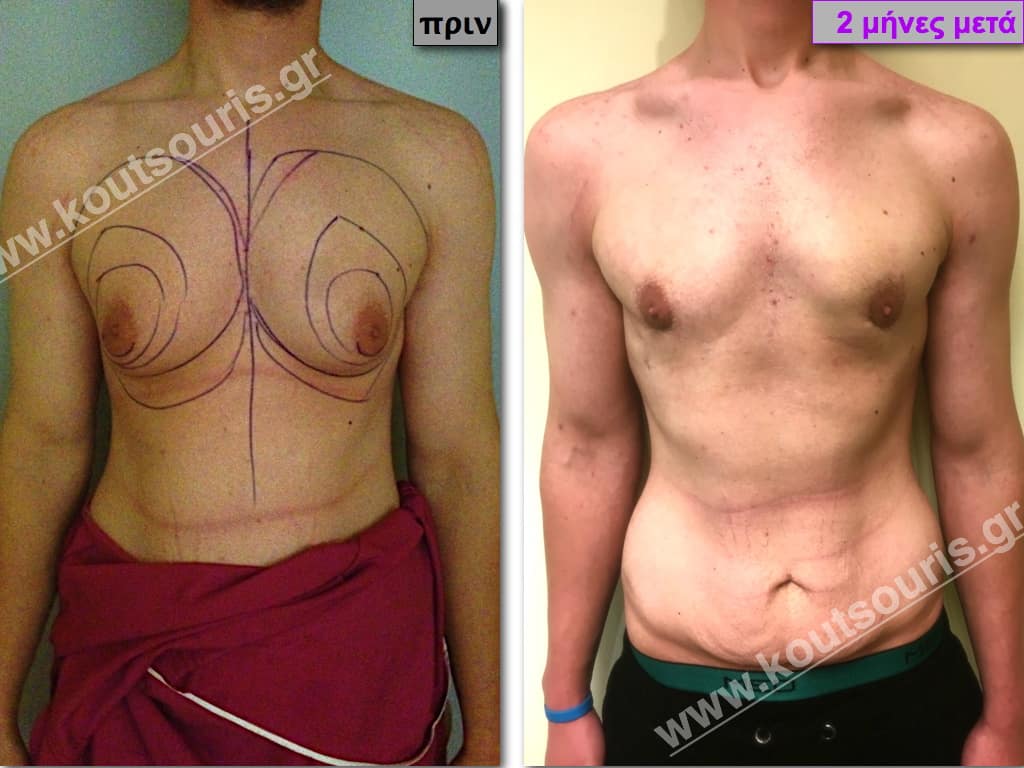
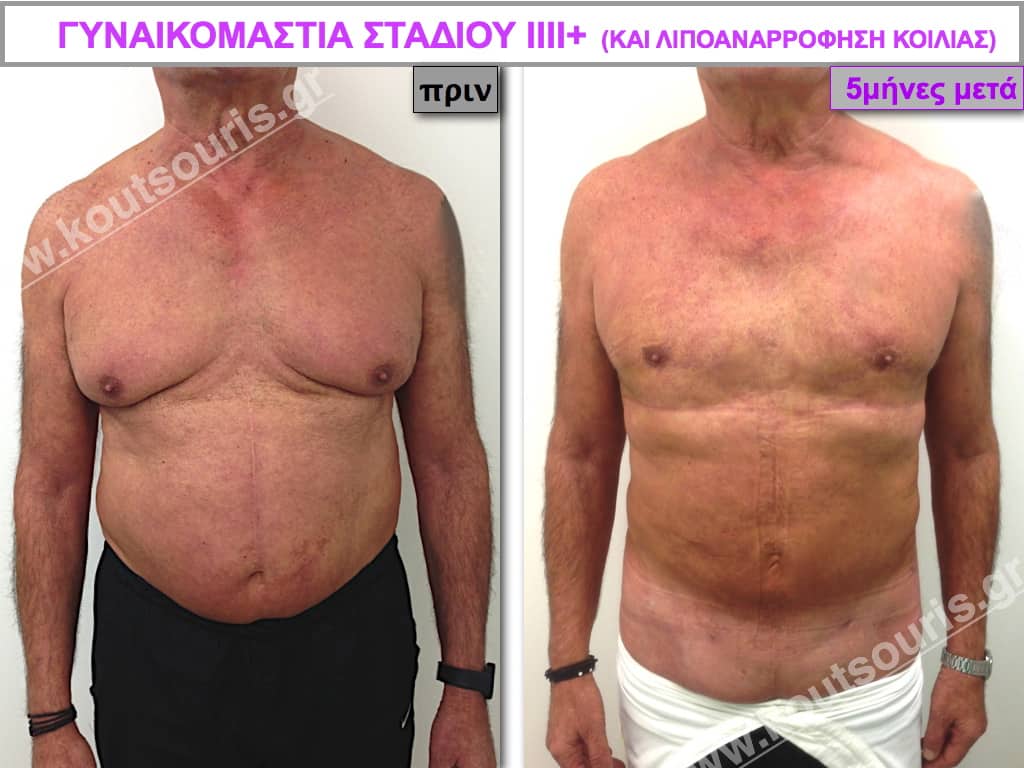
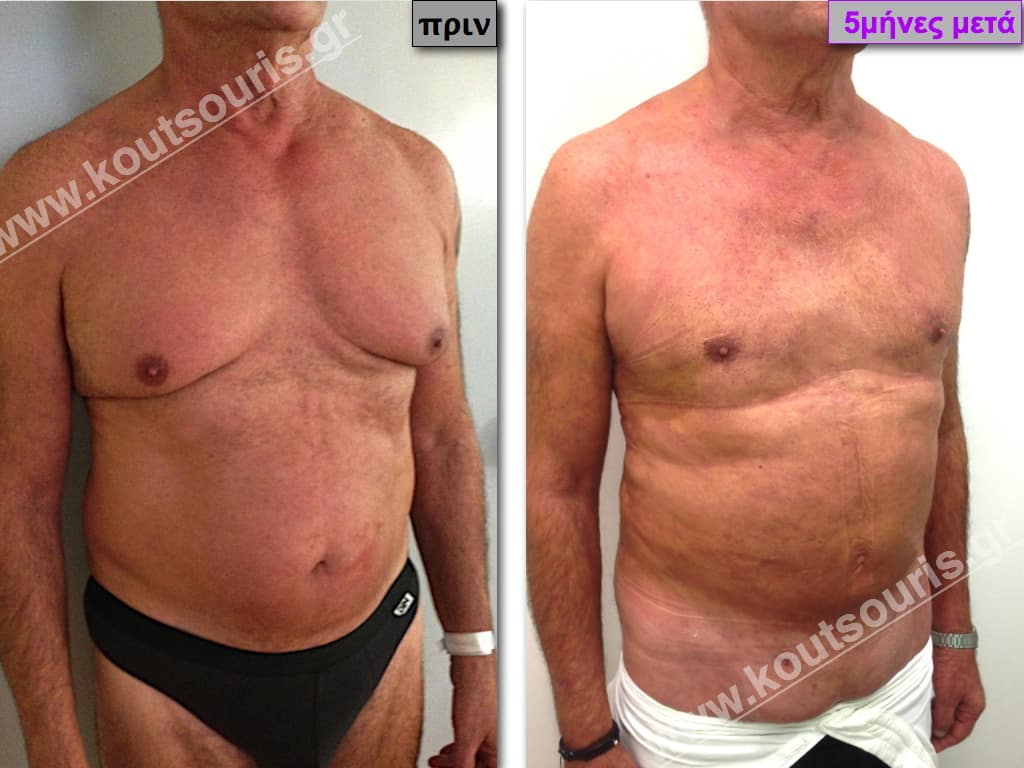
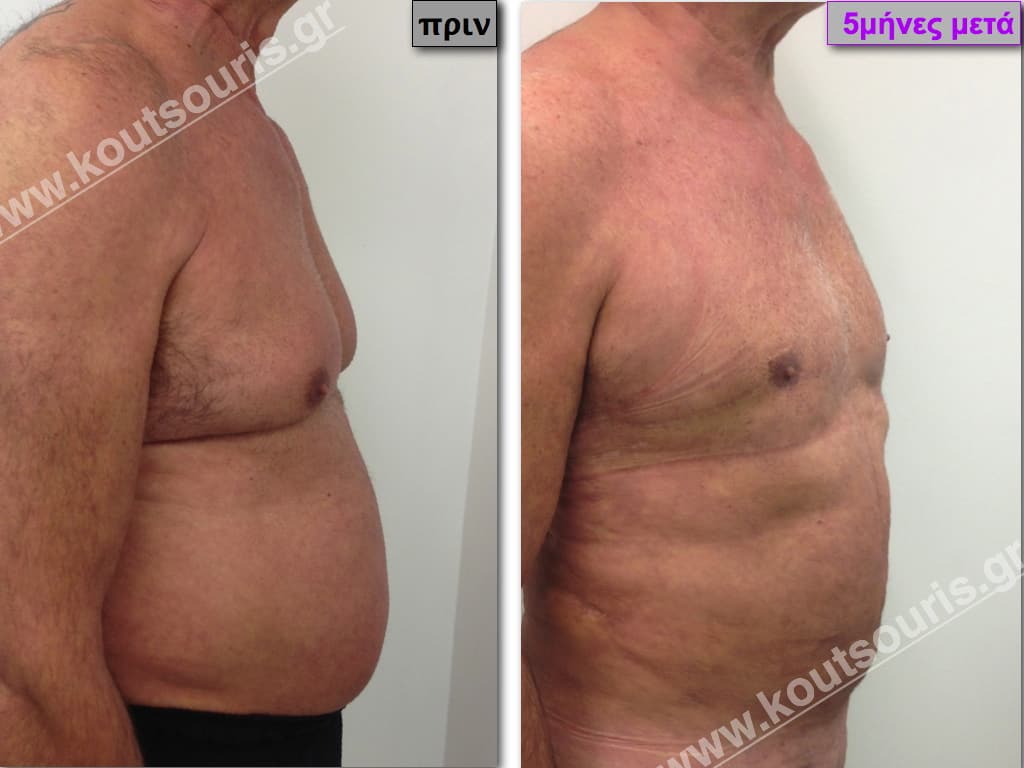
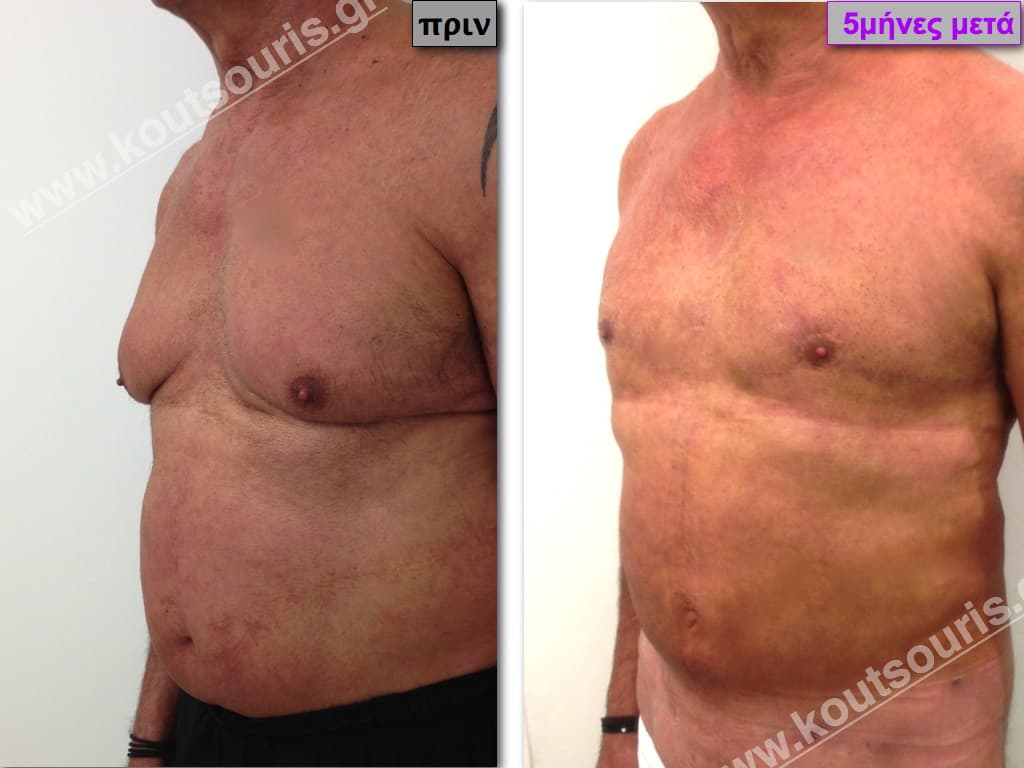
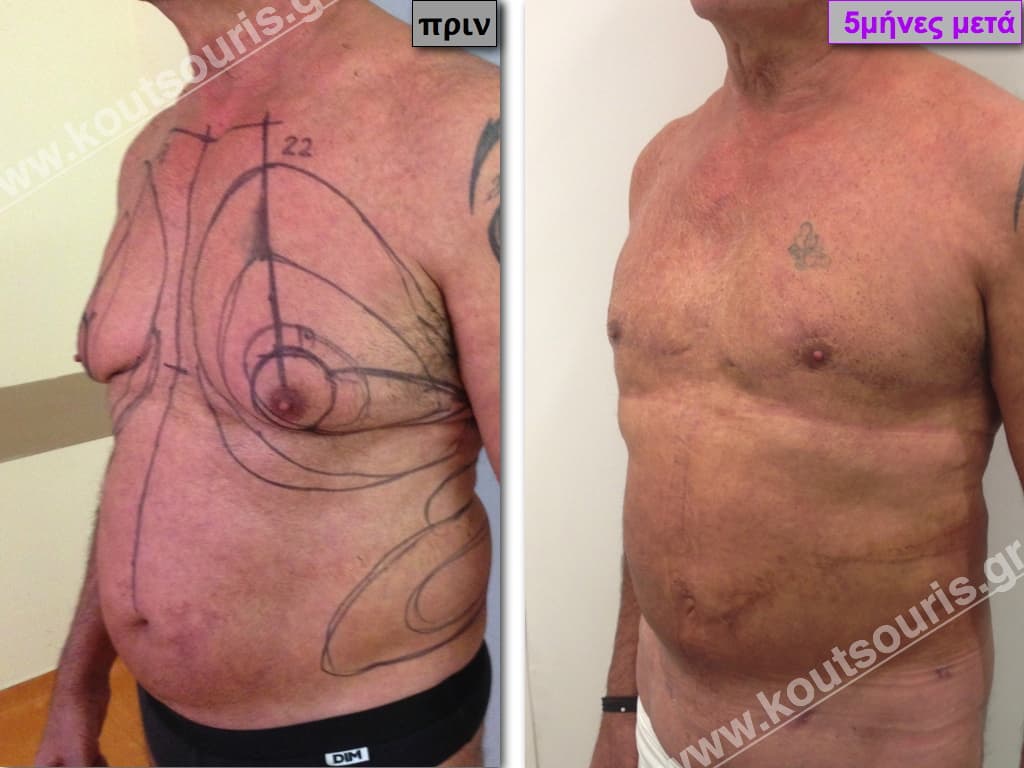
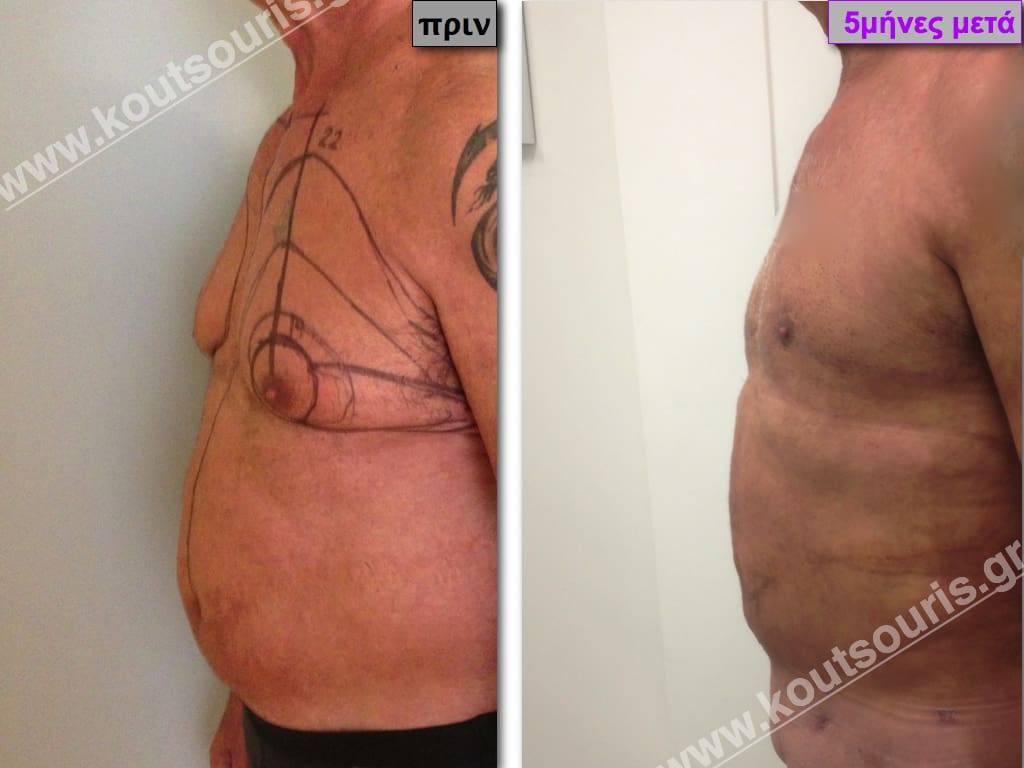
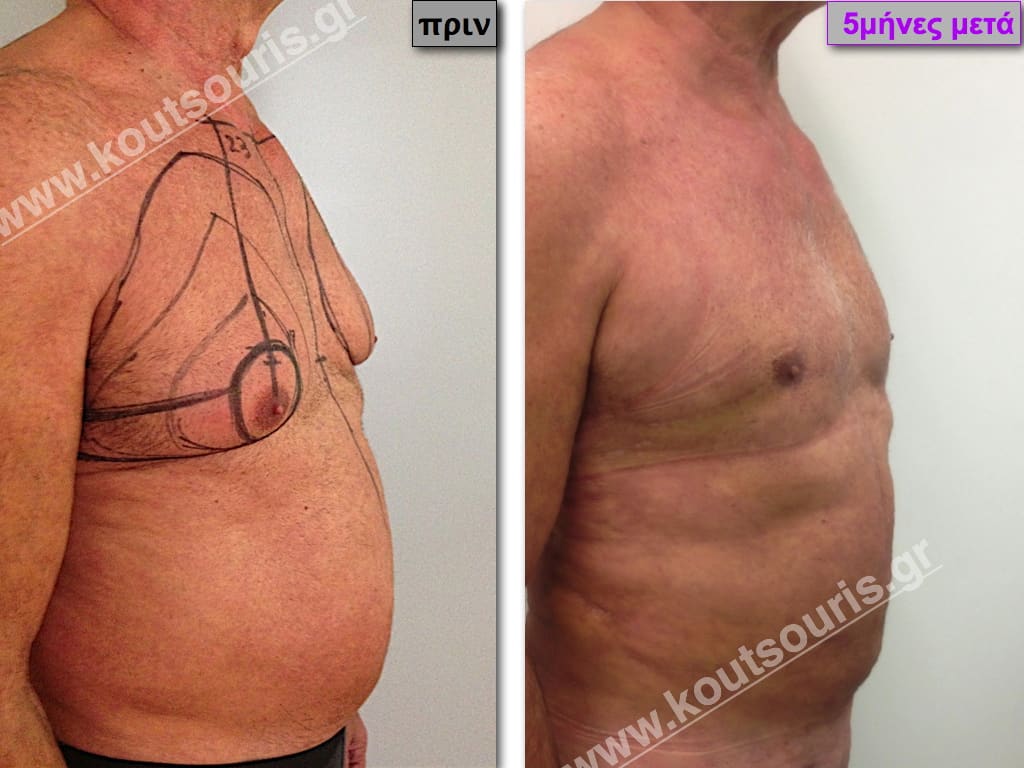
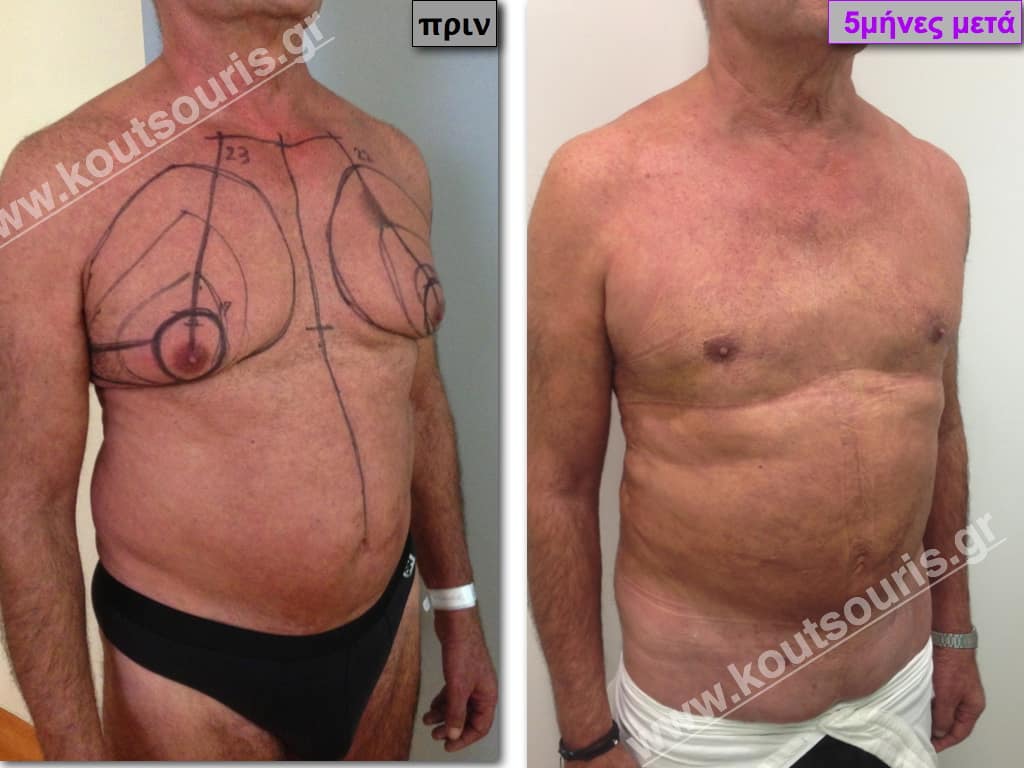
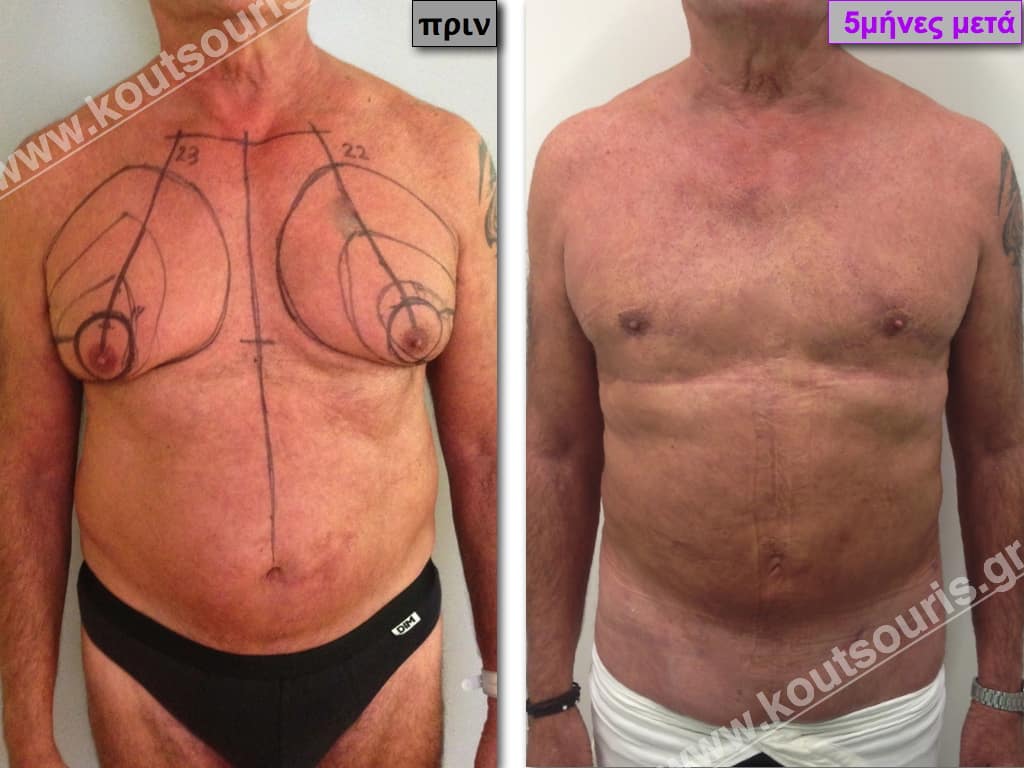
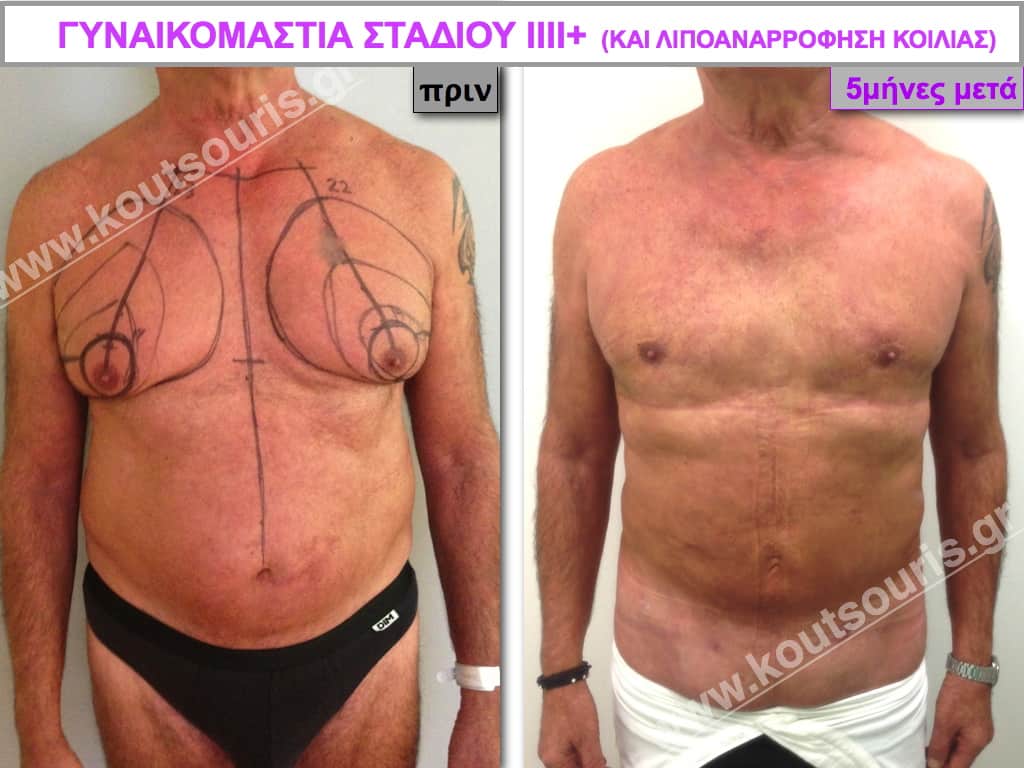
In the following pictures we can observe the result of gynecomastia restorative surgery after two weeks. It is an early image of the results since it takes about 3-4 months for the incisions to be invisible.
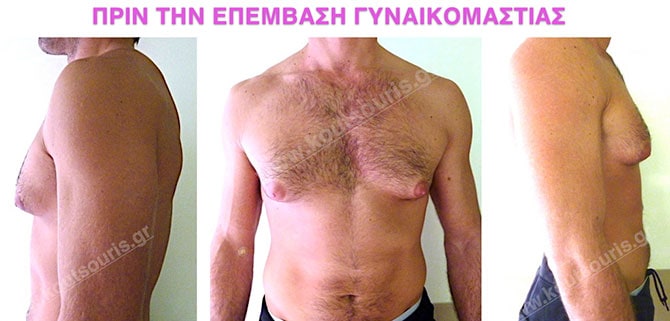
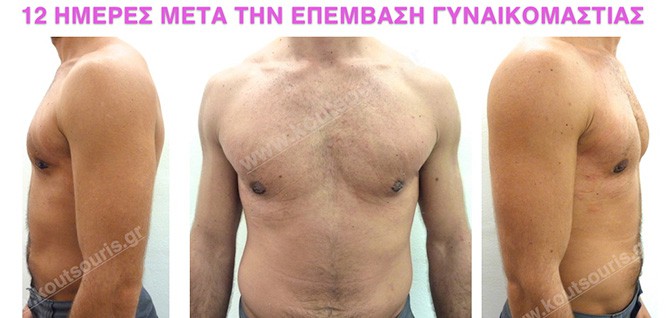
What should I do after the surgery?
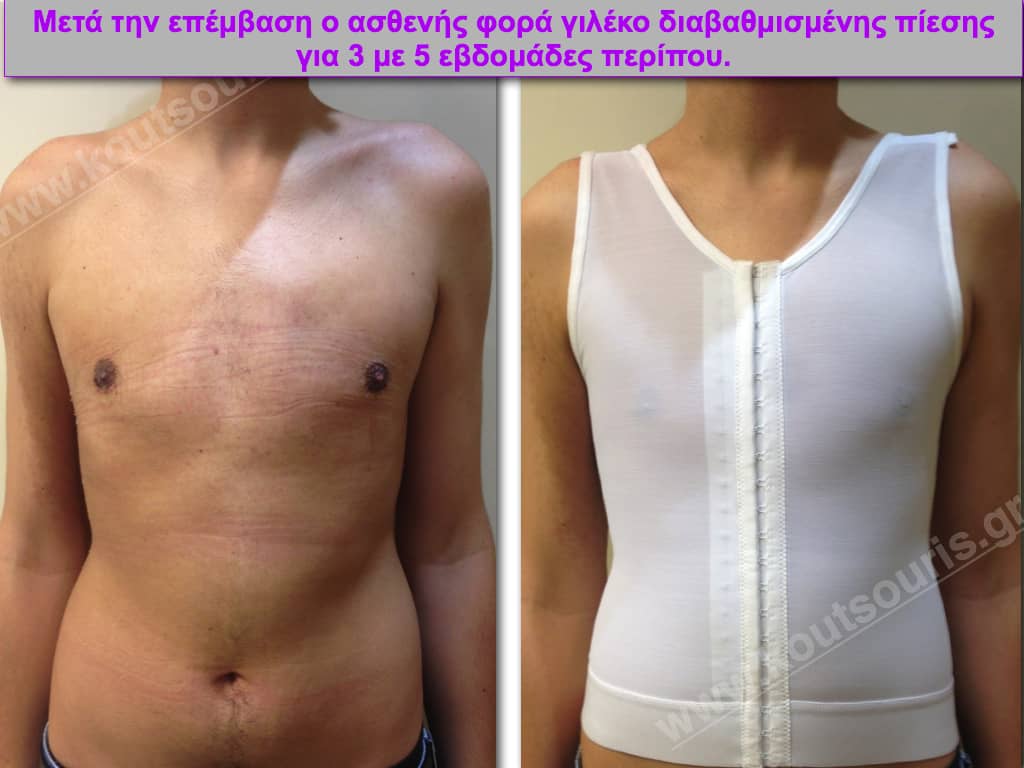
After surgery the patient goes back to home, since it has been placed in the breast a special compression bandage. This protective dressing remains in the area for 24 hours for 10 days and then for the next month it is removed only during the night.
The stitches in the nipple area are usually absorbable and it is not required to be removed. Otherwise all stitches are removed in 7 days.
After surgery the area may usually appear some bruises, which is completely normal and automatically disappears in 10-15 days. After surgery the breast area may usually appear a swelling due to lymphatic stasis. The solution for the regression of this swelling is the lymphatic massage for 2-3 times a week for one and a half month, where it completely disappears.
Are there any side effects or complications after surgery?
Potential side effects or complications associated with surgical gynecomastia have to do with the formation of hematoma or inflammation in the area, which should be immediately treated with drainage and antibiotics, or with the appearance of hypoaesthesia usually in the area around the nipple that disappears within 3 – 6 months. Small asymmetries in the area may also occur usually treated with local anesthesia after six months.
We must bear in mind that, as it happens in the majority of plastic surgery procedures, in order to complete the results of surgical gynecomastia, this procedue takes about 3-6 months. However the restorative gynecomastia technique of Plastic Surgery can be achieved with high safety, while the result of surgery is satisfying.
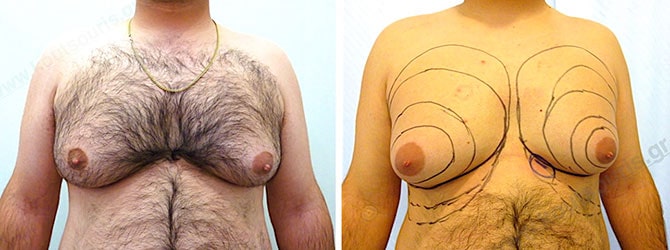
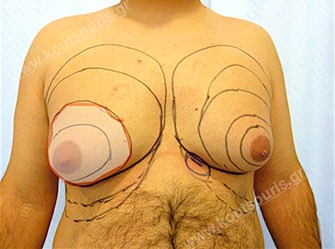
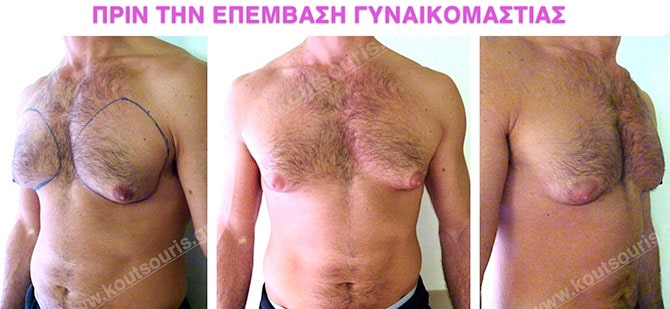
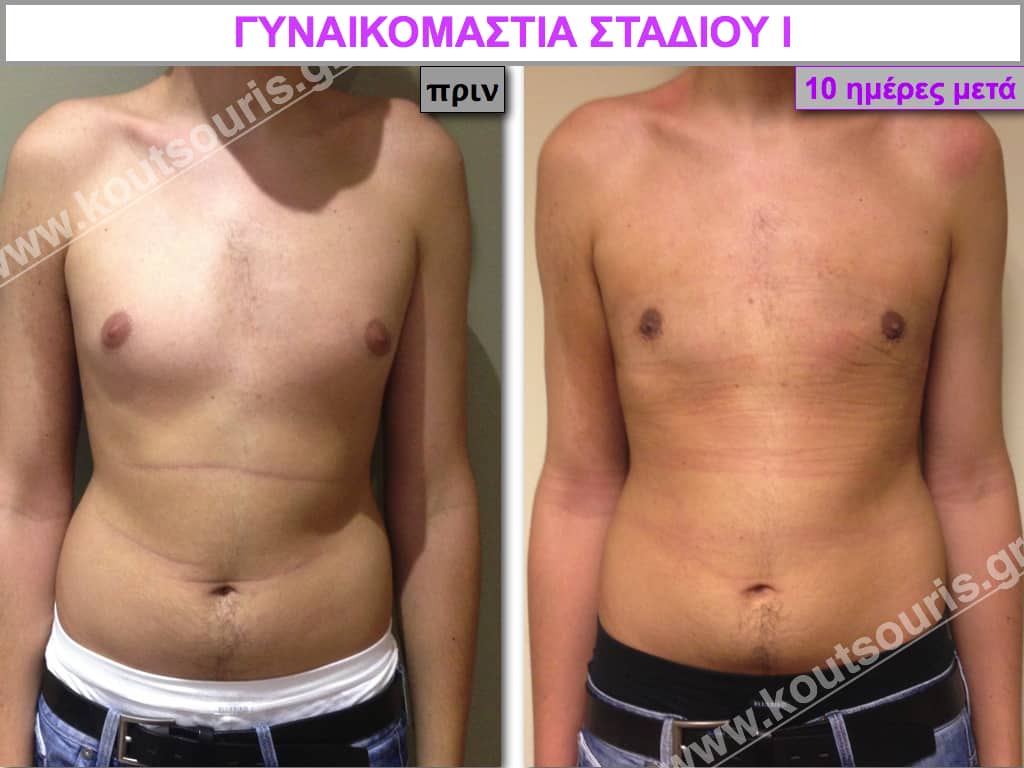
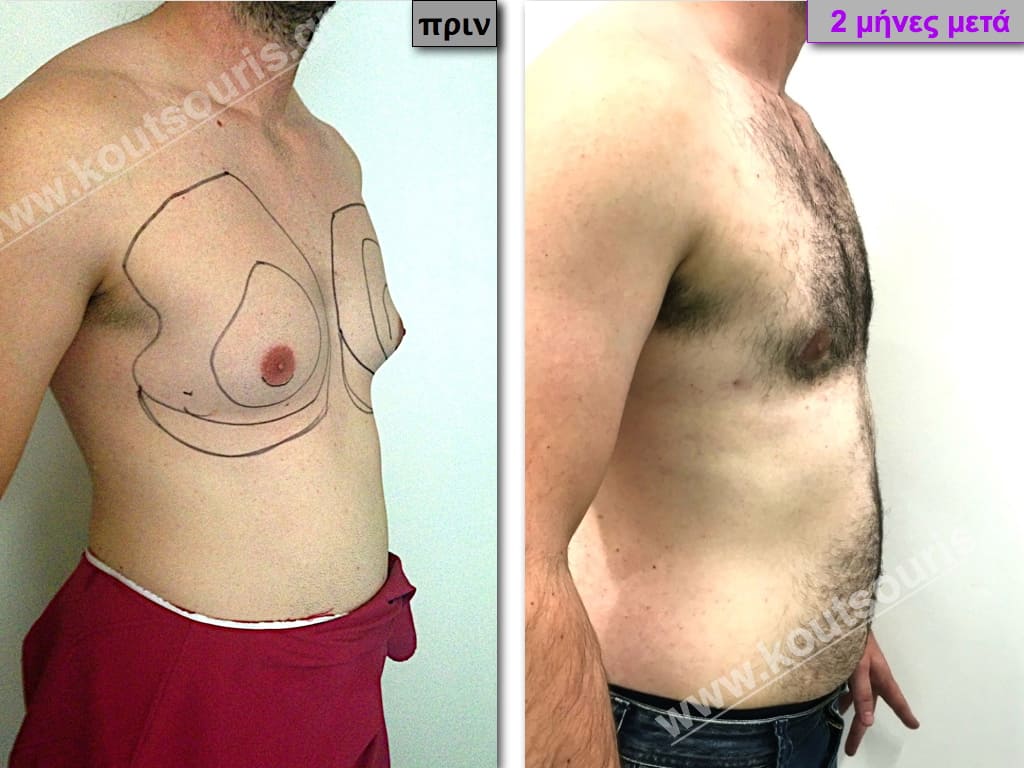
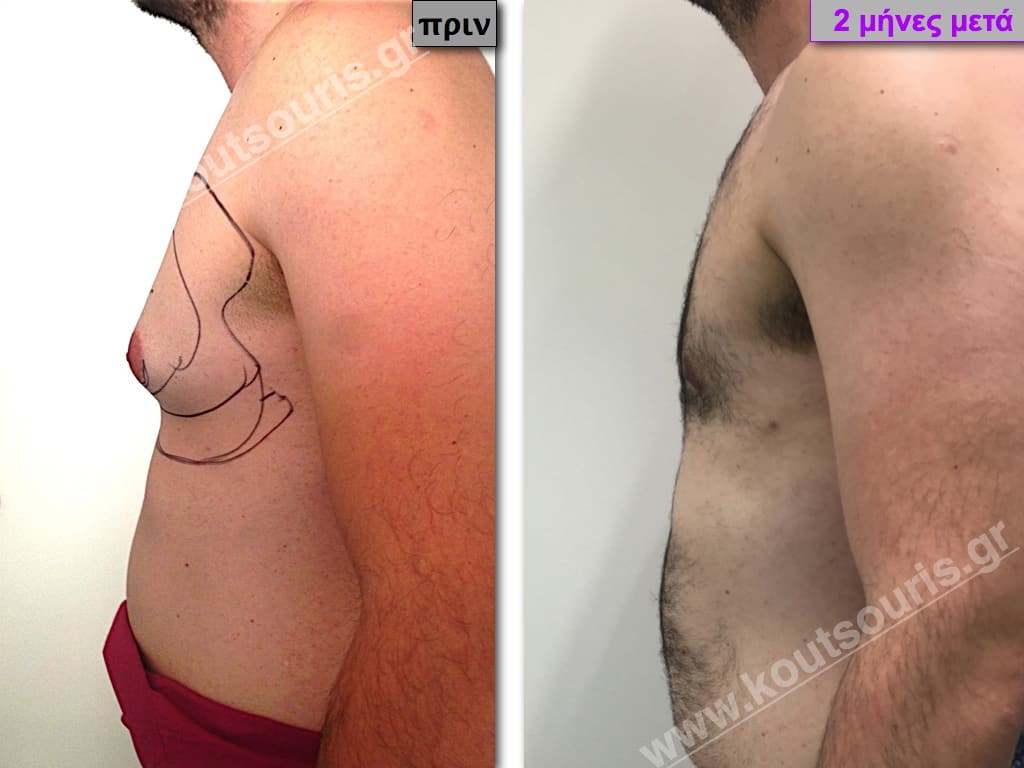
Pictures with incidents of restorative gynecomastia.
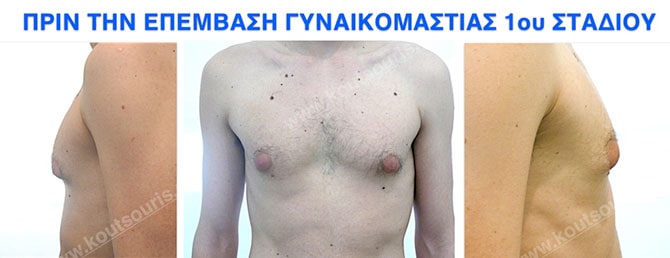
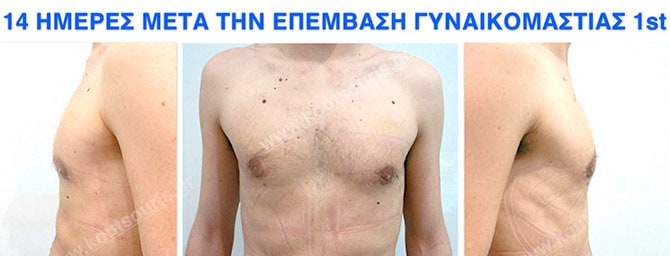
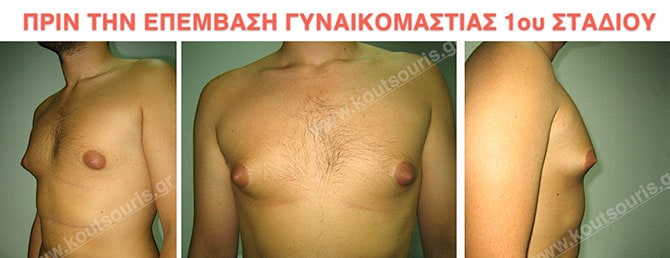
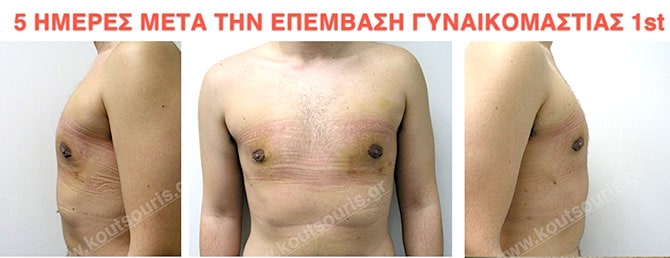
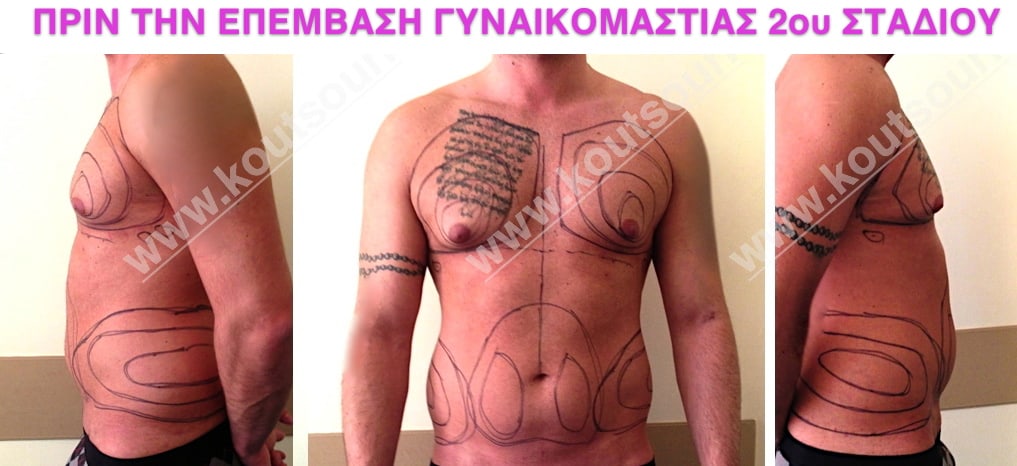
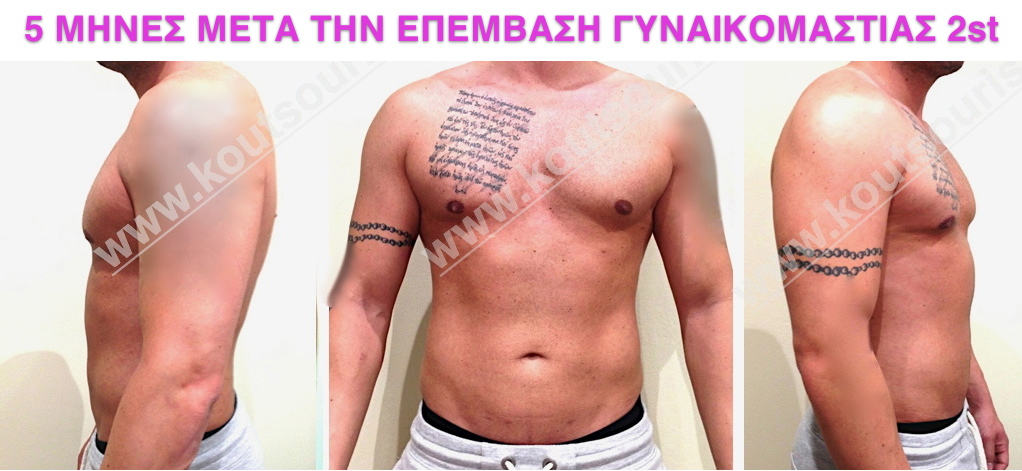
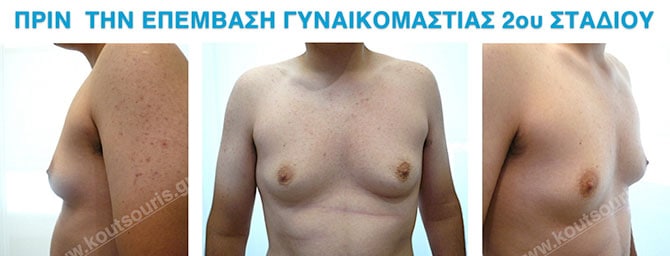
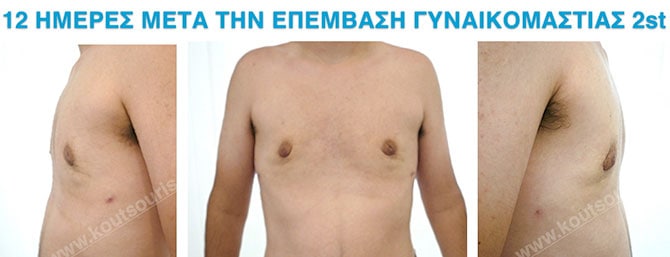
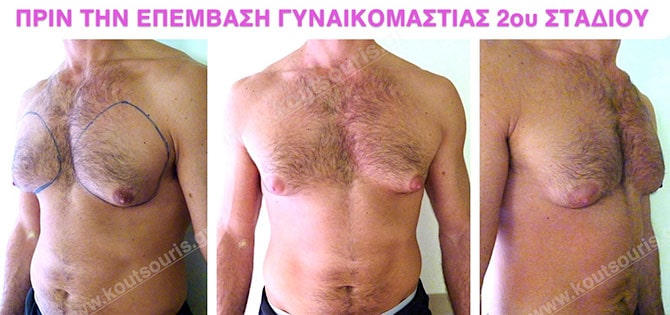
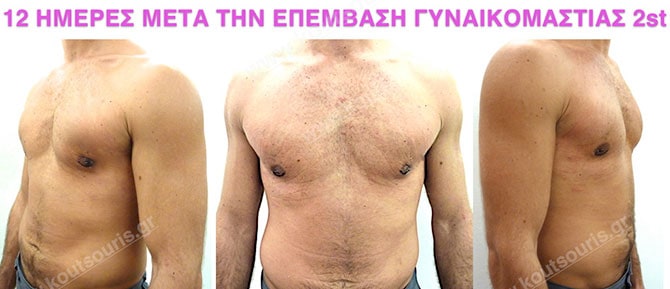
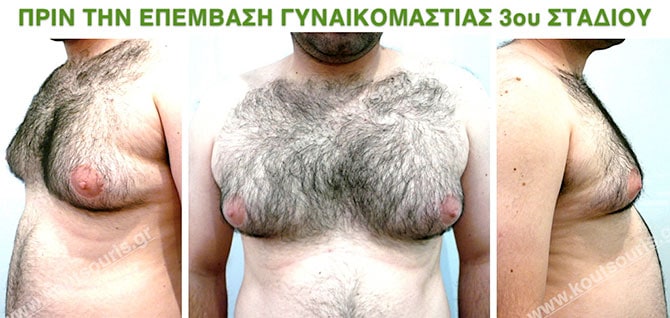
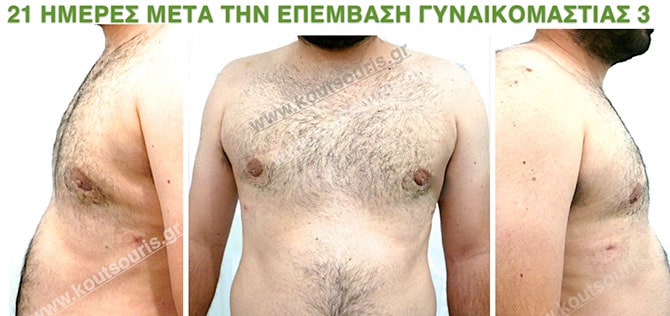
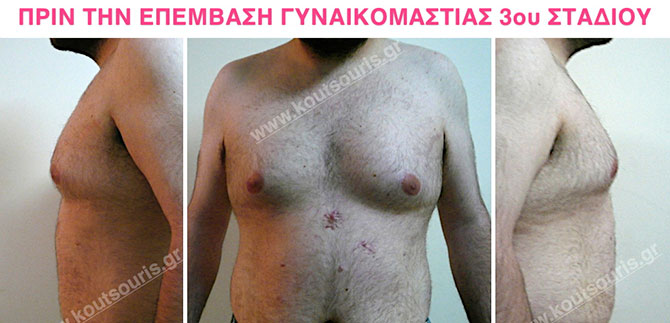
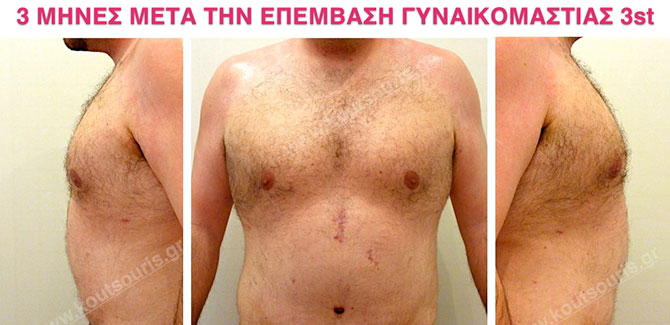
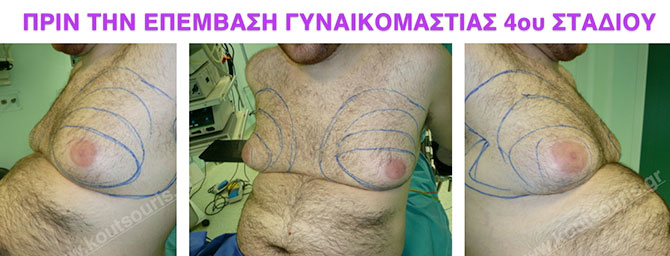
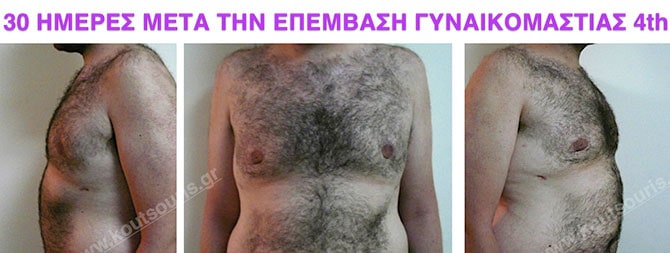
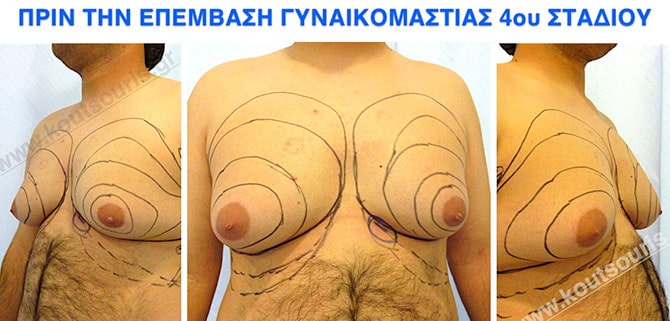
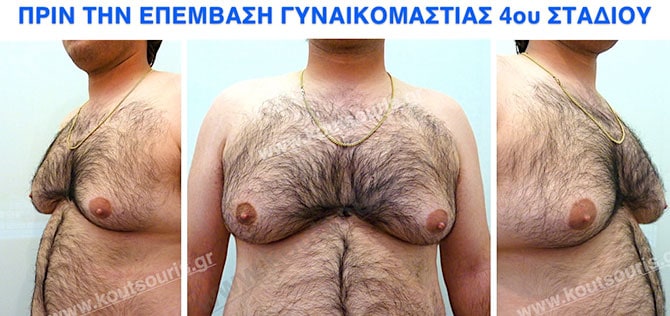
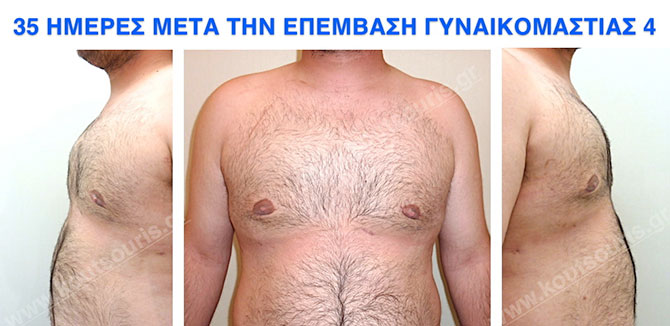
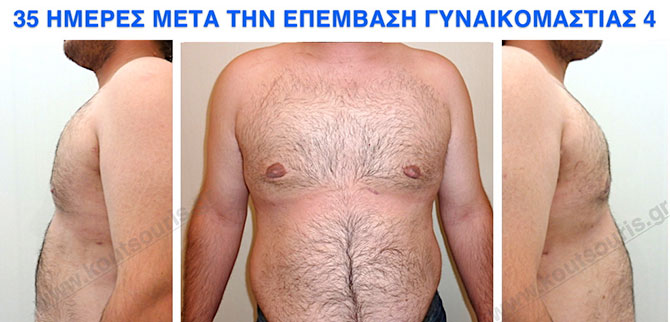
Εικόνες αποκατάστασης Γυναικομαστίας ΠΡΙΝ και ΜΕΤΑ



 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_imageframe]
 [/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_text/]
[/fusion_imageframe]
[/fusion_text/]